How to Write a Body of a Research Paper

The main part of your research paper is called “the body.” To write this important part of your paper, include only relevant information, or information that gets to the point. Organize your ideas in a logical order—one that makes sense—and provide enough details—facts and examples—to support the points you want to make.

Logical Order
Transition words and phrases, adding evidence, phrases for supporting topic sentences.
- Transition Phrases for Comparisons
- Transition Phrases for Contrast
- Transition Phrases to Show a Process
- Phrases to Introduce Examples
- Transition Phrases for Presenting Evidence
How to Make Effective Transitions
Examples of effective transitions, drafting your conclusion, writing the body paragraphs.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
- The third and fourth paragraphs follow the same format as the second:
- Transition or topic sentence.
- Topic sentence (if not included in the first sentence).
- Supporting sentences including a discussion, quotations, or examples that support the topic sentence.
- Concluding sentence that transitions to the next paragraph.
The topic of each paragraph will be supported by the evidence you itemized in your outline. However, just as smooth transitions are required to connect your paragraphs, the sentences you write to present your evidence should possess transition words that connect ideas, focus attention on relevant information, and continue your discussion in a smooth and fluid manner.
You presented the main idea of your paper in the thesis statement. In the body, every single paragraph must support that main idea. If any paragraph in your paper does not, in some way, back up the main idea expressed in your thesis statement, it is not relevant, which means it doesn’t have a purpose and shouldn’t be there.
Each paragraph also has a main idea of its own. That main idea is stated in a topic sentence, either at the beginning or somewhere else in the paragraph. Just as every paragraph in your paper supports your thesis statement, every sentence in each paragraph supports the main idea of that paragraph by providing facts or examples that back up that main idea. If a sentence does not support the main idea of the paragraph, it is not relevant and should be left out.
A paper that makes claims or states ideas without backing them up with facts or clarifying them with examples won’t mean much to readers. Make sure you provide enough supporting details for all your ideas. And remember that a paragraph can’t contain just one sentence. A paragraph needs at least two or more sentences to be complete. If a paragraph has only one or two sentences, you probably haven’t provided enough support for your main idea. Or, if you have trouble finding the main idea, maybe you don’t have one. In that case, you can make the sentences part of another paragraph or leave them out.
Arrange the paragraphs in the body of your paper in an order that makes sense, so that each main idea follows logically from the previous one. Likewise, arrange the sentences in each paragraph in a logical order.
If you carefully organized your notes and made your outline, your ideas will fall into place naturally as you write your draft. The main ideas, which are building blocks of each section or each paragraph in your paper, come from the Roman-numeral headings in your outline. The supporting details under each of those main ideas come from the capital-letter headings. In a shorter paper, the capital-letter headings may become sentences that include supporting details, which come from the Arabic numerals in your outline. In a longer paper, the capital letter headings may become paragraphs of their own, which contain sentences with the supporting details, which come from the Arabic numerals in your outline.
In addition to keeping your ideas in logical order, transitions are another way to guide readers from one idea to another. Transition words and phrases are important when you are suggesting or pointing out similarities between ideas, themes, opinions, or a set of facts. As with any perfect phrase, transition words within paragraphs should not be used gratuitously. Their meaning must conform to what you are trying to point out, as shown in the examples below:
- “Accordingly” or “in accordance with” indicates agreement. For example :Thomas Edison’s experiments with electricity accordingly followed the theories of Benjamin Franklin, J. B. Priestly, and other pioneers of the previous century.
- “Analogous” or “analogously” contrasts different things or ideas that perform similar functions or make similar expressions. For example: A computer hard drive is analogous to a filing cabinet. Each stores important documents and data.
- “By comparison” or “comparatively”points out differences between things that otherwise are similar. For example: Roses require an alkaline soil. Azaleas, by comparison, prefer an acidic soil.
- “Corresponds to” or “correspondingly” indicates agreement or conformity. For example: The U.S. Constitution corresponds to England’s Magna Carta in so far as both established a framework for a parliamentary system.
- “Equals,”“equal to,” or “equally” indicates the same degree or quality. For example:Vitamin C is equally as important as minerals in a well-balanced diet.
- “Equivalent” or “equivalently” indicates two ideas or things of approximately the same importance, size, or volume. For example:The notions of individual liberty and the right to a fair and speedy trial hold equivalent importance in the American legal system.
- “Common” or “in common with” indicates similar traits or qualities. For example: Darwin did not argue that humans were descended from the apes. Instead, he maintained that they shared a common ancestor.
- “In the same way,”“in the same manner,”“in the same vein,” or “likewise,” connects comparable traits, ideas, patterns, or activities. For example: John Roebling’s suspension bridges in Brooklyn and Cincinnati were built in the same manner, with strong cables to support a metallic roadway. Example 2: Despite its delicate appearance, John Roebling’s Brooklyn Bridge was built as a suspension bridge supported by strong cables. Example 3: Cincinnati’s Suspension Bridge, which Roebling also designed, was likewise supported by cables.
- “Kindred” indicates that two ideas or things are related by quality or character. For example: Artists Vincent Van Gogh and Paul Gauguin are considered kindred spirits in the Impressionist Movement. “Like” or “as” are used to create a simile that builds reader understanding by comparing two dissimilar things. (Never use “like” as slang, as in: John Roebling was like a bridge designer.) For examples: Her eyes shone like the sun. Her eyes were as bright as the sun.
- “Parallel” describes events, things, or ideas that occurred at the same time or that follow similar logic or patterns of behavior. For example:The original Ocktoberfests were held to occur in parallel with the autumn harvest.
- “Obviously” emphasizes a point that should be clear from the discussion. For example: Obviously, raccoons and other wildlife will attempt to find food and shelter in suburban areas as their woodland habitats disappear.
- “Similar” and “similarly” are used to make like comparisons. For example: Horses and ponies have similar physical characteristics although, as working farm animals, each was bred to perform different functions.
- “There is little debate” or “there is consensus” can be used to point out agreement. For example:There is little debate that the polar ice caps are melting.The question is whether global warming results from natural or human-made causes.
Other phrases that can be used to make transitions or connect ideas within paragraphs include:
- Use “alternately” or “alternatively” to suggest a different option.
- Use “antithesis” to indicate a direct opposite.
- Use “contradict” to indicate disagreement.
- Use “on the contrary” or “conversely” to indicate that something is different from what it seems.
- Use “dissimilar” to point out differences between two things.
- Use “diverse” to discuss differences among many things or people.
- Use “distinct” or “distinctly” to point out unique qualities.
- Use “inversely” to indicate an opposite idea.
- Use “it is debatable,” “there is debate,” or “there is disagreement” to suggest that there is more than one opinion about a subject.
- Use “rather” or “rather than” to point out an exception.
- Use “unique” or “uniquely” to indicate qualities that can be found nowhere else.
- Use “unlike” to indicate dissimilarities.
- Use “various” to indicate more than one kind.
Writing Topic Sentences
Remember, a sentence should express a complete thought, one thought per sentence—no more, no less. The longer and more convoluted your sentences become, the more likely you are to muddle the meaning, become repetitive, and bog yourself down in issues of grammar and construction. In your first draft, it is generally a good idea to keep those sentences relatively short and to the point. That way your ideas will be clearly stated.You will be able to clearly see the content that you have put down—what is there and what is missing—and add or subtract material as it is needed. The sentences will probably seem choppy and even simplistic.The purpose of a first draft is to ensure that you have recorded all the content you will need to make a convincing argument. You will work on smoothing and perfecting the language in subsequent drafts.
Transitioning from your topic sentence to the evidence that supports it can be problematic. It requires a transition, much like the transitions needed to move from one paragraph to the next. Choose phrases that connect the evidence directly to your topic sentence.
- Consider this: (give an example or state evidence).
- If (identify one condition or event) then (identify the condition or event that will follow).
- It should go without saying that (point out an obvious condition).
- Note that (provide an example or observation).
- Take a look at (identify a condition; follow with an explanation of why you think it is important to the discussion).
- The authors had (identify their idea) in mind when they wrote “(use a quotation from their text that illustrates the idea).”
- The point is that (summarize the conclusion your reader should draw from your research).
- This becomes evident when (name the author) says that (paraphrase a quote from the author’s writing).
- We see this in the following example: (provide an example of your own).
- (The author’s name) offers the example of (summarize an example given by the author).
If an idea is controversial, you may need to add extra evidence to your paragraphs to persuade your reader. You may also find that a logical argument, one based solely on your evidence, is not persuasive enough and that you need to appeal to the reader’s emotions. Look for ways to incorporate your research without detracting from your argument.
Writing Transition Sentences
It is often difficult to write transitions that carry a reader clearly and logically on to the next paragraph (and the next topic) in an essay. Because you are moving from one topic to another, it is easy to simply stop one and start another. Great research papers, however, include good transitions that link the ideas in an interesting discussion so that readers can move smoothly and easily through your presentation. Close each of your paragraphs with an interesting transition sentence that introduces the topic coming up in the next paragraph.
Transition sentences should show a relationship between the two topics.Your transition will perform one of the following functions to introduce the new idea:
- Indicate that you will be expanding on information in a different way in the upcoming paragraph.
- Indicate that a comparison, contrast, or a cause-and-effect relationship between the topics will be discussed.
- Indicate that an example will be presented in the next paragraph.
- Indicate that a conclusion is coming up.
Transitions make a paper flow smoothly by showing readers how ideas and facts follow one another to point logically to a conclusion. They show relationships among the ideas, help the reader to understand, and, in a persuasive paper, lead the reader to the writer’s conclusion.
Each paragraph should end with a transition sentence to conclude the discussion of the topic in the paragraph and gently introduce the reader to the topic that will be raised in the next paragraph. However, transitions also occur within paragraphs—from sentence to sentence—to add evidence, provide examples, or introduce a quotation.
The type of paper you are writing and the kinds of topics you are introducing will determine what type of transitional phrase you should use. Some useful phrases for transitions appear below. They are grouped according to the function they normally play in a paper. Transitions, however, are not simply phrases that are dropped into sentences. They are constructed to highlight meaning. Choose transitions that are appropriate to your topic and what you want the reader to do. Edit them to be sure they fit properly within the sentence to enhance the reader’s understanding.
Transition Phrases for Comparisons:
- We also see
- In addition to
- Notice that
- Beside that,
- In comparison,
- Once again,
- Identically,
- For example,
- Comparatively, it can be seen that
- We see this when
- This corresponds to
- In other words,
- At the same time,
- By the same token,
Transition Phrases for Contrast:
- By contrast,
- On the contrary,
- Nevertheless,
- An exception to this would be …
- Alongside that,we find …
- On one hand … on the other hand …
- [New information] presents an opposite view …
- Conversely, it could be argued …
- Other than that,we find that …
- We get an entirely different impression from …
- One point of differentiation is …
- Further investigation shows …
- An exception can be found in the fact that …
Transition Phrases to Show a Process:
- At the top we have … Near the bottom we have …
- Here we have … There we have …
- Continuing on,
- We progress to …
- Close up … In the distance …
- With this in mind,
- Moving in sequence,
- Proceeding sequentially,
- Moving to the next step,
- First, Second,Third,…
- Examining the activities in sequence,
- Sequentially,
- As a result,
- The end result is …
- To illustrate …
- Subsequently,
- One consequence of …
- If … then …
- It follows that …
- This is chiefly due to …
- The next step …
- Later we find …
Phrases to Introduce Examples:
- For instance,
- Particularly,
- In particular,
- This includes,
- Specifically,
- To illustrate,
- One illustration is
- One example is
- This is illustrated by
- This can be seen when
- This is especially seen in
- This is chiefly seen when
Transition Phrases for Presenting Evidence:
- Another point worthy of consideration is
- At the center of the issue is the notion that
- Before moving on, it should be pointed out that
- Another important point is
- Another idea worth considering is
- Consequently,
- Especially,
- Even more important,
- Getting beyond the obvious,
- In spite of all this,
- It follows that
- It is clear that
- More importantly,
- Most importantly,
How to make effective transitions between sections of a research paper? There are two distinct issues in making strong transitions:
- Does the upcoming section actually belong where you have placed it?
- Have you adequately signaled the reader why you are taking this next step?
The first is the most important: Does the upcoming section actually belong in the next spot? The sections in your research paper need to add up to your big point (or thesis statement) in a sensible progression. One way of putting that is, “Does the architecture of your paper correspond to the argument you are making?” Getting this architecture right is the goal of “large-scale editing,” which focuses on the order of the sections, their relationship to each other, and ultimately their correspondence to your thesis argument.
It’s easy to craft graceful transitions when the sections are laid out in the right order. When they’re not, the transitions are bound to be rough. This difficulty, if you encounter it, is actually a valuable warning. It tells you that something is wrong and you need to change it. If the transitions are awkward and difficult to write, warning bells should ring. Something is wrong with the research paper’s overall structure.
After you’ve placed the sections in the right order, you still need to tell the reader when he is changing sections and briefly explain why. That’s an important part of line-by-line editing, which focuses on writing effective sentences and paragraphs.
Effective transition sentences and paragraphs often glance forward or backward, signaling that you are switching sections. Take this example from J. M. Roberts’s History of Europe . He is finishing a discussion of the Punic Wars between Rome and its great rival, Carthage. The last of these wars, he says, broke out in 149 B.C. and “ended with so complete a defeat for the Carthaginians that their city was destroyed . . . .” Now he turns to a new section on “Empire.” Here is the first sentence: “By then a Roman empire was in being in fact if not in name.”(J. M. Roberts, A History of Europe . London: Allen Lane, 1997, p. 48) Roberts signals the transition with just two words: “By then.” He is referring to the date (149 B.C.) given near the end of the previous section. Simple and smooth.
Michael Mandelbaum also accomplishes this transition between sections effortlessly, without bringing his narrative to a halt. In The Ideas That Conquered the World: Peace, Democracy, and Free Markets , one chapter shows how countries of the North Atlantic region invented the idea of peace and made it a reality among themselves. Here is his transition from one section of that chapter discussing “the idea of warlessness” to another section dealing with the history of that idea in Europe.
The widespread aversion to war within the countries of the Western core formed the foundation for common security, which in turn expressed the spirit of warlessness. To be sure, the rise of common security in Europe did not abolish war in other parts of the world and could not guarantee its permanent abolition even on the European continent. Neither, however, was it a flukish, transient product . . . . The European common security order did have historical precedents, and its principal features began to appear in other parts of the world. Precedents for Common Security The security arrangements in Europe at the dawn of the twenty-first century incorporated features of three different periods of the modern age: the nineteenth century, the interwar period, and the ColdWar. (Michael Mandelbaum, The Ideas That Conquered the World: Peace, Democracy, and Free Markets . New York: Public Affairs, 2002, p. 128)
It’s easier to make smooth transitions when neighboring sections deal with closely related subjects, as Mandelbaum’s do. Sometimes, however, you need to end one section with greater finality so you can switch to a different topic. The best way to do that is with a few summary comments at the end of the section. Your readers will understand you are drawing this topic to a close, and they won’t be blindsided by your shift to a new topic in the next section.
Here’s an example from economic historian Joel Mokyr’s book The Lever of Riches: Technological Creativity and Economic Progress . Mokyr is completing a section on social values in early industrial societies. The next section deals with a quite different aspect of technological progress: the role of property rights and institutions. So Mokyr needs to take the reader across a more abrupt change than Mandelbaum did. Mokyr does that in two ways. First, he summarizes his findings on social values, letting the reader know the section is ending. Then he says the impact of values is complicated, a point he illustrates in the final sentences, while the impact of property rights and institutions seems to be more straightforward. So he begins the new section with a nod to the old one, noting the contrast.
In commerce, war and politics, what was functional was often preferred [within Europe] to what was aesthetic or moral, and when it was not, natural selection saw to it that such pragmatism was never entirely absent in any society. . . . The contempt in which physical labor, commerce, and other economic activity were held did not disappear rapidly; much of European social history can be interpreted as a struggle between wealth and other values for a higher step in the hierarchy. The French concepts of bourgeois gentilhomme and nouveau riche still convey some contempt for people who joined the upper classes through economic success. Even in the nineteenth century, the accumulation of wealth was viewed as an admission ticket to social respectability to be abandoned as soon as a secure membership in the upper classes had been achieved. Institutions and Property Rights The institutional background of technological progress seems, on the surface, more straightforward. (Joel Mokyr, The Lever of Riches: Technological Creativity and Economic Progress . New York: Oxford University Press, 1990, p. 176)
Note the phrase, “on the surface.” Mokyr is hinting at his next point, that surface appearances are deceiving in this case. Good transitions between sections of your research paper depend on:
- Getting the sections in the right order
- Moving smoothly from one section to the next
- Signaling readers that they are taking the next step in your argument
- Explaining why this next step comes where it does
Every good paper ends with a strong concluding paragraph. To write a good conclusion, sum up the main points in your paper. To write an even better conclusion, include a sentence or two that helps the reader answer the question, “So what?” or “Why does all this matter?” If you choose to include one or more “So What?” sentences, remember that you still need to support any point you make with facts or examples. Remember, too, that this is not the place to introduce new ideas from “out of the blue.” Make sure that everything you write in your conclusion refers to what you’ve already written in the body of your paper.
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution.
Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis.
- picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph
Purdue Online Writing Lab College of Liberal Arts
Body Paragraphs

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information
Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more focused on the argument ending with specific, detailed evidence supporting a claim. Lastly, the author explains how and why the information she has just provided connects to and supports her thesis (a brief wrap-up or warrant).

Moving from General to Specific Information
The four elements of a good paragraph (TTEB)
A good paragraph should contain at least the following four elements: T ransition, T opic sentence, specific E vidence and analysis, and a B rief wrap-up sentence (also known as a warrant ) –TTEB!
- A T ransition sentence leading in from a previous paragraph to assure smooth reading. This acts as a hand-off from one idea to the next.
- A T opic sentence that tells the reader what you will be discussing in the paragraph.
- Specific E vidence and analysis that supports one of your claims and that provides a deeper level of detail than your topic sentence.
- A B rief wrap-up sentence that tells the reader how and why this information supports the paper’s thesis. The brief wrap-up is also known as the warrant. The warrant is important to your argument because it connects your reasoning and support to your thesis, and it shows that the information in the paragraph is related to your thesis and helps defend it.
Supporting evidence (induction and deduction)
Induction is the type of reasoning that moves from specific facts to a general conclusion. When you use induction in your paper, you will state your thesis (which is actually the conclusion you have come to after looking at all the facts) and then support your thesis with the facts. The following is an example of induction taken from Dorothy U. Seyler’s Understanding Argument :
There is the dead body of Smith. Smith was shot in his bedroom between the hours of 11:00 p.m. and 2:00 a.m., according to the coroner. Smith was shot with a .32 caliber pistol. The pistol left in the bedroom contains Jones’s fingerprints. Jones was seen, by a neighbor, entering the Smith home at around 11:00 p.m. the night of Smith’s death. A coworker heard Smith and Jones arguing in Smith’s office the morning of the day Smith died.
Conclusion: Jones killed Smith.
Here, then, is the example in bullet form:
- Conclusion: Jones killed Smith
- Support: Smith was shot by Jones’ gun, Jones was seen entering the scene of the crime, Jones and Smith argued earlier in the day Smith died.
- Assumption: The facts are representative, not isolated incidents, and thus reveal a trend, justifying the conclusion drawn.
When you use deduction in an argument, you begin with general premises and move to a specific conclusion. There is a precise pattern you must use when you reason deductively. This pattern is called syllogistic reasoning (the syllogism). Syllogistic reasoning (deduction) is organized in three steps:
- Major premise
- Minor premise
In order for the syllogism (deduction) to work, you must accept that the relationship of the two premises lead, logically, to the conclusion. Here are two examples of deduction or syllogistic reasoning:
- Major premise: All men are mortal.
- Minor premise: Socrates is a man.
- Conclusion: Socrates is mortal.
- Major premise: People who perform with courage and clear purpose in a crisis are great leaders.
- Minor premise: Lincoln was a person who performed with courage and a clear purpose in a crisis.
- Conclusion: Lincoln was a great leader.
So in order for deduction to work in the example involving Socrates, you must agree that (1) all men are mortal (they all die); and (2) Socrates is a man. If you disagree with either of these premises, the conclusion is invalid. The example using Socrates isn’t so difficult to validate. But when you move into more murky water (when you use terms such as courage , clear purpose , and great ), the connections get tenuous.
For example, some historians might argue that Lincoln didn’t really shine until a few years into the Civil War, after many Union losses to Southern leaders such as Robert E. Lee.
The following is a clear example of deduction gone awry:
- Major premise: All dogs make good pets.
- Minor premise: Doogle is a dog.
- Conclusion: Doogle will make a good pet.
If you don’t agree that all dogs make good pets, then the conclusion that Doogle will make a good pet is invalid.
When a premise in a syllogism is missing, the syllogism becomes an enthymeme. Enthymemes can be very effective in argument, but they can also be unethical and lead to invalid conclusions. Authors often use enthymemes to persuade audiences. The following is an example of an enthymeme:
If you have a plasma TV, you are not poor.
The first part of the enthymeme (If you have a plasma TV) is the stated premise. The second part of the statement (you are not poor) is the conclusion. Therefore, the unstated premise is “Only rich people have plasma TVs.” The enthymeme above leads us to an invalid conclusion (people who own plasma TVs are not poor) because there are plenty of people who own plasma TVs who are poor. Let’s look at this enthymeme in a syllogistic structure:
- Major premise: People who own plasma TVs are rich (unstated above).
- Minor premise: You own a plasma TV.
- Conclusion: You are not poor.
To help you understand how induction and deduction can work together to form a solid argument, you may want to look at the United States Declaration of Independence. The first section of the Declaration contains a series of syllogisms, while the middle section is an inductive list of examples. The final section brings the first and second sections together in a compelling conclusion.
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Body Paragraph Structure
Introduction.
- Referrences
- Ways to start paragraph
- Step by step guide
- Research paragraph examples

Learning the basics of a paragraph structure
- Title (cover page).
- Introduction.
- Literature review.
- Research methodology.
- Data analysis.
- Conclusion.
- Reference page.
5 winning ways to start a body paragraph
- Topic Sentence : it should provide a clear focus and introduce the specific aspect you will discuss. For example, “One key factor influencing climate change is…”.
- Opening Statement: grab your readers’ attention with a thought-provoking or surprising statement related to your topic. For instance, “The alarming increase in global temperatures has reached a critical point, demanding immediate action.”
- Quotation: find a relevant quote from a reputable source. It won’t only add credibility to your research but will also engage the reader right from the start.
- Anecdote or example: start your academic paragraph with a funny story or a real-world example that illustrates the significance of your research topic.
- Background information : provide a brief background or context for the topic you are about to discuss. For example, “In recent years, the prevalence of cyber-attacks has skyrocketed, posing a severe threat to individuals, organizations, and even national security.”
A step-by-step guide to starting a concise body paragraph
Step 1: introduce the main point or argument., step 2: provide evidence or examples., step 3: explain and analyze., step 4: connect to the main argument., step 5: review and revise., flawless body paragraph example: how does it look.
- Topic Sentence: Rising global temperatures have significant implications for ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Evidence/Example 1: According to a study by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), global average temperatures have increased by 1.1 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times (IPCC, 2021). This temperature rise has led to melting polar ice caps and glaciers, rising sea levels, and coastal erosion (Smith et al., 2019).
- Explanation/Analysis 1: The significant increase in global temperatures has caused observable changes in the Earth’s physical environment. The melting of polar ice caps not only contributes to the rise in sea levels but also disrupts marine ecosystems.
- Evidence/Example 2: In addition to the loss of coastal habitats, higher temperatures have also resulted in shifts in the geographical distribution of species. Research by Parmesan and Yohe (2019) indicates that many plant and animal species have altered their ranges and migration patterns in response to changing climate conditions.
- Explanation/Analysis 2: The observed shifts in species distribution highlight the vulnerability of ecosystems to climate change. As temperature zone modification, species that cannot adapt or migrate to suitable habitats may face reduced reproductive success and increased risk of extinction.
- Connect to the main argument: These examples demonstrate that the rising global temperatures associated with climate change have profound implications for ecosystems and biodiversity.
The bottom line

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account

How to write an essay: Body
- What's in this guide
- Introduction
- Essay structure
- Additional resources
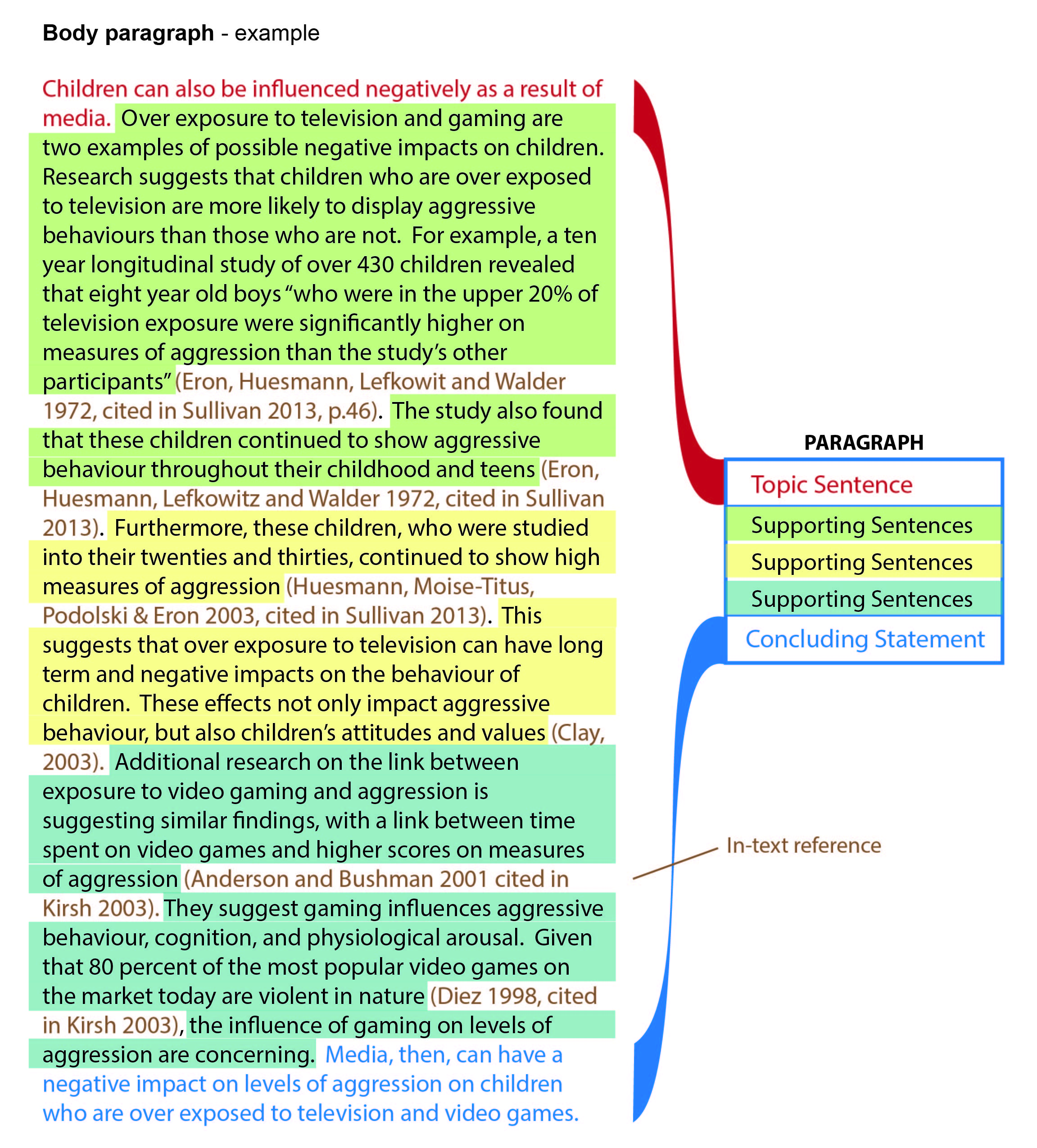
Body paragraphs
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly.
Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence . This lets the reader know what the paragraph is going to be about and the main point it will make. It gives the paragraph’s point straight away. Next – and largest – is the supporting sentences . These expand on the central idea, explaining it in more detail, exploring what it means, and of course giving the evidence and argument that back it up. This is where you use your research to support your argument. Then there is a concluding sentence . This restates the idea in the topic sentence, to remind the reader of your main point. It also shows how that point helps answer the question.
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay
Research Paper
How to write a body of a research paper.

The main part of your research paper is called “the body.” To write this important part of your paper, include only relevant information, or information that gets to the point. Organize your ideas in a logical order—one that makes sense—and provide enough details—facts and examples—to support the points you want to make.
The first sentence of your second paragraph should continue the transition from the end of your introduction to present your first topic.Often too, your first sentence will be your “topic sentence,” the sentence that presents the topic, point, or argument that will be presented in the paragraph. The body of the paragraph should contain evidence, in the form of a discussion using quotations and examples, that supports or “proves” the topic. The final sentence of the paragraph should provide a transition to the third paragraph of the paper where the second topic will be presented.
- The third and fourth paragraphs follow the same format as the second:
- Transition or topic sentence.
- Topic sentence (if not included in the first sentence).
- Supporting sentences including a discussion, quotations, or examples that support the topic sentence.
- Concluding sentence that transitions to the next paragraph.
The topic of each paragraph will be supported by the evidence you itemized in your outline. However, just as smooth transitions are required to connect your paragraphs, the sentences you write to present your evidence should possess transition words that connect ideas, focus attention on relevant information, and continue your discussion in a smooth and fluid manner.
You presented the main idea of your paper in the thesis statement. In the body, every single paragraph must support that main idea. If any paragraph in your paper does not, in some way, back up the main idea expressed in your thesis statement, it is not relevant, which means it doesn’t have a purpose and shouldn’t be there.
Each paragraph also has a main idea of its own. That main idea is stated in a topic sentence, either at the beginning or somewhere else in the paragraph. Just as every paragraph in your paper supports your thesis statement, every sentence in each paragraph supports the main idea of that paragraph by providing facts or examples that back up that main idea. If a sentence does not support the main idea of the paragraph, it is not relevant and should be left out.
A paper that makes claims or states ideas without backing them up with facts or clarifying them with examples won’t mean much to readers. Make sure you provide enough supporting details for all your ideas. And remember that a paragraph can’t contain just one sentence. A paragraph needs at least two or more sentences to be complete. If a paragraph has only one or two sentences, you probably haven’t provided enough support for your main idea. Or, if you have trouble finding the main idea, maybe you don’t have one. In that case, you can make the sentences part of another paragraph or leave them out.
Logical order
Arrange the paragraphs in the body of your paper in an order that makes sense, so that each main idea follows logically from the previous one. Likewise, arrange the sentences in each paragraph in a logical order.
If you carefully organized your notes and made your outline, your ideas will fall into place naturally as you write your draft. The main ideas, which are building blocks of each section or each paragraph in your paper, come from the Roman-numeral headings in your outline. The supporting details under each of those main ideas come from the capital-letter headings. In a shorter paper, the capital-letter headings may become sentences that include supporting details, which come from the Arabic numerals in your outline. In a longer paper, the capital letter headings may become paragraphs of their own, which contain sentences with the supporting details, which come from the Arabic numerals in your outline.
Transition Words and Phrases
In addition to keeping your ideas in logical order, transitions are another way to guide readers from one idea to another. Transition words and phrases are important when you are suggesting or pointing out similarities between ideas, themes, opinions, or a set of facts. As with any perfect phrase, transition words within paragraphs should not be used gratuitously. Their meaning must conform to what you are trying to point out, as shown in the examples below:
- “Accordingly” or “in accordance with” indicates agreement. For example :Thomas Edison’s experiments with electricity accordingly followed the theories of Benjamin Franklin, J. B. Priestly, and other pioneers of the previous century.
- “Analogous” or “analogously” contrasts different things or ideas that perform similar functions or make similar expressions. For example: A computer hard drive is analogous to a filing cabinet. Each stores important documents and data.
- “By comparison” or “comparatively”points out differences between things that otherwise are similar. For example: Roses require an alkaline soil. Azaleas, by comparison, prefer an acidic soil.
- “Corresponds to” or “correspondingly” indicates agreement or conformity. For example: The U.S. Constitution corresponds to England’s Magna Carta in so far as both established a framework for a parliamentary system.
- “Equals,”“equal to,” or “equally” indicates the same degree or quality. For example:Vitamin C is equally as important as minerals in a well-balanced diet.
- “Equivalent” or “equivalently” indicates two ideas or things of approximately the same importance, size, or volume. For example:The notions of individual liberty and the right to a fair and speedy trial hold equivalent importance in the American legal system.
- “Common” or “in common with” indicates similar traits or qualities. For example: Darwin did not argue that humans were descended from the apes. Instead, he maintained that they shared a common ancestor.
- “In the same way,”“in the same manner,”“in the same vein,” or “likewise,” connects comparable traits, ideas, patterns, or activities. For example: John Roebling’s suspension bridges in Brooklyn and Cincinnati were built in the same manner, with strong cables to support a metallic roadway. Example 2: Despite its delicate appearance, John Roebling’s Brooklyn Bridge was built as a suspension bridge supported by strong cables. Example 3: Cincinnati’s Suspension Bridge, which Roebling also designed, was likewise supported by cables.
- “Kindred” indicates that two ideas or things are related by quality or character. For example: Artists Vincent Van Gogh and Paul Gauguin are considered kindred spirits in the Impressionist Movement. “Like” or “as” are used to create a simile that builds reader understanding by comparing two dissimilar things. (Never use “like” as slang, as in: John Roebling was like a bridge designer.) For examples: Her eyes shone like the sun. Her eyes were as bright as the sun.
- “Parallel” describes events, things, or ideas that occurred at the same time or that follow similar logic or patterns of behavior. For example:The original Ocktoberfests were held to occur in parallel with the autumn harvest.
- “Obviously” emphasizes a point that should be clear from the discussion. For example: Obviously, raccoons and other wildlife will attempt to find food and shelter in suburban areas as their woodland habitats disappear.
- “Similar” and “similarly” are used to make like comparisons. For example: Horses and ponies have similar physical characteristics although, as working farm animals, each was bred to perform different functions.
- “There is little debate” or “there is consensus” can be used to point out agreement. For example:There is little debate that the polar ice caps are melting.The question is whether global warming results from natural or human-made causes.
Other phrases that can be used to make transitions or connect ideas within paragraphs include:

- Use “alternately” or “alternatively” to suggest a different option.
- Use “antithesis” to indicate a direct opposite.
- Use “contradict” to indicate disagreement.
- Use “on the contrary” or “conversely” to indicate that something is different from what it seems.
- Use “dissimilar” to point out differences between two things.
- Use “diverse” to discuss differences among many things or people.
- Use “distinct” or “distinctly” to point out unique qualities.
- Use “inversely” to indicate an opposite idea.
- Use “it is debatable,” “there is debate,” or “there is disagreement” to suggest that there is more than one opinion about a subject.
- Use “rather” or “rather than” to point out an exception.
- Use “unique” or “uniquely” to indicate qualities that can be found nowhere else.
- Use “unlike” to indicate dissimilarities.
- Use “various” to indicate more than one kind.
Writing Topic Sentences
Remember, a sentence should express a complete thought, one thought per sentence—no more, no less. The longer and more convoluted your sentences become, the more likely you are to muddle the meaning, become repetitive, and bog yourself down in issues of grammar and construction. In your first draft, it is generally a good idea to keep those sentences relatively short and to the point. That way your ideas will be clearly stated.You will be able to clearly see the content that you have put down—what is there and what is missing—and add or subtract material as it is needed. The sentences will probably seem choppy and even simplistic.The purpose of a first draft is to ensure that you have recorded all the content you will need to make a convincing argument. You will work on smoothing and perfecting the language in subsequent drafts.

Adding Evidence
Transitioning from your topic sentence to the evidence that supports it can be problematic. It requires a transition, much like the transitions needed to move from one paragraph to the next. Choose phrases that connect the evidence directly to your topic sentence.
Phrases for Supporting Topic Sentences
- Consider this: (give an example or state evidence).
- If (identify one condition or event) then (identify the condition or event that will follow).
- It should go without saying that (point out an obvious condition).
- Note that (provide an example or observation).
- Take a look at (identify a condition; follow with an explanation of why you think it is important to the discussion).
- The authors had (identify their idea) in mind when they wrote “(use a quotation from their text that illustrates the idea).”
- The point is that (summarize the conclusion your reader should draw from your research).
- This becomes evident when (name the author) says that (paraphrase a quote from the author’s writing).
- We see this in the following example: (provide an example of your own).
- (The author’s name) offers the example of (summarize an example given by the author).
If an idea is controversial, you may need to add extra evidence to your paragraphs to persuade your reader. You may also find that a logical argument, one based solely on your evidence, is not persuasive enough and that you need to appeal to the reader’s emotions. Look for ways to incorporate your research without detracting from your argument.
Writing Transition Sentences
It is often difficult to write transitions that carry a reader clearly and logically on to the next paragraph (and the next topic) in an essay. Because you are moving from one topic to another, it is easy to simply stop one and start another. Great research papers, however, include good transitions that link the ideas in an interesting discussion so that readers can move smoothly and easily through your presentation. Close each of your paragraphs with an interesting transition sentence that introduces the topic coming up in the next paragraph.
Transition sentences should show a relationship between the two topics.Your transition will perform one of the following functions to introduce the new idea:
- Indicate that you will be expanding on information in a different way in the upcoming paragraph.
- Indicate that a comparison, contrast, or a cause-and-effect relationship between the topics will be discussed.
- Indicate that an example will be presented in the next paragraph.
- Indicate that a conclusion is coming up.
Transitions make a paper flow smoothly by showing readers how ideas and facts follow one another to point logically to a conclusion. They show relationships among the ideas, help the reader to understand, and, in a persuasive paper, lead the reader to the writer’s conclusion.
Each paragraph should end with a transition sentence to conclude the discussion of the topic in the paragraph and gently introduce the reader to the topic that will be raised in the next paragraph. However, transitions also occur within paragraphs—from sentence to sentence—to add evidence, provide examples, or introduce a quotation.
The type of paper you are writing and the kinds of topics you are introducing will determine what type of transitional phrase you should use. Some useful phrases for transitions appear below. They are grouped according to the function they normally play in a paper. Transitions, however, are not simply phrases that are dropped into sentences. They are constructed to highlight meaning. Choose transitions that are appropriate to your topic and what you want the reader to do. Edit them to be sure they fit properly within the sentence to enhance the reader’s understanding.
Transition Phrases for Comparisons:
- We also see
- In addition to
- Notice that
- Beside that,
- In comparison,
- Once again,
- Identically,
- For example,
- Comparatively, it can be seen that
- We see this when
- This corresponds to
- In other words,
- At the same time,
- By the same token,
Transition Phrases for Contrast:
- By contrast,
- On the contrary,
- Nevertheless,
- An exception to this would be …
- Alongside that,we find …
- On one hand … on the other hand …
- [New information] presents an opposite view …
- Conversely, it could be argued …
- Other than that,we find that …
- We get an entirely different impression from …
- One point of differentiation is …
- Further investigation shows …
- An exception can be found in the fact that …
Transition Phrases to Show a Process:
- At the top we have … Near the bottom we have …
- Here we have … There we have …
- Continuing on,
- We progress to …
- Close up … In the distance …
- With this in mind,
- Moving in sequence,
- Proceeding sequentially,
- Moving to the next step,
- First, Second,Third,…
- Examining the activities in sequence,
- Sequentially,
- As a result,
- The end result is …
- To illustrate …
- Subsequently,
- One consequence of …
- If … then …
- It follows that …
- This is chiefly due to …
- The next step …
- Later we find …
Phrases to Introduce Examples:
- For instance,
- Particularly,
- In particular,
- This includes,
- Specifically,
- To illustrate,
- One illustration is
- One example is
- This is illustrated by
- This can be seen when
- This is especially seen in
- This is chiefly seen when
Transition Phrases for Presenting Evidence:
- Another point worthy of consideration is
- At the center of the issue is the notion that
- Before moving on, it should be pointed out that
- Another important point is
- Another idea worth considering is
- Consequently,
- Especially,
- Even more important,
- Getting beyond the obvious,
- In spite of all this,
- It follows that
- It is clear that
- More importantly,
- Most importantly,
See the examples of effective transitions for more.
Draft Your Conclusion
Every good paper ends with a strong concluding paragraph. To write a good conclusion, sum up the main points in your paper. To write an even better conclusion, include a sentence or two that helps the reader answer the question, “So what?” or “Why does all this matter?” If you choose to include one or more “So What?” sentences, remember that you still need to support any point you make with facts or examples. Remember, too, that this is not the place to introduce new ideas from “out of the blue.” Make sure that everything you write in your conclusion refers to what you’ve already written in the body of your paper.
Read more on How to Write a Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


4c. Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs present the reasoning and evidence to demonstrate your thesis. In academic essays, body paragraphs are typically a bit more substantial than in news reporting so a writer can share their own ideas, develop their reasoning, cite evidence, and engage in conversation with other writers and scholars. A typical body paragraph in a college essay contains the following elements, which can be remembered through the useful acronym TREAT.
The TREAT Method
- T opic Sentence – an assertion that supports the thesis and presents the main idea of the paragraph
- R easoning – critical thinking and rhetorical appeals: ethos, logos, and pathos
- E vidence – facts, examples, and other evidence integrated into the paragraph using summaries, paraphrases, and quotations
- A nalysis – examination and contextualization of the evidence and reasoning
- T ransition – the flow of ideas from one paragraph to the next
Effective body paragraphs are:
- Specific and narrow . Topic sentences provide your audience a point of transition and flow from paragraph to paragraph. Topic sentences help you expand and develop your thesis and set up the organization of each paragraph. Developing specific reasoning and specific, concrete examples and evidence in each paragraph will build your credibility with readers. If used properly, well-developed reasoning and evidence are more compelling than general facts and observations.
- Relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Body paragraphs should show, explain, and prove your thesis without delving into irrelevant details. With practice and the understanding that there is always another essay, effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Keeping your audience and purpose in mind when choosing examples will help you make sure to stay focused on your thesis.
- Detailed . Academic paragraphs are typically longer than newspaper and magazine paragraphs because scholars need space to develop their reasoning and provide sufficiently detailed evidence to support their claims. Using multiple examples and precise details shows readers that you have considered the facts carefully and enhances the impact of your ideas.
- Organized . If your paragraph starts to include information or ideas that stray from your topic sentence, either the paragraph or the topic sentence might need to change.
Reasoning and Evidence
In written and oral communication, we demonstrate our critical thinking skills through the various types of rhetorical appeals we make to our audience. The purpose and audience for a writing task shape the way writers develop reasoning and select evidence to support their ideas. Writers develop reasoning in body paragraphs through three primary methods: ethos, logos, and pathos. Writers can deploy many forms of evidence to support their reasoning, including: facts, examples, judgments, testimony, and personal experience.
The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle developed a simple method for categorizing forms of reasoning by identifying three primary modes of argumentative reasoning: ethos, logos, and pathos.
- Ethos is reasoning that establishes a writer’s credibility. By showing yourself to be a critical and sympathetic reader, who considers multiple perspectives and demonstrates ethical thinking, you can establish ethos in your body paragraphs.
- Logos is reasoning that develops logical arguments and demonstrates a writer’s command of the facts. Demonstrating your knowledge of the facts and showing that you can distinguish between competing claims at truth will ground your writing in common sense and objectivity.
- Pathos is reasoning that appeals to human emotions and psychological motivations. Humans are subjective animals, and our ability to develop an emotional connection with an audience can have a powerful or subtle impact on whether they will agree with a writer’s reasoning.
A fourth form of reasoning, kairos , can occasionally be used to make an appeal to an audience that the perfect moment or right opportunity has arisen for action. Arguments for changing policies, ending wars, starting revolutions, or engaging in radical social change typically deploy kairos in addition to ethos, logos, and pathos in order to motivate people to take action a critical times in history.
Evidence includes anything that can help you support your reasoning and develop your thesis. As you develop body paragraphs, you reveal evidence to your readers and then provide analysis to help the reader understand how the evidence supports the reasoning and assertions you are making in each body paragraph. Be sure to check with each instructor to confirm what types of evidence are appropriate for each writing task you are assigned. The following kinds of evidence are commonly used in academic essays:
- Facts . Facts are the best kind of evidence to use for academic essays because they often cannot be disputed or distorted. Facts can support your stance by providing background information or a solid evidence-based foundation for your point of view. Remember that facts need explanations. Be sure to use signal phrases like “according to” and “as demonstrated by” to introduce facts and use analysis to explain the relevance of facts to your readers.
- Examples show readers that your ideas are grounded in real situations and contexts. Examples help you highlight general trends and ground your facts in the real world. Be careful not to take examples out of context or overgeneralize based on individual cases.
- Judgments . Judgments are the conclusions of experts drawn from a set of examples or evidence. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and a thorough examination of a topic. Citing a credible expert to support your opinion can be a powerful way to build ethos in your writing.
- Testimony . Testimony consists of direct quotations from eyewitnesses or expert witnesses. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; they add authenticity and credibility to an argument or perspective based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive expertise or experience with a topic. This person provides commentary based on their interpretation of the facts or extensive knowledge on a topic or event.
- Personal Experience . Personal observation is similar to eyewitness or expert testimony but consists of your own experiences and/or expertise. Personal experience can be effective in academic essays if directly relevant to the topic and suited to the purpose of a writing task.
Key Takeaways
- Always be aware of your purpose for writing and the needs of your audience. Cater to those needs in every sensible way.
- Write paragraphs of an appropriate length for your writing assignment. Paragraphs in college-level writing can be up to a page long, as long as they cover the main topics in your outline.
- Use your prewriting and outline to guide the development of your paragraphs and the elaboration of your ideas.
Addressing Counterarguments and Different Perspectives
“Few things are more difficult than to see outside the bounds of your own perspective—to be able to identify assumptions that you take as universal truths but which, instead, have been crafted by your own unique identity and experiences in the world.”
~David Takacs
Why acknowledge and respond to other points of view?
- Address potential weaknesses in your argument before others can point them out to you.
- Acknowledge the complexity of an issue by considering different perspectives and aspects of an issue. No issue has a simple solution or is just Side A versus Side B.
- Establish your writing ethos (can your reader trust you?): your reader is more likely to trust you if you thoughtfully analyze an issue from multiple angles.
- Add to your essay’s word count!
Four steps to acknowledging and responding to other points of view
Step one: know your standpoint, what is my standpoint and why should i know it.
- Standpoint is the unique perspective from which you view the world. It includes: your background and experiences, your political and religious beliefs, your identity (gender, ethnicity, class, sexuality, and ability), your relationship to others, and your social privilege. These are things that will affect how you view and understand an issue.
- It’s important to acknowledge your standpoint because it affects what and how you argue.
Good writers are good readers! And good readers. . .

- Who are you?
- Make a list of what you’ll bring to a conversation about the issue on which you’re writing. What are your assumptions, your background and experience, your knowledge and expertise? Be honest!
Consider writing your standpoint into your essay
- Writing your standpoint into your essay builds trust with your readers. Even if they have a different standpoint, they will respect your honesty and hopefully listen respectfully to what you have to say.
- Writing from your standpoint can make your writing feel more authentic , to you and your reader. “This is me!”
Even if you don’t explicitly reveal your standpoint to your reader, you’ll want to know your standpoint so that you are aware of your own implicit bias as you write.
How do I write in my standpoint? Can I use “I”?
Try one of these templates:
- “What concerns me as a business major . . .”
- “I write this essay during a time when . . .”
- “I am concerned about. . .”
See how other writers we’ve read have done it:
- “Now, as a professor at the Harvard Graduate School of Education , I. . .” [From Anthony Abraham Jack, “I Was a Low-Income College Student. Classes Weren’t the Hard Part.” The New York Times Magazine ]
- “From my first day as a sociology professor at a university with a Division I football and men’s basketball team , education and athletics struck me as being inherently at odds. . .” [From Jasmine Harris, “It’s Naive to Think College Athletes Have Time for School,” The Conversation ]
- “In this society, that norm is usually defined as white, thin, male, young, heterosexual, Christian, and financially secure. It is within this mythical norm that the trappings of power reside. Those of us who stand outside that power , for any reason, often identify one way in which we are different, and we assume that quality to be the primary reason for all oppression. . .” [From Audre Lorde, “The Transformation of Silence into Language and Action”]
- “I might not carry with me the feeling of my audience in stating my own belief. . .” [From Ralph Waldo Emerson, “The American Scholar”]
Step Two: C onsider potential weaknesses in your argument and different points of view on the issue
What potential weaknesses in your argument might you address.
- Logic : would a reader question any of your assumptions?
- between your reasoning and your claim: your main unstated assumption
- or between your evidence and your reasoning: is there evidence or types of evidence a reader might be skeptical of?
- Does the reader hold false assumptions about the issue?
- Could a reader give a different explanation of the issue ?
- Could a reader draw a different conclusion from the evidence ?
- Is there a specific reader who would disagree?
What alternative points of view on the issue might you consider?
- How might someone think differently about the issue?
- How might someone approach the issue from a different standpoint?
- What might keep someone from trusting or believing a claim or point you make?
- What might make someone tentative about taking action?
- What might keep a person from having an open mind?
Which one should I choose to address?
It depends on the essay’s length. You might consider 1-2 counterarguments that are most important for you to address in a paper (depending on the length).
- this could be a view your audience/community is likely to hold themselves
- or a common-knowledge one you think everyone will think of while reading
- and of course the one that is most specific to your argument
- if you can get one that fits more than one of these criteria, that’s even better!
What NOT to do when considering a counterargument

Build a straw man counterargument
- A straw man argument is a logical fallacy where the writer misrepresents or oversimplifies someone else’s argument in order to make it easier to refute.
- Writers also create straw man arguments when they make up a potential counterargument that is easy to refute, but isn’t something most people would reasonably believe.
Step Three: It’s time to write your counterargument into your essay
An exemplary counterargument:.
- exists as its own paragraph
- you fully acknowledge and respond to it
- Note: You don’t have to refute a counterargument for your argument to work. Our world is big enough to hold multiple points of view. The paragraph should ultimately support your thesis, but you may amend, qualify, complicate, or open up your claim, which is often why, organizationally, discussion of counterarguments or different points of view work best in the introduction of your essay to set up your claim or as the last body paragraph to lead into your conclusion.
- relates to your audience/community’s likely concerns and interests
- seems like a realistic thing someone might think (is not a straw man or caricature)
- ideally, is specific to your argument, not your topic in general
- considers both sides respectfully
- may be more than one counterargument or different perspective, but you’d need a separate paragraph for each in order to give them full consideration
Addressing a counterargument versus a different perspective
A true counterargument is the opposing claim on an issue:
- Claim: Academic probation does not help students progress.
- Counterargument: Academic probation does help students progress.
Different perspectives might offer different reasoning, consider different factors or conditions, or ask about different groups of people or situations.
A counterargument needs to be rebutted. Different perspectives can help you amend, qualify, complicate, or open up your claim.
You might use a counterargument to qualify your thesis
An example:
Reasoned thesis : Hook-up culture is now at the center of the institution of higher education because it is thick, palpable, the air students breathe, and we find it on almost every residential campus in America. [From Lisa Wade, “Sociology and the New Culture of Hooking Up on College Campuses“]
A counterargument : Research findings suggest that the sexual practices of college students haven’t changed much since the 1980s. [From David Ludden, “Is Hook-Up Culture Dominating College Campuses?”]
Qualified claim : Although sexual practices of college students haven’t changed much in the last few decades , hook-up culture is now at the center of the institution of higher education because it is thick, palpable. . .
Counterargument paragraph : “The topic of my book, then, isn’t just hooking up; it’s hook-up culture . . .” (Wade).
A template for a counterargument paragraph
I recognize that others may have a different perspective than [state your claim*]. They might believe that [state their claim]. They believe this because [provide several sentences of support]. However, [restate your claim and explain in several sentences why you believe the way you do].
*You can also consider counterpoints to your reasoning, evidence, or standpoint.
Step Four: Decide where to organize your counterargument paragraph
Being aware of different perspectives can also help you develop your conclusion paragraph. In your conclusion, you can reaffirm your claim and then:
- amend part of your claim
- qualify your claim
- complicate your claim
- open up your claim
Writing as collaboration
Think of adding in counterarguments or different perspectives as collaborating with others on addressing an issue. . .

Brazuca illustrations by Cezar Berje, CC0
Opening up our minds and our hearts to different perspectives makes us stronger.
Writing as Inquiry Copyright © 2021 by Kara Clevinger and Stephen Rust is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The main part of your research paper is called “the body.” To write this important part of your paper, include only relevant information, or information that gets to the point.… How it Works Prices +1 312 56 68 949 Chat now Sign in Order
Nov 5, 2014 · The body is the longest part of an essay. This is where you lead the reader through your ideas, elaborating arguments and evidence for your thesis. The body is always divided into paragraphs. You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order.
A strong paragraph in an academic essay will usually include these three elements: A topic sentence. The topic sentence does double duty for a paragraph. First, a strong topic sentence makes a claim or states a main idea that is then developed in the rest of the paragraph. Second, the topic sentence signals to readers how the paragraph is ...
This resource outlines the generally accepted structure for introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions in an academic argument paper. Keep in mind that this resource contains guidelines and not strict rules about organization. Your structure needs to be flexible enough to meet the requirements of your purpose and audience.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader’s attention.
Formula for a Research Body Paragraph ***Make sure each paragraph goes in a logical, sequential order. For example, you cannot discuss the fall of the Roman Empire without first discussing how to came into power*** Writing is often very similar to a math problem. While putting together a research paper or essay, each paragraph
May 22, 2023 · A primary research paper involves writing body paragraphs to effectively communicate the study’s purpose, methods, results, and conclusions. While there may be some variations depending on the discipline and journal guidelines, the following paragraph structure is commonly used: Introduction. The body of research paper sets the stage.
Nov 29, 2023 · The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly. Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence.
The main part of your research paper is called “the body.” To write this important part of your paper, include only relevant information, or information that gets to the point. Organize your ideas in a logical order—one that makes sense—and provide enough details—facts and examples—to support the points you want to make.
4c. Body Paragraphs Body paragraphs present the reasoning and evidence to demonstrate your thesis. In academic essays, body paragraphs are typically a bit more substantial than in news reporting so a writer can share their own ideas, develop their reasoning, cite evidence, and engage in conversation with other writers and scholars.