Quantitative Market Research: Fundamentals, Methods, and Applications
- Updated on August 16, 2024

Did you know that 99% of successful businesses use data to drive their decisions? In our increasingly digital world, quantitative market research has become an essential tool. It doesn’t just provide random facts; it offers precise insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes, giving businesses the edge they need to storm ahead.
This article explores the fundamentals, methods, and applications of quantitative market research, helping business owners, marketing professionals, and entrepreneurs improve their decision-making and drive their businesses forward.

What is Quantitative Market Research?
Quantitative market research is a methodical approach to gather and analyze numerical data, offering businesses a practical understanding of customer behavior and market trends.
This can be part of both primary and secondary market research. Quantitative market research predominantly relies on structured tools like surveys, polls, and questionnaires to collect quantifiable pieces of information such as percentages, frequencies, and ratings. This research is carried out on a large, representative sample of the target audience to ensure accurate reflection of widespread attitudes and behaviors.
Following the data collection, statistical techniques are applied to reveal patterns, track trends, and identify relationships, effectively converting raw data into actionable insights to guide marketing strategies.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
To fully appreciate quantitative research, it’s essential to understand how it differs from qualitative market research:
While quantitative research provides broad, generalizable insights, qualitative research offers deeper, context-rich understanding. Many successful market research strategies combine both approaches to gain a comprehensive view of the market.
Applications of Quantitative Market Research
Quantitative market research finds applications across various business functions and industries. Here are some key areas where this research method proves invaluable:
Product Development
- Measuring consumer preferences for product features: This involves surveying potential customers to rank or rate different product features, helping companies prioritize which features to include or improve.
- Assessing market demand for new products: Researchers can use quantitative methods to estimate the potential market size and gauge consumer interest in a new product concept before investing in development .
- Evaluating pricing strategies: Through techniques like conjoint analysis or price sensitivity meters, companies can determine optimal price points that maximize both sales and profitability.
Brand Management
- Tracking brand awareness and perception: Regular surveys can measure how many consumers recognize a brand and what associations they have with it, allowing companies to monitor their brand’s health over time.
- Measuring brand loyalty and customer satisfaction: Quantitative research can assess how likely customers are to repurchase or recommend a brand, providing insights into customer retention strategies.
- Comparing brand performance against competitors: Competitive benchmarking surveys can reveal a brand’s strengths and weaknesses relative to competitors in various attributes.
Customer Segmentation
- Identifying distinct customer groups: By analyzing survey data on demographics, behaviors, and preferences, researchers can use cluster analysis to group customers with similar characteristics.
- Determining the size and value of different market segments: Once segments are identified, quantitative research can estimate the size of each segment and its potential value to the business.
Advertising Effectiveness
- Measuring ad recall and recognition: Surveys conducted after ad campaigns can quantify how many people remember seeing an ad and can correctly identify the brand associated with it.
- Assessing the impact of advertising on purchase intent: Researchers can measure how exposure to ads influences consumers’ likelihood to buy a product, helping to justify advertising spend.
- Evaluating return on investment for marketing campaigns: By linking advertising exposure data with sales data, companies can calculate the ROI of their marketing efforts.
Market Sizing and Forecasting
- Estimating market size and growth potential: Using survey data and secondary sources, researchers can quantify the current market size and project future growth based on trends and economic factors.
- Projecting future sales and market share: Time series analysis and regression models can be used to forecast a company’s sales and market share based on historical data and market conditions.
Customer Experience
- Measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty: Regular surveys can track customer satisfaction scores and Net Promoter Scores (NPS) to gauge overall customer sentiment and loyalty.
- Identifying pain points in the customer journey: Quantitative analysis of customer feedback can highlight common issues or areas of dissatisfaction in the customer experience.
- Quantifying the impact of service improvements: By measuring customer satisfaction before and after implementing changes, companies can assess the effectiveness of their improvement initiatives.
Competitive Analysis
- Benchmarking product or service performance: Surveys can compare how a company’s offerings stack up against competitors on various attributes, helping identify areas for improvement.
- Assessing market share and competitive positioning: Regular tracking studies can monitor changes in market share and brand positioning relative to competitors, informing strategic decisions.
Collect Insights From Your True Customers
Benefits and Challenges of Quantitative Market Research
Quantitative market research offers a range of advantages that make it a valuable tool for businesses seeking data-driven insights. Understanding these benefits can help organizations leverage this research method effectively to inform their strategies and decision-making processes.
Objectivity: Quantitative research provides unbiased, numerical data that can be statistically analyzed. This objectivity ensures that the findings are not influenced by the researcher’s personal biases or perspectives.
Generalizability: Results derived from large sample sizes can be extrapolated to represent the broader population. This means that the findings are more likely to be valid for all individuals within the target group, enhancing the reliability of the study.
Comparability: Standardized data collection methods allow for easy comparison across different time periods or market segments. This comparability is crucial for tracking changes and trends over time, as well as for identifying differences between various subgroups.
Scalability: Quantitative research methods can efficiently gather data from large sample sizes. This scalability makes it possible to conduct studies on a much larger scale, providing more comprehensive insights into the research question.
Hypothesis testing: Quantitative research enables researchers to test specific theories or assumptions about market behavior. By confirming or disproving these hypotheses, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the factors driving market trends and consumer behaviors.
Decision support: The concrete data obtained from quantitative research provides a solid foundation to support strategic decision-making. This evidence-based approach facilitates more informed and effective decisions, reducing the risk of error and improving outcomes.
While quantitative market research provides numerous advantages, it’s important to recognize that this approach also comes with its own set of limitations and potential pitfalls. Being aware of these challenges can help researchers and businesses plan more effectively and interpret results with appropriate caution.
Limited depth: Quantitative research methods may not capture the nuanced reasons behind consumer behavior or attitudes, often resulting in a superficial understanding of complex issues.
Inflexibility: Structured surveys and experiments may miss unexpected insights that could emerge in more open-ended research methods, limiting the scope of discovery.
Response bias: Respondents may not always provide honest or accurate answers, particularly on sensitive or personal topics, leading to skewed data and unreliable conclusions.
Cost: Conducting large-scale surveys or experiments can be expensive, often requiring significant financial resources for data collection, participant incentives, and analysis.
Time-consuming: The proper design, implementation, and analysis of quantitative research can be time-intensive, potentially delaying the results and impacting project timelines.
Expertise required: Quantitative research requires extensive knowledge of statistical analysis and research methodologies, necessitating skilled professionals to ensure accurate and reliable outcomes.
Examples of Quantitative Market Research
To illustrate the practical applications of quantitative market research, let’s explore some real-world examples:
Netflix A/B Testing Titles
Ever noticed how Netflix displays different titles or artwork for the same movie or show depending on your profile? This is A/B testing, a form of quantitative research. Netflix uses surveys and click-through rates to determine which title or artwork generates the most clicks and engagement.
Spotify Optimizing Playlists
How does Spotify create those eerily perfect playlists that seem to know exactly what you’re in the mood for? Quantitative research plays a role! Spotify analyzes user listening habits, including skip rates, play time, and song popularity, to curate playlists that resonate with different user preferences.
Coca-Cola Testing New Flavors
Developing a new beverage flavor requires understanding consumer preferences. Coca-Cola uses surveys and taste tests to gather quantitative data on sweetness levels, flavor combinations, and overall appeal. This data helps them refine new flavors before a full-scale launch.
Apple gauging iPhone Screen Size Preferences
Before increasing iPhone screen sizes, Apple likely conducted quantitative research. Online surveys and focus groups could have gathered data on user preferences for screen size, one-handed usability, and content viewing experience. This data likely helped Apple determine the optimal screen size for future iPhones.
Dominos Revamping its Pizza Recipe
In 2009, Domino ‘s faced declining sales. Quantitative research came to the rescue. Domino’s conducted customer surveys and taste tests to understand customer dissatisfaction with its pizza crust and sauce. Based on the findings, they revamped the recipe, leading to a significant turnaround in customer satisfaction and sales.
These are just a few examples, but they showcase the power of quantitative research in helping businesses make data-driven decisions that resonate with their target audiences.
Tools and Resources for Quantitative Research
To conduct effective quantitative market research, consider utilizing these tools and resources :
Survey Platforms
Qualtrics : Comprehensive survey software with advanced analytics
Prelaunch : Lets you gather data via a landing page that concisely presents your product
SurveyMonkey : User-friendly platform for creating and distributing surveys
Google Forms : Free tool for basic surveys and data collection
Statistical Analysis Software
SPSS : Powerful software for complex statistical analysis
R : Open-source programming language for statistical computing
Prelaunch : The platform is a comprehensive concept-validating tool that complies and presents the data you gather via your product’s landing page into insightful section that make it easier to make data-driven decisions.
Excel : Suitable for basic data analysis and visualization
Online Panel Providers
Dynata : Large global panel for diverse respondent recruitment
Amazon Mechanical Turk : Platform for crowdsourcing survey participants
Data Visualization Tools
Tableau : Creates interactive data visualizations and dashboards
Power BI : Microsoft’s business analytics tool for data visualization
Datawrapper : User-friendly tool for creating charts and maps
Market Research Associations
ESOMAR : Global voice of the data, research, and insights community
Insights Association : Leading voice, resource, and network of the marketing research and data analytics community
Academic Resources
Journal of Marketing Research : Scholarly journal featuring cutting-edge research methodologies
Market Research Society (MRS) : Provides training, qualifications, and resources for market researchers
Remember to choose tools that align with your research objectives, budget, and level of expertise. Many of these platforms offer free trials or basic versions, allowing you to experiment before committing to a paid solution.
Quantitative market research is a powerful tool for making data-driven decisions. By providing objective, measurable insights into consumer behavior and market trends, it helps businesses develop targeted strategies and stay ahead of the competition.
While it has its limitations, combining quantitative methods with qualitative approaches can offer a comprehensive market understanding. Careful planning, rigorous methodology, and thoughtful interpretation of results are key to successful quantitative research.
Embrace the power of numbers and let data guide your business success.
Related Articles

Top Fashion Tech Startups Worth Knowing About
- by Iskouhie Poladian
- Updated on January 26, 2024

B2B Market Research: Benefits, Methods, and Examples
- by Alice Ananian
- Updated on June 28, 2024
Statistics Resources
- Career Guides
- Interview Prep Guides
- Free Practice Tests
- Excel Cheatsheets
💡 Expert-Led Sessions 📊 Build Financial Models ⏳ 60+ Hours Learning

Quantitative Analysis
Publication Date :
28 Jul, 2022
Blog Author :
WallStreetMojo Team
Edited by :
Ashish Kumar Srivastav
Reviewed by :
Dheeraj Vaidya, CFA, FRM
Table Of Contents
What is Quantitative Analysis?
Quantitative analysis (QA) is a mathematical approach that collects data, studies, measures, and analyzes it. It uses various techniques like statistical research, financial modeling, and other scientific methods. The main objective of QA is to use simplified, refined data to make better decisions and forecast trends.

Quantitative analysis of data is a very important statistical tool with countless applications. For example, governments employ quantitative analysis to measure the economic parameters and is used by businesses to evaluate their financial performance. Investors also adopt it to select investments.
Table of contents
Quantitative analysis explained, complexity of quantitative analysis, quantitative analysis in business, quantitative analysis in finance, quantitative analysis vs. qualitative analysis, frequently asked questions (faqs), recommended articles.
- Quantitative analysis is a statistical tool that collects and studies vast amounts of relevant data. Insights gained from the data can help understand the behavior and trends.
- It is a diversely adopted approach as it has many benefits and can help achieve corporate, public, or individual objectives.
- Like QA, qualitative analysis is another important tool that uses intangible information in decision-making. One can incorporate quantitative and qualitative analysis for best results.
- Major types of quantitative analysis include descriptive, correlational, quasi-experimental, and experimental analysis.
Quantitative analysis of data is a concept that has always been used. For example, since people moved on from the barter system and started using commodity money, they have estimated and evaluated their profits and losses in value.
However, the QA techniques now in use are very complex. There are tons of data available, each important in its way. For instance, suppose there's an e-retailer. There are many factors the retailer has to consider, such as the number of people visiting the website, the number of people who make purchases, the average bill amount, etc. These are the basic factors any retailer will consider.
But in the digital era, the e-retailer will also have to evaluate the performance of online advertisements and social media marketing and even account for why visitors are not making purchases or why a certain marketing campaign is ineffective. Nevertheless, fortunately for the retailer, there is data.
The complexity of the QA can be attributed to technology and digitization. As a result, there are many metrics to track, many variables to measure, and many parameters to evaluate. Especially in big establishments like governmental organizations, there are numerous factors to consider.
For example, governments measure different parameters related to national income, expenditure, public health, international and domestic trade, education, employment, etc. They also analyze past trends, understand present conditions, and predict changes in the future.
There are mainly four methods or types of quantitative analysis – descriptive, correlational, quasi-experimental, and experimental analysis.
- Descriptive analysis – This type of analysis is mostly observational, i.e., the analyst observes the area of study, collects data, and develops insights. There is not much technical aspect here, except in the compilation and differentiation of data. It helps measure a variable, and to an extent, it is possible to establish relationships between two variables. Descriptive analysis is used in case studies or mostly for understanding the present situation of the analysts' field of study. For example, how do teenagers react to a strict reduction in screen time at home? Or what are the unemployment patterns in a country? These questions need to be answered.
- Correlational analysis – In this method, analysts establish the correlation between multiple variables. It quantifies how a change in one variable can alter the other dependent variables. The correlational analysis is a type of descriptive analysis, as its scope only extends to studying the relationship. Such a type of analysis can be used in understanding the improvement in living standards when per capita income increases by a certain amount or the increase in sales of a particular product when a new version of its complementary product is introduced. The correlational analysis doesn't require complex tools. Small amounts of data can be analyzed with simple excel tools.
- Quasi-experimental analysis – Also known as causal-comparative analysis, it evaluates data and establishes the cause-effect relationship between multiple variables. Therefore, it is more complex than descriptive and correlational analyzes. In addition, such a study would require the participation of different study groups. It studies why two variables show a certain relationship. For example, how do gender and culturally diverse decision-making groups come up with better decisions? Or, why does the Russia-Ukraine war change the consumption patterns of people globally? These questions need to be studied.
- Experimental analysis – In this type of analysis, the analyst or experimenter first develops a hypothesis. Then, study groups are formed with diverse participants. The method is very complex and time-consuming. It uses scientific approaches to test the hypothesis by employing vast amounts of data and other inputs. Examples of this analysis include proving a hypothesis that encouraging creativity in the workspace can increase employees' productivity.
Let's look at an example of how quantitative analysis helps to navigate uncertain markets for investments. Geopolitical risks are one of the major issues concerning those investing in foreign markets. The risk only becomes intense after the COVID-19 pandemic and worldwide surging inflation.
A recent online survey by Bloomberg shows that around 70% of investors spend too much time analyzing and optimizing risk exposure. This is where the QA tools step in, like the 'Factor Evaluation Model' created by Bloomberg Intelligence. It considers factors like value, volatility, dividend yield, etc.
In this model, investors can research and find the country-wise geopolitical trends in the past and how they affected the markets. For example, investors can check the effects of the 2020 presidential election, Greece's financial crisis, the 2011 Japan earthquake, etc. Such a tool will help investors consider different perspectives, understand the markets, and invest wisely. It also gives them better returns and assists in diversifying their portfolio by reducing risk.
Applications
QA has many real-world applications precisely because of its benefits. It can provide many insights and advantages to the entity or individual undertaking it. Check out a few applications of QA in business and finance .
Quantitative analysis research in business is a very important tool at the companies' disposal because everything depends on data in this digital era. Today, data makes or breaks a business. But most importantly, it provides them a competitive edge if used correctly.
Businesses use QA techniques to understand consumption patterns, forecast demand, optimize supply and demand levels, organize production activities, and plan the budget. It can also tell them about customers' likes and dislikes and the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns.
The financial quantitative analysis finds applications in economies, businesses, and investments. For example, governments usually have to consider many financial aspects of an economy , like GDP , fiscal deficit , per capita income, etc. Similarly, QA in companies evaluate their financial performance, measures the value of assets, and is also necessary for financing the firm's operations. Finally, investors too analyze the performance of companies over the years, track the performance of stocks, and consider ratios like EPS , P/E , etc., before investing.
Like QA, qualitative analysis helps analysts study data, make better decisions, and predict outcomes. However, there are certain basic differences between the two:
Despite these differences, both these methods are extremely significant in understanding any specific issue. Not only that, both these analyzes have different applications and are equally important in the bigger picture.
Quantitative analysis research can be done using statistical techniques like descriptive, correlational, quasi-experimental, and experimental analyses. In addition, analysts can use technological resources like computers, people's participation, and, most importantly, data.
No. QA is not a difficult concept. It can be complex, as an analyst has to consider various facets of a problem and think from many different perspectives. Also, the complexity of QA depends on the industry and the problem at hand. However, aspiring analysts can take up educational courses like data science, operations research, etc. Financial quantitative analysis at the most basic level for investors needs some degree of commitment and effort from the individuals to help them get equipped with the necessary tools. And again, there are many online courses available for this.
QA is used by governments, businesses, and even independent investors. Firstly, it can be used to study a situation, measure the variables, and predict outcomes. Secondly, it can help a great deal in decision-making.
This has been a guide to Quantitative Analysis and its definition. Here we discuss how Quantitative Analysis works with its methods, applications and example. You can learn more from the following articles -
- Decision Analysis
- Statistical Analysis
- Risk Analysis
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Get Started Free
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
What Is Quantitative Research? Types, Characteristics & Methods

Market Research Specialist
Emma David, a seasoned market research professional, specializes in employee engagement, survey administration, and data management. Her expertise in leveraging data for informed decisions has positively impacted several brands, enhancing their market position.

Ever wondered how companies figure out what we want? The answer lies in numbers. Quantitative research is the art of turning numerical data into valuable insights by uncovering hidden trends and patterns.
From understanding customer behaviors to making smarter business decisions, numbers can tell a powerful story.
In this blog, we’ll explore how this research method can help your business and learn about its types, examples, and expert-backed tips.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is a method that uses numbers and statistics to gather precise, measurable data on the research subject.
Offering numbers and stats-based insights, this research methodology is a crucial part of primary research and helps understand how well an organizational decision will work out.
This approach mainly uses online surveys, questionnaires , polls , and quizzes to collect measurable and unbiased data from large groups.
For example, qualitative research can let you know whether your product is a hit or miss, but quantitative data allows you to know exactly what percentage of consumers like it, and what numbers think you still need to improve. As a result of this precision , you can make decisions that are likely to be more in tune with the market demands
Quantitative research thus provides crucial, numbers-based insights that help organizations make informed decisions and predict outcomes effectively .
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research clarifies the fuzziness of research data from qualitative research analysis. With numerical insights, you can formulate a better and more profitable business decision.
Hence, quantitative research is more readily contestable, sharpens intelligent discussion, helps you see the rival hypotheses, and dynamically contributes to the research process.
Let us have a quick look at some of its characteristics.
1. Measurable Variables
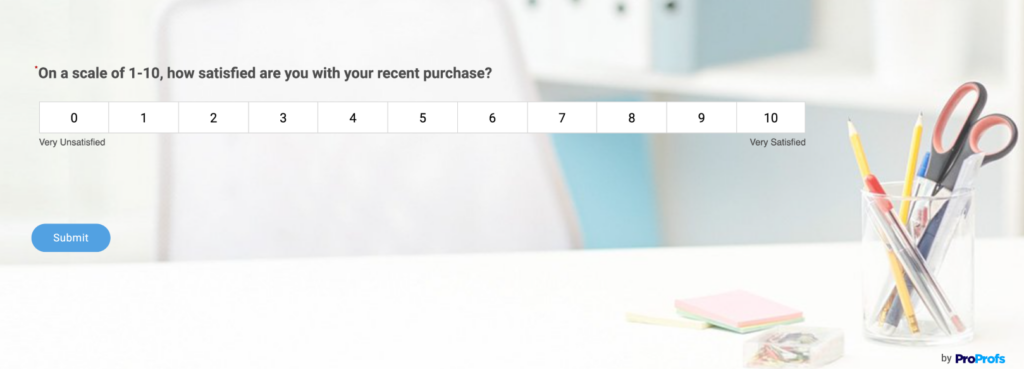
The data collection methods in quantitative research are structured and contain items requiring measurable variables, such as age, number of family members, salary range, highest education, etc.
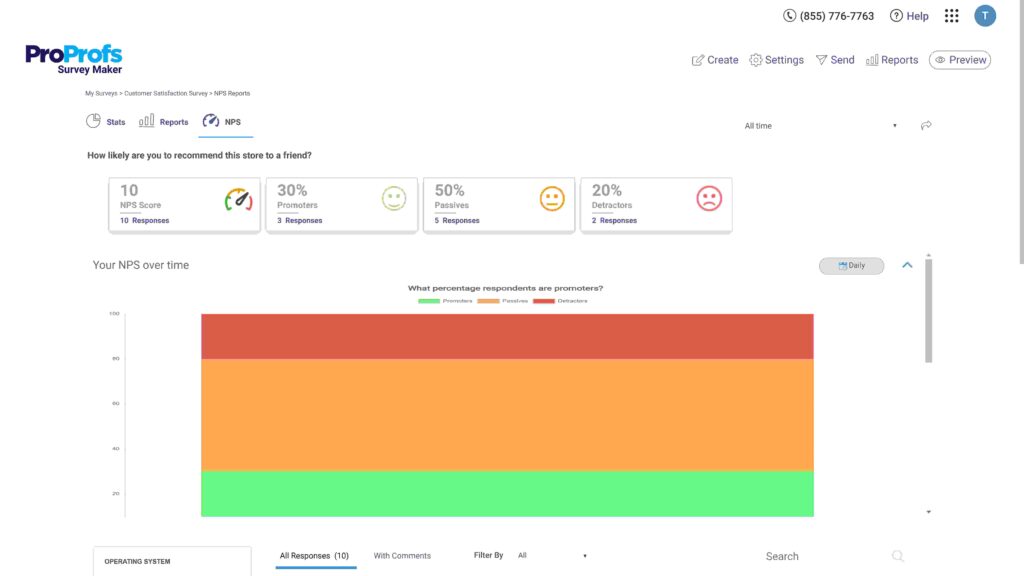
These structured data collection methods comprise polls, surveys, questionnaires, etc., and may have questions like the ones shown in the following image:

As you can see, all the variables are measurable. This ensures the research is in-depth and provides less erroneous data for reliable, actionable insights.
2. Sample Size
No matter what data analysis methods are used for quantitative research, the sample size is kept small enough to represent the target market.
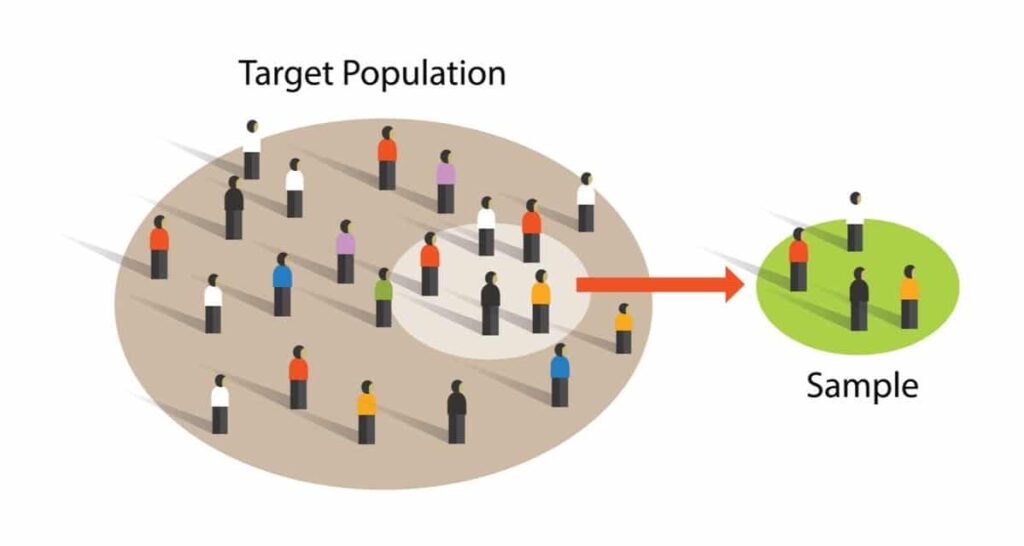
The main aim of the research methodology is to obtain numerical insights, so the sample size should be fairly large. Depending on the survey objective and scope, it might include hundreds of thousands of people.
3. Normal Population Distribution
To maintain the reliability of a quantitative research methodology, we assume that the population distribution curve is normal.
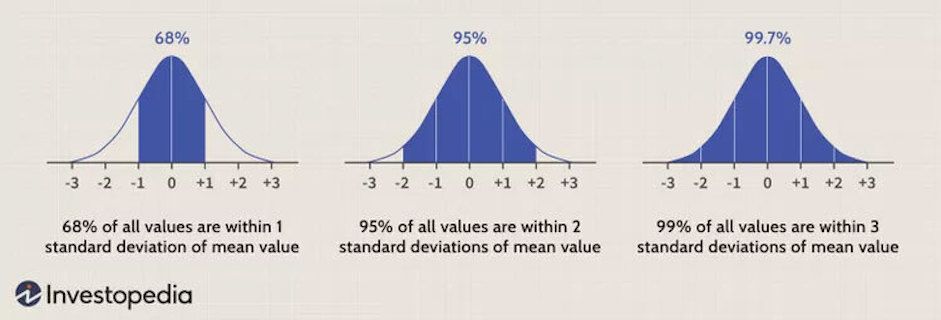
This type of population distribution curve is preferred over a non-normal distribution as the sample size is large, and the characteristics of the sample vary with its size.
This requires adhering to the random sampling principle to avoid the researcher’s bias in interpreting the results. Any bias can ruin the fairness of the entire process and defeat the purpose of the research.
4. Well-Structured Data Representation
Data analysis in quantitative research produces highly structured results and can form well-defined graphical representations. Some common examples include tables, figures, graphs, etc., that combine large blocks of data.
This way, you can discover hidden data trends, relationships, and differences among various measurable variables. This can help researchers understand the survey data and formulate actionable insights for decision-making.
5. Predictable Outcomes
Quantitative data analysis can also be used to estimate and predict outcomes. You can construct if-then scenarios and analyze the data to identify upcoming trends or events.
However, this requires advanced analytics and involves complex mathematical computations. So, it is mostly done via quantitative research tools with advanced analytics capabilities.
What Are the Types and Examples of Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is usually conducted using two methods. They are-
- Primary quantitative research methods
- Secondary quantitative research methods
Let’s discuss each type in detail.
I. Primary Methods
Primary quantitative research is the most popular method of conducting market research. This method differs from others in that the researcher collects data firsthand instead of using data collected from previous research.
There are multiple types of primary quantitative research. They can be distinguished based on three distinctive aspects: Techniques & types of studies, Data collection methodologies, and Data analysis techniques .
A. Techniques & Types of Studies:
1. survey research.
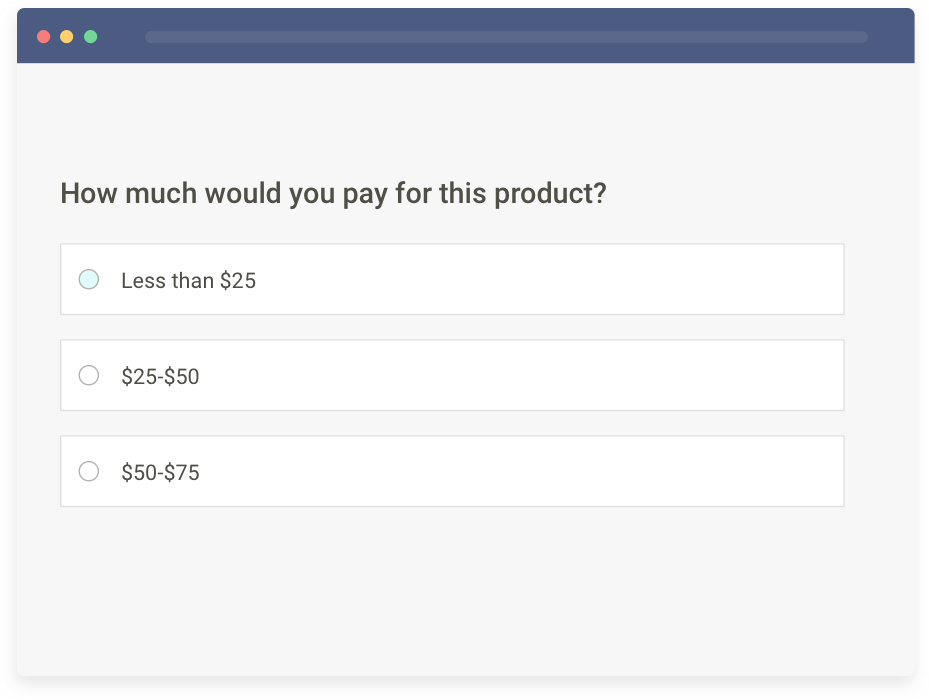
Surveys are the easiest, most common, and one of the most sought-after quantitative research techniques. The main aim of a survey is to widely gather and describe the characteristics of a target population or customers. Surveys are the foremost quantitative method preferred by both small and large organizations.
Surveys can be conducted using various methods, such as online polls, web-based surveys, paper questionnaires, phone calls, or face-to-face interviews. Survey research allows organizations to understand customer opinions, preferences, and behavior, making it crucial for market research and decision-making.
You can watch this quick video to learn more about creating surveys.
Watch: How to Create a Survey Using ProProfs Survey Maker
Surveys, again, are of two types:
2. Cross-Sectional Surveys
Cross-sectional surveys are used to collect data from a sample of the target population at a specific point in time. Researchers evaluate various variables simultaneously to understand the relationships and patterns within the data.
Cross-sectional surveys are popular in retail, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and healthcare industries, where they assess customer satisfaction, market trends, and product feedback.
3. Longitudinal Surveys
Longitudinal surveys are conducted over an extended period, observing changes in respondent behavior and thought processes.
Researchers gather data from the same sample multiple times, enabling them to study trends and developments over time. These surveys are valuable in fields such as medicine, applied sciences, and market trend analysis.
4. Correlational Research:
Correlational research aims to establish relationships between two or more variables.
Researchers use statistical analysis to identify patterns and trends in the data, but it does not determine causality between the variables. This method helps understand how changes in one variable may impact another.
Examples of correlational research questions include studying the relationship between stress and depression, fame and money, or classroom activities and student performance.
5. Causal-Comparative Research:
Causal-comparative research, or quasi-experimental research, seeks to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
Researchers analyze how an independent variable influences a dependent variable, but they do not manipulate the independent variable. Instead, they observe and compare different groups to conclude.
Causal-comparative research is useful when it’s not ethical or feasible to conduct true experiments.
Questions for this type of research include analyzing the effect of training programs on employee performance, studying the influence of customer support on client retention, investigating the impact of supply chain efficiency on cost reduction, etc.
6. Experimental Research:
Experimental research is based on testing theories to validate or disprove them. Researchers conduct experiments and manipulate variables to observe their impact on the outcomes.
This type of research is prevalent in natural and social sciences, and it is a powerful method to establish cause-and-effect relationships. By randomly assigning participants to experimental and control groups, researchers can draw more confident conclusions.
Examples of experimental research include studying the effectiveness of a new drug, the impact of teaching methods on student performance, or the outcomes of a marketing campaign.
B. Data Collection Methodologies
After defining research objectives, the next significant step in primary quantitative research is data collection. This involves using two main methods: sampling and conducting surveys or polls. Quantitative research can also be categorized according to their sampling methods .
In quantitative research, there are two primary sampling methods: Probability and Non-probability sampling .
1. Probability Sampling
In probability sampling, researchers use the concept of probability to create samples from a population. This method ensures that every individual in the target audience has an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
There are four main types of probability sampling:
- Simple random sampling : Here, the elements or participants of a sample are selected randomly, and this technique is used in studies that are conducted over considerably large audiences. It works well for large target populations.
- Stratified random sampling : In this method, the entire population is divided into strata or groups, and the sample members get chosen randomly from these strata only. It is always ensured that different segregated strata do not overlap with each other.
- Cluster sampling : Here, researchers divide the population into clusters, often based on geography or demographics. Then, random clusters are selected for the sample.
- Systematic sampling : In this method, only the starting point of the sample is randomly chosen. All the other participants are chosen using a fixed interval. Researchers calculate this interval by dividing the size of the study population by the target sample size.
2. Non-probability Sampling
Non-probability sampling is a method where the researcher’s knowledge and experience guide the selection of samples. This approach doesn’t give all members of the target population an equal chance of being included in the sample.
There are five non-probability sampling models:
- Convenience sampling : The elements or participants are chosen on the basis of their nearness to the researcher. The people in close proximity can be studied and analyzed easily and quickly, as there is no other selection criterion involved. Researchers simply choose samples based on what is most convenient for them.
- Consecutive sampling : Similar to convenience sampling, researchers select samples one after another over a significant period. They can opt for a single participant or a group of samples to conduct quantitative research in a consecutive manner for a significant period of time. Once this is over, they can conduct the research from the start.
- Quota sampling : With quota sampling, researchers use their understanding of target traits and personalities to form groups (strata). They then choose samples from each stratum based on their own judgment.
- Snowball sampling : This method is used where the target audiences are difficult to contact and interviewed for data collection. Researchers start with a few participants and then ask them to refer others, creating a snowball effect.
- Judgmental sampling : In judgmental sampling, researchers rely solely on their experience and research skills to handpick samples that they believe will be most relevant to the study.
C. Data Analysis Techniques
Once the raw data is collected, the next step in primary quantitative research is data analysis. This crucial process helps draw inferences from the research. It’s essential to connect the results with the objectives and determine their statistical significance.
To analyze the quantitative data accurately, you’ll need to use specific statistical methods such as:
- SWOT Analysis : This stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats analysis. Organizations use SWOT analysis to evaluate their performance internally and externally. It helps develop effective improvement strategies.
- Conjoint Analysis : This market research method uncovers how individuals make complex purchasing decisions. It involves considering trade-offs in their daily activities when choosing from a list of product/service options.
- Cross-tabulation : A preliminary statistical market analysis method that reveals relationships, patterns, and trends within various research study parameters.
- TURF Analysis : Short for Totally Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis, this method helps analyze the reach and frequency of favorable communication sources. It provides insights into the potential of a target market.
By using these statistical techniques and inferential statistics methods like confidence intervals and margin of error , you can draw meaningful insights from your primary quantitative research that you can use in making informed decisions.
II. Secondary Methods
Secondary quantitative research, also known as desk research, is a valuable method that uses existing data, called secondary data.
Instead of collecting new data, researchers analyze and combine already available information to enhance their research. This approach involves gathering quantitative data from various sources such as the internet, government databases, libraries, and research reports.
Secondary quantitative research is crucial in validating data collected through primary quantitative research. It helps reinforce or challenge existing findings.
Here are five commonly used secondary quantitative research methods :
A. Data Available on the Internet:
The Internet has become a vast repository of data, making it easier for researchers to access a wealth of information. Online databases, websites, and research repositories provide valuable quantitative data for researchers to analyze and validate their primary research findings.
B. Government and Non-Government Sources:
Government agencies and non-government organizations often conduct extensive research and publish reports. These reports cover a wide range of topics, providing researchers with reliable and comprehensive data for quantitative analysis.
C. Public Libraries:
While less commonly used in the digital age, public libraries still hold valuable research reports, historical data, and publications that can contribute to quantitative research.
D. Educational Institutions:
Educational institutions frequently conduct research on various subjects. Their research reports and publications can serve as valuable sources of information for researchers, validating and supporting primary quantitative research outcomes.

E. Commercial Information Sources:
Commercial sources such as local newspapers, journals, magazines, and media outlets often publish relevant data on economic trends, market research, and demographic analyses. Researchers can access this data to supplement their own findings and draw better conclusions.
Now, let’s discuss some real-world examples of quantitative research.
Here are two excellent examples of quantitative research methods used by highly distinguished business and consulting organizations. Both examples show how different types of analysis can be performed with qualitative approaches and how the analysis is done once the data is collected.
1. STEP Project Global Consortium / KPMG 2019 Global Family Business Survey
This research utilized quantitative methods to identify ways that kept the family businesses sustainably profitable with time.
The study also identified the ways in which the family business behavior changed with demographic changes and had “why” and “how” questions. Their qualitative research methods allowed the KPMG team to dig deeper into the mindsets and perspectives of the business owners and uncover unexpected research avenues as well.
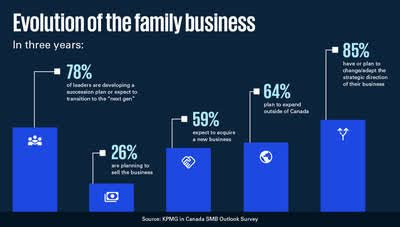
It was a joint effort in which STEP Project Global Consortium collected 26 cases, and KPMG collected 11 cases.
The research reached the stage of data analysis in 2020, and the analysis process spanned over 4 stages.
The results, which were also the reasons why family businesses tend to lose their strength with time, were found to be:
- Family governance
- Family business legacy
2. EY Seren Teams Research 2020
This is yet another commendable example of qualitative research where the EY Seren Team digs into the unexplored depths of human behavior and how it affected their brand or service expectations.
The research was done across 200+ sources and involved in-depth virtual interviews with people in their homes, exploring their current needs and wishes. It also involved diary studies across the entire UK customer base to analyze human behavior changes and patterns.
The study also included interviews with professionals and design leaders from a wide range of industries to explore how COVID-19 transformed their industries. Finally, quantitative surveys were conducted to gain insights into the EY community after every 15 days.
The insights and results were:
- A culture of fear, daily resilience, and hopes for a better world and a better life – these were the macro trends.
- People felt massive digitization was a resourceful yet demanding aspect as they had to adapt every day.
- Some people wished to have a new world with lots of possibilities, and some were looking for a new purpose.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research data is often standardized and can be easily used to generalize findings for making crucial business decisions and uncover insights to supplement the qualitative research findings.
Here are some core benefits this research methodology offers.
A. Objectivity and Reliability
- Unbiased Insights: By relying on numerical data, quantitative research minimizes researcher bias, leading to more objective findings.
- Reproducibility: The standardized methods used in quantitative research allow for the replication of studies, enhancing the reliability and credibility of results.
B. Efficiency and Scalability
- Large Sample Sizes: Quantitative methods enable researchers to gather data from large populations, providing a comprehensive understanding of trends and patterns.
- Rapid Data Collection: Efficient data collection techniques, such as online surveys, expedite the research process.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to qualitative research, quantitative methods can be more cost-effective due to their efficiency and scalability.
C. Precision and Generalizability
- Numerical Precision: Quantitative data provides precise measurements and statistical analysis, allowing for accurate comparisons and predictions.
- Generalizability: Findings from large, representative samples can be generalized to the broader population more confidently.
D. Data-Driven Decision-Making
- Informed Choices: Quantitative research offers actionable insights to inform strategic decisions in business, healthcare, policymaking, and other fields.
- Performance Measurement: By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), organizations can measure the effectiveness of their initiatives and make necessary adjustments.
Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Despite its numerous benefits, quantitative research has some cons as well, such as:
A. Lack of Depth and Context
Quantitative research excels at providing numerical data but falls short when it comes to understanding the underlying reasons for behaviors or opinions. It offers a snapshot of what happened but not necessarily why it happened. Researchers may struggle to delve into the complexities of human experiences and motivations.
B. Overreliance on Structured Data
The rigid nature of quantitative research limits the exploration of unexpected findings. Researchers are confined to pre-determined questions and response options, potentially overlooking valuable insights from open-ended exploration.
C. Potential for Bias
While striving for objectivity, quantitative research is not immune to bias. Factors such as sample selection, question-wording, and data analysis methods can introduce biases that distort the results. Careful planning and execution are essential to mitigate these risks.
E. Difficulty Establishing Causality
Correlation does not equal causation. While quantitative research can identify relationships between variables, establishing definitive cause-and-effect links is challenging. Other factors may influence the observed relationship, making it difficult to isolate the true cause.
F. Resource Intensive
Conducting quantitative research often requires significant time and financial resources. Collecting large datasets, employing statistical analysis, and ensuring data quality can be costly and time-consuming. Additionally, specialized expertise may be needed for data analysis and interpretation.
When to Use Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is particularly suited for the following scenarios:
1. Testing Hypotheses and Theories
- Hypothesis Verification: When you have a specific prediction about a relationship between variables, quantitative research can be used to test its validity.
- Theory Building: By gathering numerical data, you can identify patterns and trends that contribute to the development of new theories or the refinement of existing ones.
2. Measuring and Comparing
- Market Research: Assessing market size, share, and customer preferences to inform product development or marketing strategies.
- Performance Evaluation: Quantifying the effectiveness of programs, policies, or interventions through metrics and benchmarks.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing different groups or conditions to identify similarities, differences, and relationships.
3. Generalizing Findings
- Population Representation: When you aim to draw conclusions about a larger population based on a representative sample.
- Predictive Modeling: Building models to forecast future trends or outcomes based on historical data.
4. Identifying Cause-and-Effect Relationships
- Experimental Design: While challenging, quantitative research can be used to establish causal relationships through controlled experiments.
- Correlational Analysis: Identifying patterns and associations between variables, though caution is needed to avoid assuming causation.
In essence, quantitative research is most appropriate when you seek precise, measurable data to answer specific research questions and make informed decisions.
What Is the Purpose of Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is the backbone of evidence-based decision-making. Its core purpose is to transform raw data into actionable insights. Researchers can uncover hidden patterns, trends, and relationships that might otherwise go unnoticed by employing statistical methods to analyze numerical information.
Here’s an in-depth analysis of its true objectives:
- Prediction: Quantitative research excels at forecasting future trends or outcomes. By identifying historical patterns, researchers can model potential scenarios and make informed predictions.
- Generalization: By studying a representative sample, researchers can draw conclusions about a larger population. This allows for extrapolating findings to broader groups, providing valuable insights for businesses, policymakers, and scientists.
- Testing Hypotheses: Quantitative research is essential for testing theories and hypotheses. By collecting empirical data, researchers can determine if their assumptions are supported by evidence.
- Measuring Outcomes: Evaluating the effectiveness of interventions or programs is a key application of quantitative research. By tracking specific metrics, researchers can assess the impact of initiatives and make necessary adjustments.
- Understanding Relationships: This research method helps uncover correlations and causal relationships between variables. By identifying how factors influence each other, researchers can develop strategies to optimize outcomes.
Best Practices for Conducting Quantitative Research
Here are some best practices to keep in mind while conducting quantitative research:
1. Understand Your Research Objectives
There are many ways to collect data via quantitative research methods chosen according to the research objective and scope . These methods allow you to make your own observations regarding any hypotheses—unknown, entirely new, or unexplained.
Based on that, you can hypothesize proof and build a prediction of outcomes that support the same. You can also create a detailed stepwise plan for data collection, analysis, and testing.
2. Keep Your Questions Simple
The surveys are meant to reach people en-masse, including a wide demographic range with recipients from all walks of life. Asking simple questions will ensure that they grasp what’s being asked easily.
3. Develop a Solid Research Design
Choose an appropriate research design that aligns with your objectives, whether experimental, quasi-experimental, or correlational . You also need to pay attention to the sample size and sampling technique so that they accurately represent the target population.
4. Use Reliable & Valid Instruments
It’s crucial to select or develop measurement instruments such as questionnaires, scales, or tests that have been validated and are reliable. Before proceeding with the main study, pilot-test these instruments on a small sample to assess their effectiveness and make any necessary improvements.
5. Ensure Data Quality
Double-check data entries and cleaning procedures to eliminate any inconsistencies or missing values that may affect the accuracy of your results. For instance, you might regularly cross-verify data entries to identify and correct any discrepancies.
6. Employ Appropriate Data Analysis Techniques
Select statistical methods that match the nature of your data and research questions. Whether it’s regression analysis, t-tests, ANOVA, or other techniques, using the right approach is important for drawing meaningful conclusions. Utilize software tools like SPSS or R for data analysis to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of your findings.
7. Interpret Results Objectively
Present your findings clearly and unbiasedly . Avoid making unwarranted causal claims, especially in correlational studies . Instead, focus on describing the relationships and patterns observed in your data.
8. Address Ethical Considerations
Prioritize ethical considerations throughout your research process. Obtain informed consent from participants, ensuring their voluntary participation and confidentiality of data . Comply with ethical guidelines and gain approval from a governing body if necessary.
Enhance Your Quantitative Research With Cutting-Edge Software
While no single research methodology can produce 100% reliable results, you can always opt for a hybrid method by selecting the most relevant methods for your objective.
For the best results, opt for smart, efficient, and scalable research tools that offer delightful reporting and advanced analytics. These tools will make every research initiative a success.
Advanced software tools, such as ProProfs Survey Maker, come with pre-built survey templates and question libraries and allow you to create a high-converting survey in just a few minutes.

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Related Posts

How to Ask Race & Ethnicity Survey Questions: A Professional Guide [With Examples]

Close Ended Questions: A Complete Guide With Types & Examples

45+ Post Webinar Survey Questions to Improve Your Webinar Experience – ProProfs

How To Write a Good Research Question: Guide with Definition, Tips & Examples

How Demographics Surveys Make Marketing Metrics Stand-Out

What Are Pre-Event Survey Questions? Types, Examples & How to Send Them

- Agile & Development
- Prioritization
- Product Management
- Product Marketing & Growth
- Product Metrics
- Product Strategy
Home » Quantitative Research: Definition, Methods, and Examples
Quantitative Research: Definition, Methods, and Examples
June 13, 2023 max 8min read.

This article covers:
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research methods .
- Data Collection and Analysis
Types of Quantitative Research
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Examples of Quantitative Research
Picture this: you’re a product or project manager and must make a crucial decision. You need data-driven insights to guide your choices, understand customer preferences, and predict market trends. That’s where quantitative research comes into play. It’s like having a secret weapon that empowers you to make informed decisions confidently.
Quantitative research is all about numbers, statistics, and measurable data. It’s a systematic approach that allows you to gather and analyze numerical information to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations.
Quantitative research provides concrete, objective data to drive your strategies, whether conducting surveys, analyzing large datasets, or crunching numbers.
In this article, we’ll dive and learn all about quantitative research; get ready to uncover the power of numbers.
Quantitative Research Definition:
Quantitative research is a systematic and objective approach to collecting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data. It measures and quantifies variables, employing statistical methods to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends.
Quantitative research gets utilized across a wide range of fields, including market research, social sciences, psychology, economics, and healthcare. It follows a structured methodology that uses standardized instruments, such as surveys, experiments, or polls, to collect data. This data is then analyzed using statistical techniques to uncover patterns and relationships.
The purpose of quantitative research is to measure and quantify variables, assess the connections between variables, and draw objective and generalizable conclusions. Its benefits are numerous:
- Rigorous and scientific approach : Quantitative research provides a comprehensive and scientific approach to studying phenomena. It enables researchers to gather empirical evidence and draw reliable conclusions based on solid data.
- Evidence-based decision-making : By utilizing quantitative research, researchers can make evidence-based decisions. It helps in developing informed strategies and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions or policies by relying on data-driven insights.
- Advancement of knowledge : Quantitative research contributes to the advancement of knowledge by building upon existing theories. It expands understanding in various fields and informs future research directions, allowing for continued growth and development.
Here are various quantitative research methods:
Survey research : This method involves collecting data from a sample of individuals through questionnaires, interviews, or online surveys. Surveys gather information about people’s attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and characteristics.
Experimentation: It is a research method that allows researchers to determine cause-and-effect relationships. In an experiment, participants randomly get assigned to different groups. While the other group does not receive treatment or intervention, one group does. The outcomes of the two groups then get measured to analyze the effects of the treatment or intervention.
Here are the steps involved in an experiment:
- Define the research question. What do you want to learn about?
- Develop a hypothesis. What do you think the answer to your research question is?
- Design the experiment. How will you manipulate the variables and measure the outcomes?
- Recruit participants. Who will you study?
- Randomly assign participants to groups. This ensures that the groups are as similar as possible.
- Apply the treatments or interventions. This is what the researcher is attempting to test the effects of.
- Measure the outcomes. This is how the researcher will determine whether the treatments or interventions had any effect.
- Analyze the data. This is how the researcher will determine whether the results support the hypothesis.
- Draw conclusions. What do the results mean?
- Content analysis : Content analysis is a systematic approach to analyzing written, verbal, or visual communication. Researchers identify and categorize specific content, themes, or patterns in various forms of media, such as books, articles, speeches, or social media posts.
- Secondary data analysis : It is a research method that involves analyzing data already collected by someone else. This data can be from various sources, such as government reports, previous research studies, or large datasets like surveys or medical records.
Researchers use secondary data analysis to answer new research questions or gain additional insights into a topic.
Data Collection and Analysis for Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is research that uses numbers and statistics to answer questions. It often measures things like attitudes, behaviors, and opinions.
There are three main methods for collecting quantitative data:
- Surveys and questionnaires: These are structured instruments used to gather data from a sample of people.
- Experiments and controlled observations: These are conducted in a controlled setting to measure variables and determine cause-and-effect relationships.
- Existing data sources (secondary data): This data gets collected from databases, archives, or previous studies.
Data preprocessing and cleaning is the first step in data analysis. It involves identifying and correcting errors, removing outliers, and ensuring the data is consistent.
Descriptive statistics is a branch of statistics that deals with the description of the data. It summarizes and describes the data using central tendency, variability, and shape measures.
Inferential statistics again comes under statistics which deals with the inference of properties of a population from a sample. It tests hypotheses, estimates parameters, and makes predictions.
Here are some of the most common inferential statistical techniques:
- Hypothesis testing : This assesses the significance of relationships or differences between variables.
- Confidence intervals : This estimates the range within which population parameters likely fall.
- Correlation and regression analysis : This examines relationships and predicts outcomes based on variables.
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) : This compare means across multiple groups or conditions.
Statistical software and tools for data analysis can perform complex statistical analyses efficiently. Some of the most popular statistical software packages include SPSS, SAS, and R.
Here are some of the main types of quantitative research methodology:
- Descriptive research describes a particular population’s characteristics, trends, or behaviors. For example, a descriptive study might look at the average height of students in a school, the number of people who voted in an election, or the types of food people eat.
- Correlational research checks the relationship between two or more variables. For example, a correlational study might examine the relationship between income and happiness or stress and weight gain. Correlational research can show that two variables are related but cannot show that one variable causes the other.
- Experimental research is a type of research that investigates cause-and-effect relationships. In an experiment, researchers manipulate one variable (the independent variable) and measure the impact on another variable (the dependent variable). This allows researchers to make inferences about the relationship between the two variables.
- Quasi-experimental research is similar to experimental research. However, it does not involve random assignment of participants to groups. This can be due to practical or ethical considerations, such as when assigning people to receive a new medication randomly is impossible. In quasi-experimental research, researchers try to control for other factors affecting the results, such as the participant’s age, gender, or health status.
- Longitudinal research studies change patterns over an extended time. For example, a longitudinal study might examine how children’s reading skills develop over a few years or how people’s attitudes change as they age. But longitudinal research can be expensive and time-consuming. Still, it can offer valuable insights into how people and things change over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Here are the advantages and downsides of quantitative research:
Advantages of Quantitative Research:
- Objectivity: Quantitative research aims to be objective and unbiased. This is because it relies on numbers and statistical methods, which reduce the potential for researcher bias and subjective interpretation.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research often involves large sample sizes, which increases the likelihood of obtaining representative data. The study findings are more likely to apply to a wider population.
- Replicability: Using standardized procedures and measurement instruments in quantitative research enhances replicability. This means that other researchers can repeat the study using the same methods to test the reliability of the findings.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research employs various statistical techniques for data analysis. This allows researchers to identify data patterns, relationships, and associations. Additionally, statistical analysis can provide precision and help draw objective conclusions.
- Numerical precision: Quantitative research produces numerical data that can be analyzed using mathematical calculations. This numeric precision allows for clear comparisons and quantitative interpretations.
Disadvantages of Quantitative Research :
- Lack of Contextual Understanding : Quantitative research often focuses on measurable variables, which may limit the exploration of complex phenomena. It may overlook the social, cultural, and contextual factors that could influence the research findings.
- Limited Insight : While quantitative research can identify correlations and associations, it may not uncover underlying causes or explanations of these relationships. It may provide answers to “what” and “how much,” but not necessarily “why.”
- Potential for Simplification : The quantification of data can lead to oversimplification, as it may reduce complex phenomena into numerical values. This simplification may overlook nuances and intricacies important to understanding the research topic fully.
- Cost and Time-Intensive : Quantitative research requires significant resources. It includes time, funding, and specialized expertise. Researchers must collect and analyze large amounts of numerical data, which can be lengthy and expensive.
- Limited Flexibility : A systematic and planned strategy typically gets employed in quantitative research. It signifies the researcher’s use of a predetermined data collection and analysis approach. As a result, you may be more confident that your study gets conducted consistently and equitably. But it may also make it more difficult for the researcher to change the research plan or pose additional inquiries while gathering data. This could lead to missing valuable insights.
Here are some real-life examples of quantitative research:
- Market Research : Quantitative market research is a type of market research that uses numerical data to understand consumer preferences, buying behavior, and market trends. This data typically gets gathered through surveys and questionnaires, which are then analyzed to make informed business decisions.
- Health Studies : Quantitative research, such as clinical trials and epidemiological research, is vital in health studies. Researchers collect numerical data on treatment effectiveness, disease prevalence, risk factors, and patient outcomes. This data is then analyzed statistically to draw conclusions and make evidence-based recommendations for healthcare practices.
- Educational Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in educational studies to examine various aspects of learning, teaching methods, and academic achievement. Researchers collect data through standardized tests, surveys, or observations. The reason for this approach is to analyze factors influencing student performance, educational interventions, and educational policy effectiveness.
- Social Science Surveys : Social science researchers often employ quantitative research methods. The aim here is to study social phenomena and gather data on individuals’ or groups’ attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors. Large-scale surveys collect numerical data, then statistically analyze to identify patterns, trends, and associations within the population.
- Opinion Polls : Opinion polls and public opinion research rely heavily on quantitative research techniques. Polling organizations conduct surveys with representative samples of the population. The companies do this intending to gather numerical data on public opinions, political preferences, and social attitudes. The data then gets analyzed to gauge public sentiment and predict election outcomes or public opinion on specific issues.
- Economic Research : Quantitative research is widely used in economic studies to analyze economic indicators, trends, and patterns. Economists collect numerical data on GDP, inflation, employment, and consumer spending. Statistical analysis of this data helps understand economic phenomena, forecast future trends, and inform economic policy decisions.
More To Read :-
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Definition and Examples
- What Is Operations Management? Definition and Overview
Qualitative research is about understanding and exploring something in depth. It uses non-numerical data, like interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses, to gather rich, descriptive insights. Quantitative research is about measuring and analyzing relationships between variables using numerical data.
Quantitative research gets characterized by the following:
- The collection of numerical information
- The use of statistical analysis
- The goal of measuring and quantifying phenomena
- The purpose of examining relationships between variables
- The purpose of generalizing findings to a larger population
- The use of large sample sizes
- The use of structured surveys or experiments
- The usage of statistical techniques to analyze data objectively
The primary goal of quantitative research is to gather numerical data and analyze it statistically to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends. It aims to provide objective and generalizable insights using systematic data collection methods, standardized instruments, and statistical analysis techniques. Quantitative research seeks to test hypotheses, make predictions, and inform decision-making in various fields.
Crafting great product requires great tools. Try Chisel today, it's free forever.
Home • Knowledge hub • What is quantitative research?
What is quantitative research?
Quantitative research is an important part of market research that relies on hard facts and numerical data to gain as objective a picture of people’s opinions as possible.
It’s different from qualitative research in a number of important ways and is a highly useful tool for researchers.
Quantitative research is a systematic empirical approach used in the social sciences and various other fields to gather, analyze, and interpret numerical data. It focuses on obtaining measurable data and applying statistical methods to generalize findings to a larger population.
Researchers use structured instruments such as surveys, questionnaires, or experiments to collect data from a representative sample in quantitative research. The data collected is typically numerical values or categorical responses that can be analyzed using statistical techniques. These statistical analyses help researchers identify patterns, relationships, trends, or associations among variables.
Quantitative research aims to generate objective and reliable information about a particular phenomenon, population, or group. It aims to better understand the subject under investigation by employing statistical measures such as means, percentages, correlations, or regression analyses.
Quantitative research provides:
- A quantitative understanding of social phenomena.
- Allowing researchers to make generalizations.
- Predictions.
- Comparisons based on numerical data.
It is widely used in psychology, sociology, economics, marketing, and many other disciplines to explore and gain insights into various research questions.
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into quantitative research, why it’s important, and how to use it effectively.
How is quantitative research different from qualitative research?
Although they’re both extremely useful, there are a number of key differences between quantitative and qualitative market research strategies. A solid market research strategy will make use of both qualitative and quantitative research.
- Quantitative research relies on gathering numerical data points. Qualitative research on the other hand, as the name suggests, seeks to gather qualitative data by speaking to people in individual or group settings.
- Quantitative research normally uses closed questions, while qualitative research uses open questions more frequently.
- Quantitative research is great for establishing trends and patterns of behavior, whereas qualitative methods are great for explaining the “why” behind them.
Why is quantitative research useful?
Quantitative research has a crucial role to play in any market research strategy for a range of reasons:
- It enables you to conduct research at scale
- When quantitative research is conducted in a representative way, it can reveal insights about broader groups of people or the population as a whole
- It enables us to easily compare different groups (e.g. by age, gender or market) to understand similarities or differences
- It can help businesses understand the size of a new opportunity
- It can be helpful for reducing a complex problem or topic to a limited number of variables
Get regular insights
Keep up to date with the latest insights from our research as well as all our company news in our free monthly newsletter.
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Business Email *
Quantitative Research Design
Quantitative research design refers to the overall plan and structure that guides the collection, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data in a quantitative research study. It outlines the specific steps, procedures, and techniques used to address research questions or test hypotheses systematically and rigorously. A well-designed quantitative research study ensures that the data collected is reliable, valid, and capable of answering the research objectives.
There are several key components involved in designing a quantitative research study:
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: The research design begins with clearly defined research questions or hypotheses articulating the study’s objectives. These questions guide the selection of variables and the development of research instruments.
- Sampling: A critical aspect of quantitative research design is selecting a representative sample from the target population. The sample should be carefully chosen to ensure it adequately represents the population of interest, allowing for the generalizability of the findings.
- Variables and Operationalization: Quantitative research involves the measurement of variables. In the research design phase, researchers identify the variables they will study and determine how to operationalize them into measurable and observable forms. This includes defining the indicators or measures used to assess each variable.
- Data Collection Methods: Quantitative research typically involves collecting data through structured instruments, such as surveys, questionnaires, or tests. The research design specifies the data collection methods, including the procedures for administering the instruments, the timing of data collection, and the strategies for maximizing response rates.
- Data Analysis: Quantitative research design includes decisions about the statistical techniques and analyses applied to the collected data. This may involve descriptive statistics (e.g., means, percentages) and inferential statistics (e.g., t-tests, regression analyses) to examine variables’ relationships, differences, or associations.
- Validity and Reliability: Ensuring the validity and reliability of the data is a crucial consideration in quantitative research design. Validity refers to the extent to which a measurement instrument or procedure accurately measures what it intends to measure. Reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the measurement over time and across different conditions. Researchers employ pilot testing, validity checks, and statistical measures to enhance validity and reliability.
- Ethical Considerations: Quantitative research design also includes ethical considerations, such as obtaining informed consent from participants, protecting their privacy and confidentiality, and ensuring the study adheres to ethical guidelines and regulations.
By carefully designing a quantitative research study, researchers can ensure their investigations are methodologically sound, reliable, and valid.
Well-designed research provides a solid foundation for collecting and analyzing numerical data, allowing researchers to draw meaningful conclusions and contribute to the body of knowledge in their respective fields.
Quantitative research data collection methods
When collecting and analyzing the data you need for quantitative research, you have a number of possibilities available to you. Each has its own pros and cons, and it might be best to use a mix. Here are some of the main research methods:
Survey research
This involves sending out surveys to your target audience to collect information before statistically analyzing the results to draw conclusions and insights. It’s a great way to better understand your target customers or explore a new market and can be turned around quickly.
There are a number of different ways of conducting surveys, such as:
- Email — this is a quick way of reaching a large number of people and can be more affordable than the other methods described below.
- Phone — not everyone has access to the internet so if you’re looking to reach a particular demographic that may struggle to engage in this way (e.g. older consumers) telephone can be a better approach. That said, it can be expensive and time-consuming.
- Post or Mail — as with the phone, you can reach a wide segment of the population, but it’s expensive and takes a long time. As organizations look to identify and react to changes in consumer behavior at speed, postal surveys have become somewhat outdated.
- In-person — in some instances it makes sense to conduct quantitative research in person. Examples of this include intercepts where you need to collect quantitative data about the customer experience in the moment or taste tests or central location tests , where you need consumers to physically interact with a product to provide useful feedback. Conducting research in this way can be expensive and logistically challenging to organize and carry out.
Survey questions for quantitative research usually include closed-ended questions rather than the open-ended questions used in qualitative research. For example, instead of asking
“How do you feel about our delivery policy?”
You might ask…
“How satisfied are you with our delivery policy? “Very satisfied / Satisfied / Don’t Know / Dissatisfied / Very Dissatisfied”
This way, you’ll gain data that can be categorized and analyzed in a quantitative, numbers-based way.
Correlational Research
Correlational research is a specific type of quantitative research that examines the relationship between two or more variables. It focuses on determining whether there is a statistical association or correlation between variables without establishing causality. In other words, correlational research helps to understand how changes in one variable correspond to changes in another.
One of the critical features of correlational research is that it allows researchers to analyze data from existing sources or collect data through surveys or questionnaires. By measuring the variables of interest, researchers can calculate a correlation coefficient, such as Pearson’s, to quantify the strength and direction of the relationship. The correlation coefficient ranges from -1 to +1, where a positive value indicates a positive relationship, a negative value indicates a negative relationship and a value close to zero suggests no significant relationship. Correlational research is valuable in various fields, such as psychology, sociology, and economics, as it helps researchers explore connections between variables that may not be feasible to manipulate in an experimental setting. For example, a psychologist might use correlational research to investigate the relationship between sleep duration and student academic performance. By collecting data on these variables, they can determine whether there is a correlation between the two factors and to what extent they are related. It is important to note that correlational research does not imply causation. While a correlation suggests an association between variables, it does not provide evidence for a cause-and-effect relationship. Other factors, known as confounding variables, may be influencing the observed relationship. Therefore, researchers must exercise caution in interpreting correlational findings and consider additional research methods, such as experimental studies, to establish causality. Correlational research is vital in quantitative research and analysis by investigating relationships between variables. It provides valuable insights into the strength and direction of associations and helps researchers generate hypotheses for further investigation. By understanding the limitations of correlational research, researchers can use this method effectively to explore connections between variables in various disciplines.
Experimental Research
Experimental research is a fundamental approach within quantitative research that aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It involves the manipulation of an independent variable and measuring its effects on a dependent variable while controlling for potential confounding variables. Experimental research is highly regarded for its ability to provide rigorous evidence and draw conclusions about causal relationships. The hallmark of experimental research is the presence of at least two groups: the experimental and control groups. The experimental group receives the manipulated variable, the independent variable, while the control group does not. By comparing the outcomes or responses of the two groups, researchers can attribute any differences observed to the effects of the independent variable. Several key components are employed to ensure the reliability and validity of experimental research. Random assignment is a crucial step that involves assigning participants to either the experimental or control group in a random and unbiased manner. This minimizes the potential for pre-existing differences between groups and strengthens the study’s internal validity. Another essential feature of experimental research is the ability to control extraneous variables. By carefully designing the study environment and procedures, researchers can minimize the influence of factors other than the independent variable on the dependent variable. This control enhances the ability to isolate the manipulated variable’s effects and increases the study’s internal validity. Quantitative data is typically collected in experimental research through objective and standardized measurements. Researchers use instruments such as surveys, tests, observations, or physiological measurements to gather numerical data that can be analyzed statistically. This allows for applying various statistical techniques, such as t-tests or analysis of variance (ANOVA), to determine the significance of the observed effects and draw conclusions about the relationship between variables. Experimental research is widely used across psychology, medicine, education, and the natural sciences. It enables researchers to test hypotheses, evaluate interventions or treatments, and provide evidence-based recommendations. Experimental research offers valuable insights into the effectiveness or impact of specific variables, interventions, or strategies by establishing cause-and-effect relationships. Despite its strengths, experimental research also has limitations. The artificial nature of laboratory settings and the need for control may reduce the generalizability of findings to real-world contexts. Ethical considerations also play a crucial role in experimental research, as researchers must ensure participants’ well-being and informed consent. Experimental research is a powerful tool in the quantitative research arsenal. It enables researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships, control extraneous variables, and gather objective numerical data. Experimental research contributes to evidence-based decision-making and advances knowledge in various fields by employing rigorous methods.
Analyzing results
Once you have your results, the next step — and one of the most important overall — is to categorize and analyze them.
There are many ways to do this. One powerful method is cross-tabulation, where you separate your results into categories based on demographic subgroups. For example, of the people who answered ‘yes’ to a question, how many of them were business leaders and how many were entry-level employees?
You’ll also need to take time to clean the data (for example removing people who sped through the survey, selecting the same answer) to make sure you can confidently draw conclusions. This can all be taken care of by the right team of experts.
The importance of quantitative research
Quantitative research is a powerful tool for anyone looking to learn more about their market and customers. It allows you to gain reliable, objective insights from data and clearly understand trends and patterns.
Where quantitative research falls short is in explaining the ‘why’. This is where you need to turn to other methods, like qualitative research, where you’ll actually talk to your audience and delve into the more subjective factors driving their decision-making.
At Kadence, it’s our job to help you with every aspect of your research strategy. We’ve done this with countless businesses, and we’d love to do it with you. To find out more, get in touch with us .
Helping brands uncover valuable insights
We’ve been working with Kadence on a couple of strategic projects, which influenced our product roadmap roll-out within the region. Their work has been exceptional in providing me the insights that I need. Senior Marketing Executive Arla Foods
Kadence’s reports give us the insight, conclusion and recommended execution needed to give us a different perspective, which provided us with an opportunity to relook at our go to market strategy in a different direction which we are now reaping the benefits from. Sales & Marketing Bridgestone
Kadence helped us not only conduct a thorough and insightful piece of research, its interpretation of the data provided many useful and unexpected good-news stories that we were able to use in our communications and interactions with government bodies. General Manager PR -Internal Communications & Government Affairs Mitsubishi
Kadence team is more like a partner to us. We have run a number of projects together and … the pro-activeness, out of the box thinking and delivering in spite of tight deadlines are some of the key reasons we always reach out to them. Vital Strategies
Kadence were an excellent partner on this project; they took time to really understand our business challenges, and developed a research approach that would tackle the exam question from all directions. The impact of the work is still being felt now, several years later. Customer Intelligence Director Wall Street Journal
Get In Touch
" (Required) " indicates required fields
Privacy Overview
Program Type
Quantitative marketing research: definition and applications.
Home » Blog » Business » Quantitative Marketing Research: Definition and Applications
Organizations of any size and in any industry can benefit from better understanding their customers, employees and competitors. One way organizations use this information is to generate actionable insights that inform business decisions.
What is Quantitative Marketing Research?
Perhaps the simplest definition of quantitative research is that it is numbers-based. Quantitative data allows the researcher to quantify results through some form of objective measurement followed by statistical, mathematical or numerical analysis of data. This type of research enables researchers and business leaders to draw general conclusions and is structured and rooted in statistics; it is a measure.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
Although quantitative research is very different from qualitative research, the two can be complementary, offering both breadth (quantitative) and depth (qualitative). If quantitative marketing research provides you the numbers to measure something, then qualitative gives you the words and details to describe it. For example, using quantitative research, a business leader may learn that just 50% of customers are satisfied with delivery times. Using qualitative research, she may discover that customers are infuriated by the way delayed deliveries are handled.
Reasons to Conduct Qualitative Research Qualitative research is often a solid launchpad because it helps the researcher start to gather specific, detailed information on a topic and better understand how people are thinking about the topic. This insight often informs the way any subsequent quantitative research is designed.
Qualitative research can also add color in final findings, helping to give a human voice to many of the facts and figures shown in a report.
Reasons to Conduct Quantitative Research Quantitative research can validate a hypothesis generated from initial qualitative research. It helps business leaders and researchers understand if a sentiment (like customers are unhappy with the approach when delivery is delayed) is widespread, or just one person’s beliefs. Quantitative research introduces objectivity into the observations.
Quantitative research can also help business leaders understand answers to questions in a broader context. For example, a market research analyst might use quantitative research to answer questions like: Which company do consumers prefer most for their coffee? Which ad should we run for the Super Bowl? What features are most important to consumers buying a new computer?
Quantitative Market Research Techniques
Quantitative market research must be very scientific, allowing conclusive and actionable insights to be produced from the resulting data. Here are some techniques:
Surveys : Surveys used to be paper-based, but today they are typically digital. Survey questions are usually closed-ended (respondents select from a list of answer options). Surveys enable researchers to generalize an entire population with relative accuracy. Healthcare marketers, for example, are beginning to pay more attention to patient satisfaction surveys to improve services.
Cross-Sectional Research Survey : This type of market research analyzes the data from multiple variables collected at a single point in time across a sample population. Participants may be similar in every demographic except the one that is being reviewed. For example, a marketing team might focus on variables like age and location and use the data as a target to sell a product or service.
One-on-One Interviews : Technology has also evolved this technique from face-to-face to the telephone or online. Quantitative interviews are highly structured, and they allow for highly detailed data to be collected.
5 Steps to Creating a Quantitative Survey
To launch a successful quantitative survey, follow these five steps:
- Establish the goal . An understanding of what the outcome should be is essential to informing the research design. For example, an objective might be how to win back customer loyalty. Establishing the desired outcome also involves understanding which audiences are going to be targeted.
- Create a plan . Determine what tools will be necessary, such as an online programming platform for your questionnaire, define the audience who should participate, and draft the survey.
- Collect the data . Determine whether data is collected online or from a phone or web interview.
- Analyze the data . Analyze the data as planned in the planning phase.
- Create reports . In most instances, stakeholders aren’t interested in sifting through complex datasets and analyses. Instead, you’ll want to create charts, tables and reports that tell the data’s story clearly and concisely.
Quantitative Research Questions and Examples
Quantitative research questions should be closed-ended, which means they ask respondents to choose from a pre-populated list. Because much of the work is done for the participant, quantitative research can typically include more questions. Some common questions include:
Net promoter score . This methodology allows businesses to segment their customer base into promoters, detractors, and passives as an indication of company performance. For participants, it’s a very simple question: How likely are you to recommend this brand to a friend or colleague, where 0 is not at all likely and 10 is very likely?
Likert Scale . This scale helps to evaluate options using a scale of opposites. For example, a market researcher may ask participants: How satisfied were you with the technician’s support today? Answer options would be:
- Extremely Dissatisfied
- Dissatisfied
- Extremely Satisfied
In some cases, questions are asked as a matrix or grid to help respondents compare items or make it easier for them to answer.
Quantitative market research plays a crucial role in making business decisions. When quantitative market researchers plan thoughtful research, they can generate insights that can inform impactful business decisions and actions.
Related Reading : How to Write a Research Paper Database Reporting Analyst Career and Salary Profile
RELATED ARTICLES
What is hybrid project management, supply chain lessons from covid-19, 833-591-1092.
Risepoint maintains this website on behalf of Florida Institute of Technology. Florida Tech maintains responsibility for curriculum, teaching, admissions, tuition, financial aid, accreditation, and all other academic- and instruction-related functions and decisions.
Learn more about Risepoint.
© 2024 privacy | terms | student disclosures
Get Our Program Guide
If you are ready to learn more about our programs, get started by downloading our program guide now.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Quantitative research serves as the cornerstone of evidence-based decision-making. Its importance cannot be overstated: quantitative methods provide empirical rigor, enabling preachers (academia), practitioners (industry), and policymakers (government; i.e. the 3Ps) to derive actionable insights from data. However, despite its significance, mastering the complexities of quantitative research ...
Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio). Quantitative research is widely used in the natural and social sciences: biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc. Quantitative research question examples
Quantitative research is all about numbers.It uses mathematical analysis and data to shed light on important statistics about your business and market. This type of data, found via tactics such as multiple-choice questionnaires, can help you gauge interest in your company and its offerings.
These are just a few examples, but they showcase the power of quantitative research in helping businesses make data-driven decisions that resonate with their target audiences. Tools and Resources for Quantitative Research. To conduct effective quantitative market research, consider utilizing these tools and resources: Survey Platforms
Quantitative analysis research in business is a very important tool at the companies' disposal because everything depends on data in this digital era. Today, data makes or breaks a business. But most importantly, it provides them a competitive edge if used correctly.
Quantitative research is a method that uses numbers and statistics to gather precise, measurable data on the research subject. Offering numbers and stats-based insights, this research methodology is a crucial part of primary research and helps understand how well an organizational decision will work out.
Market Research: Quantitative market research is a type of market research that uses numerical data to understand consumer preferences, buying behavior, and market trends. This data typically gets gathered through surveys and questionnaires, which are then analyzed to make informed business decisions.
Here are examples of common ways to apply quantitative research in a business setting: Finance Quantitative research methods are easily applied to financial data. An organisation's financial information is typically collected monthly, quarterly and annually. Organisations can gather and analyse the data from financial reports, allowing them to ...
Quantitative research design refers to the overall plan and structure that guides the collection, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data in a quantitative research study. It outlines the specific steps, procedures, and techniques used to address research questions or test hypotheses systematically and rigorously.
Reasons to Conduct Quantitative Research Quantitative research can validate a hypothesis generated from initial qualitative research. It helps business leaders and researchers understand if a sentiment (like customers are unhappy with the approach when delivery is delayed) is widespread, or just one person's beliefs. Quantitative research ...