- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board

Overcoming Speech Impediment: Symptoms to Treatment
There are many causes and solutions for impaired speech
- Types and Symptoms
- Speech Therapy
- Building Confidence
Speech impediments are conditions that can cause a variety of symptoms, such as an inability to understand language or speak with a stable sense of tone, speed, or fluidity. There are many different types of speech impediments, and they can begin during childhood or develop during adulthood.
Common causes include physical trauma, neurological disorders, or anxiety. If you or your child is experiencing signs of a speech impediment, you need to know that these conditions can be diagnosed and treated with professional speech therapy.
This article will discuss what you can do if you are concerned about a speech impediment and what you can expect during your diagnostic process and therapy.
FG Trade / Getty Images
Types and Symptoms of Speech Impediment
People can have speech problems due to developmental conditions that begin to show symptoms during early childhood or as a result of conditions that may occur during adulthood.
The main classifications of speech impairment are aphasia (difficulty understanding or producing the correct words or phrases) or dysarthria (difficulty enunciating words).
Often, speech problems can be part of neurological or neurodevelopmental disorders that also cause other symptoms, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) or autism spectrum disorder .
There are several different symptoms of speech impediments, and you may experience one or more.
Can Symptoms Worsen?
Most speech disorders cause persistent symptoms and can temporarily get worse when you are tired, anxious, or sick.
Symptoms of dysarthria can include:
- Slurred speech
- Slow speech
- Choppy speech
- Hesitant speech
- Inability to control the volume of your speech
- Shaking or tremulous speech pattern
- Inability to pronounce certain sounds
Symptoms of aphasia may involve:
- Speech apraxia (difficulty coordinating speech)
- Difficulty understanding the meaning of what other people are saying
- Inability to use the correct words
- Inability to repeat words or phases
- Speech that has an irregular rhythm
You can have one or more of these speech patterns as part of your speech impediment, and their combination and frequency will help determine the type and cause of your speech problem.
Causes of Speech Impediment
The conditions that cause speech impediments can include developmental problems that are present from birth, neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s disease , or sudden neurological events, such as a stroke .
Some people can also experience temporary speech impairment due to anxiety, intoxication, medication side effects, postictal state (the time immediately after a seizure), or a change of consciousness.
Speech Impairment in Children
Children can have speech disorders associated with neurodevelopmental problems, which can interfere with speech development. Some childhood neurological or neurodevelopmental disorders may cause a regression (backsliding) of speech skills.
Common causes of childhood speech impediments include:
- Autism spectrum disorder : A neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social and interactive development
- Cerebral palsy : A congenital (from birth) disorder that affects learning and control of physical movement
- Hearing loss : Can affect the way children hear and imitate speech
- Rett syndrome : A genetic neurodevelopmental condition that causes regression of physical and social skills beginning during the early school-age years.
- Adrenoleukodystrophy : A genetic disorder that causes a decline in motor and cognitive skills beginning during early childhood
- Childhood metabolic disorders : A group of conditions that affects the way children break down nutrients, often resulting in toxic damage to organs
- Brain tumor : A growth that may damage areas of the brain, including those that control speech or language
- Encephalitis : Brain inflammation or infection that may affect the way regions in the brain function
- Hydrocephalus : Excess fluid within the skull, which may develop after brain surgery and can cause brain damage
Do Childhood Speech Disorders Persist?
Speech disorders during childhood can have persistent effects throughout life. Therapy can often help improve speech skills.
Speech Impairment in Adulthood
Adult speech disorders develop due to conditions that damage the speech areas of the brain.
Common causes of adult speech impairment include:
- Head trauma
- Nerve injury
- Throat tumor
- Stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Essential tremor
- Brain tumor
- Brain infection
Additionally, people may develop changes in speech with advancing age, even without a specific neurological cause. This can happen due to presbyphonia , which is a change in the volume and control of speech due to declining hormone levels and reduced elasticity and movement of the vocal cords.
Do Speech Disorders Resolve on Their Own?
Children and adults who have persistent speech disorders are unlikely to experience spontaneous improvement without therapy and should seek professional attention.
Steps to Treating Speech Impediment
If you or your child has a speech impediment, your healthcare providers will work to diagnose the type of speech impediment as well as the underlying condition that caused it. Defining the cause and type of speech impediment will help determine your prognosis and treatment plan.
Sometimes the cause is known before symptoms begin, as is the case with trauma or MS. Impaired speech may first be a symptom of a condition, such as a stroke that causes aphasia as the primary symptom.
The diagnosis will include a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and a thorough evaluation of speech and language. Diagnostic testing is directed by the medical history and clinical evaluation.
Diagnostic testing may include:
- Brain imaging , such as brain computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), if there’s concern about a disease process in the brain
- Swallowing evaluation if there’s concern about dysfunction of the muscles in the throat
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (aka nerve conduction velocity, or NCV) if there’s concern about nerve and muscle damage
- Blood tests, which can help in diagnosing inflammatory disorders or infections
Your diagnostic tests will help pinpoint the cause of your speech problem. Your treatment will include specific therapy to help improve your speech, as well as medication or other interventions to treat the underlying disorder.
For example, if you are diagnosed with MS, you would likely receive disease-modifying therapy to help prevent MS progression. And if you are diagnosed with a brain tumor, you may need surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation to treat the tumor.
Therapy to Address Speech Impediment
Therapy for speech impairment is interactive and directed by a specialist who is experienced in treating speech problems . Sometimes, children receive speech therapy as part of a specialized learning program at school.
The duration and frequency of your speech therapy program depend on the underlying cause of your impediment, your improvement, and approval from your health insurance.
If you or your child has a serious speech problem, you may qualify for speech therapy. Working with your therapist can help you build confidence, particularly as you begin to see improvement.
Exercises during speech therapy may include:
- Pronouncing individual sounds, such as la la la or da da da
- Practicing pronunciation of words that you have trouble pronouncing
- Adjusting the rate or volume of your speech
- Mouth exercises
- Practicing language skills by naming objects or repeating what the therapist is saying
These therapies are meant to help achieve more fluent and understandable speech as well as an increased comfort level with speech and language.
Building Confidence With Speech Problems
Some types of speech impairment might not qualify for therapy. If you have speech difficulties due to anxiety or a social phobia or if you don’t have access to therapy, you might benefit from activities that can help you practice your speech.
You might consider one or more of the following for you or your child:
- Joining a local theater group
- Volunteering in a school or community activity that involves interaction with the public
- Signing up for a class that requires a significant amount of class participation
- Joining a support group for people who have problems with speech
Activities that you do on your own to improve your confidence with speaking can be most beneficial when you are in a non-judgmental and safe space.
Many different types of speech problems can affect children and adults. Some of these are congenital (present from birth), while others are acquired due to health conditions, medication side effects, substances, or mood and anxiety disorders. Because there are so many different types of speech problems, seeking a medical diagnosis so you can get the right therapy for your specific disorder is crucial.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Language and speech disorders in children .
Han C, Tang J, Tang B, et al. The effectiveness and safety of noninvasive brain stimulation technology combined with speech training on aphasia after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(2):e36880. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000036880
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Quick statistics about voice, speech, language .
Mackey J, McCulloch H, Scheiner G, et al. Speech pathologists' perspectives on the use of augmentative and alternative communication devices with people with acquired brain injury and reflections from lived experience . Brain Impair. 2023;24(2):168-184. doi:10.1017/BrImp.2023.9
Allison KM, Doherty KM. Relation of speech-language profile and communication modality to participation of children with cerebral palsy . Am J Speech Lang Pathol . 2024:1-11. doi:10.1044/2023_AJSLP-23-00267
Saccente-Kennedy B, Gillies F, Desjardins M, et al. A systematic review of speech-language pathology interventions for presbyphonia using the rehabilitation treatment specification system . J Voice. 2024:S0892-1997(23)00396-X. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2023.12.010
By Heidi Moawad, MD Dr. Moawad is a neurologist and expert in brain health. She regularly writes and edits health content for medical books and publications.
Health Conditions
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Asthma & Allergies
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Breast Cancer
- Cardiovascular Health
- Environment & Sustainability
- Exercise & Fitness
- Headache & Migraine
- Health Equity
- HIV & AIDS
- Human Biology
- Men's Health
- Mental Health
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Parkinson's Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Sexual Health
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Women's Health
Health Products
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Vitamins & Supplements
- At-Home Testing
- Men’s Health
- Women’s Health
- Latest News
Original Series
- Medical Myths
- Honest Nutrition
- Through My Eyes
- New Normal Health
- 5 things everyone should know about menopause
- 3 ways to slow down type 2 diabetes-related brain aging
- Toxic metals in tampons: Should you be worried?
- Can tattoos cause blood or skin cancer?
- Can we really ‘outrun the Grim Reaper’?
- What makes a diet truly heart-healthy?
General Health
- Health Hubs
Health Tools
- Find a Doctor
- BMI Calculators and Charts
- Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide
- Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide
- Sleep Calculator
- RA Myths vs Facts
- Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar
- Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction
About Medical News Today
- Our Editorial Process
- Content Integrity
- Conscious Language
Find Community
- Bezzy Breast Cancer
- Bezzy Psoriasis
What are speech disorders?

A speech disorder is any condition that affects a person’s ability to produce sounds that create words. Damage to muscles, nerves, and vocal structures can cause it. Examples include stuttering and ataxia.
Speech is one of the main ways in which people communicate their thoughts, feelings, and ideas with others. The act of speaking requires the precise coordination of multiple body parts, including the head, neck, chest, and abdomen.
In this article, we explore what speech disorders are and the different types. We also cover the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of speech disorders.
What is a speech disorder?

Speech disorders affect a person’s ability to form the sounds that allow them to communicate with other people. They are not the same as language disorders.
Speech disorders prevent people from forming correct speech sounds, while language disorders affect a person’s ability to learn words or understand what others say to them.
However, both speech and language disorders can make it more difficult for a person to express their thoughts and feelings to others.
Speech disorders can affect people of all ages.
Some types of speech disorder include stuttering, apraxia, and dysarthria. We discuss each of these types below:
Stuttering refers to a speech disorder that interrupts the flow of speech. People who stutter can experience the following types of disruption:
- Repetitions occur when people involuntarily repeat sounds, vowels, or words.
- Blocks happen when people know what they want to say but have difficulty making the necessary speech sounds. Blocks may cause someone to feel as though their words are stuck.
- Prolongations refer to the stretching or drawing out of particular sounds or words.
The symptoms of stuttering can vary depending on the situation. Stress , excitement, or frustration can cause stuttering to become more severe. Some people may also find that certain words or sounds can make a stutter more pronounced.
Stuttering can cause both behavioral and physical symptoms that occur at the same time. These can include:
- tension in the face and shoulders
- rapid blinking
- lip tremors
- clenched fists
- sudden head movements
There are two main types of stuttering:
- Developmental stuttering affects young children who are still learning speech and language skills. Genetic factors significantly increase a person’s likelihood of developing this type of stutter.
- Neurogenic stuttering occurs when damage to the brain prevents proper coordination between the different regions of the brain that play a role in speech.
The brain controls every single action that people make, including speaking. Most of the brain’s involvement in speech is unconscious and automatic.
When someone decides to speak, the brain sends signals to the different structures of the body that work together to produce speech. The brain instructs these structures how and when to move to form the appropriate sounds.
For example, these speech signals open or close the vocal cords, move the tongue and shape the lips, and control the movement of air through the throat and mouth.
Apraxia is a general term referring to brain damage that impairs a person’s motor skills, and it can affect any part of the body. Apraxia of speech, or verbal apraxia, refers specifically to the impairment of motor skills that affect an individual’s ability to form the sounds of speech correctly, even when they know which words they want to say.
Dysarthria occurs when damage to the brain causes muscle weakness in a person’s face, lips, tongue, throat, or chest. Muscle weakness in these parts of the body can make speaking very difficult.
People who have dysarthria may experience the following symptoms:
- slurred speech
- speaking too slowly or too quickly
- soft or quiet speech
- difficulty moving the mouth or tongue
The symptoms of speech disorders vary widely depending on the cause and severity of the disorder. People can develop multiple speech disorders with different symptoms.
People with one or more speech disorders may experience the following symptoms:
- repeating or prolonging sounds
- distorting sounds
- adding sounds or syllables to words
- rearranging syllables
- having difficulty pronouncing words correctly
- struggling to say the correct word or sound
- speaking with a hoarse or raspy voice
- speaking very softly
Causes of speech disorders can include:
- brain damage due to a stroke or head injury
- muscle weakness
- damaged vocal cords
- a degenerative disease, such as Huntington’s disease , Parkinson’s disease , or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- cancer that affects the mouth or throat
- Down syndrome
- hearing loss
Risk factors that can increase the likelihood of a person developing a speech disorder include :
- being born prematurely
- having a low weight at birth
- having a family history of speech disorders
- experiencing problems that affect the ears, nose, or throat
A speech-language pathologist (SLP) is a healthcare professional who specializes in speech and language disorders.
An SLP will evaluate a person for groups of symptoms that indicate one type of speech disorder. To make an accurate diagnosis, SLPs need to rule out other speech and language disorders and medical conditions.
An SLP will review a person’s medical and family history. They will also examine how a person moves their lips, jaw, and tongue and may inspect the muscles of the mouth and throat.
Other methods of evaluating speech disorders include:
- Denver articulation screening examination . This test evaluates the clarity of a person’s pronunciation.
- Prosody-voice screening profile . SLPs use this test to examine multiple aspects of a person’s speech, including pitch, phrasing, speech patterns, and speaking volume.
- Dynamic evaluation of motor speech skills (DEMSS) manual . The DEMSS is a comprehensive guide for helping SLPs diagnose speech disorders.
The type of treatment will typically depend on the severity of the speech disorder and its underlying cause.
Treatment options can include:
- speech therapy exercises that focus on building familiarity with certain words or sounds
- physical exercises that focus on strengthening the muscles that produce speech sounds
We discuss some of the treatment options for speech disorders below:
Target selection
Target selection involves a person practicing specific sounds or words to familiarize themselves with particular speech patterns. Examples of therapy targets may include difficult words or sounds that trigger speech disruptions.
Contextual utilization
For this approach, SLPs teach people to recognize speech sounds in different syllable-based contexts.
Contrast therapy
Contrast therapy involves saying word pairs that contain one or more different speech sounds. An example word pair might be “beat” and “feet” or “dough” and “show.”
Oral-motor therapy
The oral-motor therapy approach focuses on improving muscle strength, motor control, and breath control. These exercises can help people develop fluency, which produces smoother speech that sounds more natural.
Ear devices are small electronic aids that fit inside the ear canal. These devices can help improve fluency in people who have a stutter.
Some ear devices replay altered versions of the wearer’s voice to make it seem as though someone else is speaking with them. Other ear devices produce a noise that helps control stuttering.
Some speech disorders can cause people to develop anxiety disorders. Stressful situations can trigger anxiety, resulting in more pronounced speech disorder symptoms. Anxiety medications may help reduce symptoms of speech disorders in some people.
Speech disorders affect a person’s ability to produce sounds that create words. They are not the same as language disorders, which make it more difficult for people to learn words or understand what others are saying to them.
Types of speech disorder include stuttering, apraxia, and dysarthria. There are many possible causes of speech disorders, including muscles weakness, brain injuries, degenerative diseases, autism, and hearing loss.
Speech disorders can affect a person’s self-esteem and their overall quality of life. However, speech therapy, breathing exercises, and, sometimes, anti-anxiety medications can help improve speech and reduce symptoms.
- Anxiety / Stress
- Ear, Nose, and Throat
- Neurology / Neuroscience
- Rehabilitation / Physical Therapy
How we reviewed this article:
- Hearnshaw, S., et al. (2018). The speech perception skills of children with and without speech sound disorder [Abstract]. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0021992417300679
- Language and speech disorders in children. (2019). https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/childdevelopment/language-disorders.html#problems
- Speech sound disorders — articulation and phonology. (n.d.). https://www.asha.org/PRPSpecificTopic.aspx?folderid=8589935321§ion=Treatment
- Statistics on voice, speech, and language. (2016). https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/statistics/statistics-voice-speech-and-language#2
- Stuttering. (2017). https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/stuttering
Share this article
Latest news
- Danish studies find higher risk of optic nerve damage with Ozempic
- 3 ways to boost longevity in 2025
- Antibiotic use does not increase dementia risk, study suggests
- Insufficient sleep and high blood pressure may raise risk of brain aging
- Why getting more deep sleep may help improve memory
Related Coverage
Vocal cord paralysis occurs when one or both vocal cords cannot move. It is often the result of nerve damage, and it can cause various complications…
Aphasia affects a person's ability to use language. It often results from a stroke. Learn about aphasia and how to help a person who has it.
Nonverbal learning disorder (NVLD) is a rare type of learning disability that impacts a person's ability to understand nonverbal information. We look…
NVLD affects the ability to process nonverbal information. This affects executive function, communication, visual-spatial skills, and motor skills…
Intellectual disability is also known as cognitive disability. In this article, learn more about what it means, its symptoms, its management options…
Understanding Speech Impediments: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Published by Healthdor Editorial on July 27, 2024
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for speech impediments, as well as coping strategies for individuals affected by this condition.
What is a Speech Impediment?
A speech impediment, also known as a communication disorder, refers to a condition that affects an individual's ability to produce sounds that create words and sentences in a fluent and understandable manner. This can result in difficulties with pronunciation, rhythm, and the overall flow of speech. Speech impediments can manifest in various forms, including stuttering, lisping, and apraxia, among others.
According to the World Health Organization , an estimated 5% to 10% of children experience some form of speech impediment during their early developmental years. Additionally, research from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders indicates that approximately 7.5 million people in the United States alone have trouble using their voices.
There are several potential causes of speech impediments, ranging from genetic factors and neurological conditions to environmental influences and traumatic brain injuries. For instance, developmental delays, hearing loss, and muscle weakness in the mouth and throat can all contribute to speech impediments. Furthermore, emotional and psychological factors, such as anxiety and stress, can exacerbate existing speech difficulties.
Common symptoms of speech impediments may include prolonged pauses or hesitations while speaking, difficulty pronouncing certain sounds or words, and a tendency to repeat or prolong sounds or syllables. In some cases, individuals with speech impediments may also experience frustration, embarrassment, and social isolation due to their communication challenges.
When it comes to treatment options for speech impediments, early intervention is crucial for improving outcomes. Speech therapy, which involves working with a trained professional to practice and refine communication skills, is often recommended. Additionally, assistive devices, such as electronic communication aids and voice amplifiers, can help individuals with severe speech impediments communicate more effectively.
Coping strategies for individuals affected by speech impediments may include seeking support from peers and professionals, practicing relaxation techniques to manage anxiety, and participating in social activities to build confidence and improve communication skills. It's important for those with speech impediments to remember that they are not alone, and that there are resources and strategies available to help them navigate their challenges.
Causes of Speech Impediments
Speech impediments, also known as speech disorders , can be caused by a variety of factors, including physical, neurological, and developmental issues. Understanding the underlying causes of speech impediments is crucial in order to provide effective treatment and support for individuals affected by this condition.
One of the common causes of speech impediments is physical abnormalities in the mouth, throat, or vocal cords. These abnormalities can include cleft palate, tongue tie, or other structural issues that affect the production of speech sounds. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association , approximately 7.7 million people in the United States have a speech disorder related to a physical condition.
Neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy, stroke, or traumatic brain injury can also result in speech impediments. These conditions can affect the brain's ability to control the muscles involved in speech production, leading to difficulties in articulation and fluency. In fact, the World Health Organization estimates that approximately 15 million people worldwide suffer from stroke-related speech impairments.
Furthermore, developmental issues, such as language delays or disorders, can contribute to speech impediments. Children with developmental disorders like autism spectrum disorder or specific language impairment may struggle with speech sound production, language comprehension, and social communication. The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders reports that approximately 8% of children in the United States have a communication disorder that affects their speech.
Other potential causes of speech impediments include hearing loss, vocal nodules, and psychological factors such as anxiety or selective mutism. It's important to note that speech impediments can also be the result of a combination of these factors, making diagnosis and treatment more complex.
In conclusion, the causes of speech impediments are diverse and multifaceted, ranging from physical abnormalities to neurological and developmental issues. By understanding these underlying causes, healthcare professionals can provide tailored treatment and support to individuals affected by speech disorders.
Common Symptoms of Speech Impediments
Speech impediments can manifest in a variety of ways, with each individual experiencing unique symptoms. However, there are some common signs that may indicate the presence of a speech impediment. It's important to note that these symptoms can vary widely in severity and may be present in individuals of all ages.
- Difficulty with articulation: One of the most common symptoms of a speech impediment is difficulty with articulating certain sounds or words. This may manifest as slurred speech, unclear pronunciation, or the inability to produce certain sounds altogether.
- Stuttering: Another prevalent symptom is stuttering, which involves the repetition or prolongation of sounds, syllables, or words. Stuttering can significantly impact an individual's ability to communicate effectively and may lead to feelings of frustration and embarrassment.
- Language delays: Some individuals with speech impediments may experience delays in language development, particularly in early childhood. This can manifest as a limited vocabulary, difficulty forming complete sentences, or challenges with understanding and following verbal instructions.
- Difficulty with social interactions: Speech impediments can also affect an individual's ability to engage in social interactions. This may be due to feelings of self-consciousness about their speech, as well as the challenges of being understood by others.
- Physical tension or struggle while speaking: Some individuals with speech impediments may exhibit physical tension or struggle while attempting to speak. This can include visible signs of strain in the face or neck, as well as difficulty coordinating the movements necessary for speech production.
It's important to recognize that speech impediments can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, affecting their academic, professional, and social experiences. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association , approximately 7.5 million people in the United States alone have trouble using their voices. This underscores the widespread prevalence of speech impediments and the need for effective support and treatment options.
For children, speech impediments can be particularly challenging, as they may face difficulties in school, social settings, and other aspects of their daily lives. In fact, the World Health Organization estimates that 1 in 12 children worldwide experiences some form of communication disorder. Early intervention and support are crucial for helping these children overcome their speech impediments and thrive in their personal and academic pursuits.
While the symptoms of speech impediments can be distressing, it's important to remember that effective treatment options are available. Speech therapy, for example, has been shown to be highly beneficial for individuals with speech impediments. According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders , speech therapy can help individuals improve their speech clarity, develop effective communication skills, and build confidence in their ability to express themselves.
In addition to professional treatment, individuals with speech impediments can benefit from various coping strategies to help them navigate their daily lives. This may include practicing relaxation techniques to reduce physical tension during speech, seeking out supportive social environments, and engaging in activities that promote self-expression and confidence.
Overall, understanding the common symptoms of speech impediments is an important step in recognizing and addressing this condition. By raising awareness and providing effective support and resources, we can help individuals with speech impediments lead fulfilling lives and reach their full potential.
Diagnosing Speech Impediments
Diagnosing speech impediments can be a complex process that requires a comprehensive evaluation by a speech-language pathologist. Speech impediments can manifest in various forms, including stuttering, lisping, and apraxia of speech. It is estimated that approximately 7.5 million people in the United States alone have trouble using their voices, with speech disorders being one of the most common disabilities in children.
When it comes to diagnosing speech impediments, the first step is to conduct a thorough assessment of the individual's speech and language abilities. This may involve evaluating their articulation, fluency, voice quality, and overall communication skills. Additionally, the speech-language pathologist may also consider the individual's medical history, family history, and any potential underlying conditions that could be contributing to the speech impediment.
Furthermore, it is important to rule out any hearing impairments or cognitive deficits that could be impacting the individual's ability to communicate effectively. Hearing tests and cognitive assessments may be included as part of the diagnostic process to ensure that all potential contributing factors are taken into account.
Another crucial aspect of diagnosing speech impediments is to assess the impact of the condition on the individual's daily life and social interactions. This may involve gathering information from parents, teachers, or other relevant individuals to gain a comprehensive understanding of how the speech impediment is affecting the individual's overall well-being.
Once a thorough assessment has been completed, the speech-language pathologist can provide a formal diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the individual's specific needs. Treatment options for speech impediments may include speech therapy, assistive devices, and in some cases, medical interventions.
It is important to note that early intervention is key when it comes to addressing speech impediments, as the sooner treatment is initiated, the better the outcomes tend to be. Therefore, timely and accurate diagnosis is essential in ensuring that individuals receive the support and resources they need to overcome their speech challenges.
In conclusion, diagnosing speech impediments involves a comprehensive evaluation of the individual's speech and language abilities, as well as an assessment of the impact of the condition on their daily life. With the right diagnosis and treatment plan in place, individuals with speech impediments can learn to effectively manage their condition and improve their overall communication skills.
Treatment Options for Speech Impediments
When it comes to speech impediments, it's important to understand the various treatment options available. Speech impediments can manifest in different forms, such as stuttering, lisping, or apraxia, and can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for speech impediments, as well as coping strategies for individuals affected by this condition.
Speech impediments can be caused by a variety of factors, including neurological conditions, developmental disorders, or physical abnormalities in the mouth or throat. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association , approximately 7.5 million people in the United States have trouble using their voices, with speech sound disorders being one of the most common types of communication disorders among children.
Symptoms of Speech Impediments
The symptoms of speech impediments can vary depending on the specific condition. Some common symptoms include difficulty pronouncing certain sounds or words, repeating sounds or words, or struggling to form coherent sentences. Children with speech impediments may also experience delays in language development and have trouble expressing themselves effectively.
Treatment Options
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for individuals with speech impediments. Speech therapy, which is provided by a speech-language pathologist, is one of the most common and effective treatments. During speech therapy sessions, individuals learn techniques to improve their speech, such as practicing specific sounds or words, using alternative communication methods, and strengthening the muscles used for speech production.
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to address underlying physical or neurological issues contributing to the speech impediment. For example, individuals with cleft palate or other structural abnormalities in the mouth or throat may require surgical procedures to correct these issues.
Coping Strategies
Living with a speech impediment can be challenging, but there are coping strategies that can help individuals manage their condition. Building self-confidence and self-acceptance is crucial, and support groups or counseling can provide valuable emotional support. Additionally, practicing good communication techniques, such as speaking slowly and clearly, can help individuals feel more comfortable when interacting with others.
It's important to remember that speech impediments are not a reflection of intelligence or capability, and with the right support and treatment, individuals with speech impediments can lead fulfilling and successful lives.
Speech Therapy for Children and Adults
Speech therapy is a crucial intervention for both children and adults who experience difficulties in speaking, also known as speech impediments. These impediments can be caused by a variety of factors, including developmental delays, neurological disorders, or physical impairments. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for speech impediments, as well as coping strategies for individuals affected by this condition.
For children, speech impediments can significantly impact their overall development and academic performance. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association , approximately 8% of children in the United States have a speech disorder. These disorders can manifest as difficulties with articulation, fluency, or voice production. Early intervention through speech therapy is crucial in helping children overcome these challenges and improve their communication skills.
Adults may also experience speech impediments due to various reasons, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, or degenerative neurological conditions. The World Health Organization reports that over 50 million people worldwide have a speech disorder, with the majority being adults. Speech therapy can play a vital role in helping adults regain their speech and language abilities, thereby enhancing their quality of life and social interactions.
Speech therapy for both children and adults typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including assessment, diagnosis, and individualized treatment plans. Speech-language pathologists, or speech therapists, are trained professionals who specialize in evaluating and treating speech and language disorders. They utilize various techniques and exercises to improve articulation, language comprehension, and overall communication skills.
Furthermore, speech therapy may also involve the use of augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices for individuals who have severe speech impairments. These devices can range from simple picture boards to sophisticated electronic devices that generate speech based on input from the user. AAC can significantly enhance the communication abilities of individuals who are unable to speak or have limited verbal output.
In addition to direct therapy sessions, speech therapists often work closely with families, caregivers, and educators to provide support and guidance in facilitating effective communication strategies at home and in educational settings. This collaborative approach is essential in ensuring that individuals with speech impediments receive consistent and comprehensive care.
It is important to note that the success of speech therapy largely depends on early detection and intervention. Therefore, it is crucial for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to be vigilant in identifying any signs of speech impediments in children and seeking timely evaluation and treatment. Similarly, adults who experience sudden or progressive changes in their speech should seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and explore appropriate therapy options.
In conclusion, speech therapy is a valuable resource for both children and adults who struggle with speech impediments. By addressing the underlying causes and providing targeted interventions, speech therapists can help individuals improve their communication skills and overcome the challenges associated with speech disorders. Through collaborative efforts and ongoing support, individuals with speech impediments can lead fulfilling and meaningful lives.
Coping Strategies for Individuals with Speech Impediments
Living with a speech impediment can be challenging, but there are coping strategies that can help individuals manage their condition and improve their quality of life. Whether the speech impediment is due to a developmental disorder, neurological condition, or injury, there are various techniques and resources that can be beneficial.
Seeking Professional Help
One of the most important coping strategies for individuals with speech impediments is seeking professional help. Speech therapists, also known as speech-language pathologists, are trained to assess and treat speech disorders. They can provide personalized therapy to improve speech clarity, fluency, and overall communication skills. It is essential to work with a qualified speech therapist to develop a treatment plan tailored to the individual's specific needs.
Practice and Persistence
Consistent practice and persistence are key components of coping with a speech impediment. Speech therapy exercises, such as tongue twisters, breathing exercises, and vocal warm-ups, can help strengthen the muscles involved in speech production. Additionally, practicing good communication habits, such as speaking slowly and clearly, can improve overall speech intelligibility. It is important for individuals with speech impediments to commit to regular practice and remain patient with their progress.
Utilizing Assistive Devices
Assistive devices can be valuable tools for individuals with speech impediments. Augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) devices, such as speech-generating devices and communication boards, can assist individuals in expressing themselves when verbal communication is challenging. These devices can enhance communication and help individuals participate more fully in social, educational, and professional settings.
Building a Support Network
Building a strong support network is essential for individuals coping with speech impediments. Family, friends, and peers can provide encouragement, understanding, and acceptance. Support groups and online communities can also offer valuable resources and connections with others who share similar experiences. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with a speech impediment can be empowering and reassuring.
Embracing Self-Advocacy
Self-advocacy is an important skill for individuals with speech impediments. Learning to assert one's needs, communicate effectively, and educate others about the nature of the speech impediment can help individuals navigate social interactions and access necessary accommodations. By advocating for themselves, individuals can promote greater awareness and understanding of speech disorders within their communities.
Seeking Emotional Support
Coping with a speech impediment can be emotionally taxing at times. It is important for individuals to seek emotional support when needed. Mental health professionals, such as psychologists or counselors, can provide guidance and support for managing the emotional impact of living with a speech impediment. Addressing feelings of frustration, anxiety, or self-consciousness is an important aspect of overall well-being.
By implementing these coping strategies, individuals with speech impediments can enhance their communication skills, build confidence, and lead fulfilling lives. It is important to remember that each person's experience with a speech impediment is unique, and finding the right combination of coping strategies may require time and experimentation.
Speech impediments can be incredibly challenging for individuals to cope with, and it's important to approach the topic with empathy and understanding. The causes of speech impediments can vary widely, from developmental issues to neurological conditions or physical injuries. It's crucial for individuals affected by speech impediments to seek professional help in order to properly diagnose the underlying cause and explore treatment options.
The symptoms of speech impediments can manifest in a variety of ways, including difficulty pronouncing certain sounds, stuttering, or struggling to articulate thoughts clearly. These challenges can impact a person's confidence and self-esteem, making it essential for them to have a strong support system in place.
Treatment options for speech impediments may include speech therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, or in some cases, medical interventions. It's important for individuals to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most effective course of action for their specific needs.
In addition to professional treatment, coping strategies can play a significant role in helping individuals manage their speech impediments. This may involve practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in supportive group therapy, or seeking out assistive devices to aid in communication.
Ultimately, it's crucial for individuals affected by speech impediments to know that they are not alone. By seeking support from loved ones, healthcare professionals, and fellow individuals facing similar challenges, it's possible to navigate the complexities of this condition with resilience and determination.
Want to join the discussion? Please login or register to reply.
Latest Sources
- article Understanding Penile Bowen Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment July 17, 2024
- article Understanding Degenerative Diseases and Their Impact on Health January 02, 2025
- article Understanding the Presence of Corneal Scars April 23, 2024
- article Tick Bites: Identification, Symptoms, and Treatment Options May 30, 2024
- article Understanding Unilateral Leg Paralysis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options January 02, 2025
- article Understanding the Difference Between Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) October 30, 2024
- article Make Your Own Hydrating Skin Blocks December 31, 2024
- article Healthy Apple Strudel with Raisins and Almonds February 04, 2024
- article Special Forces Training Program January 02, 2025
- article Make Your Own Golden Honey to Cure the Flu and Cold January 02, 2025
Similar Sources
- Understanding the Presence of Corneal Scars
- Understanding the Difference Between Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Unilateral Leg Pain and Tension in the Arch: Causes and Remedies
- Metabolic Causes of Respiratory Distress in Babies
- Understanding Catatonic Behavior: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
- Understanding Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Deadly Strain of Avian Flu Created
- Recurring Mycobacterial Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- Understanding Elevated Intracranial Pressure
- Understanding H65.0 Acute serous otitis media
Connect with Us
Health Conditions
- Breast Cancer
- Cancer Care
- Caregiving for Alzheimer's Disease
- Chronic Kidney Disease
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Digestive Health
- Heart Health
- Mental Health
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Sleep Health
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Weight Management
Condition Spotlight
Wellness Topics
- Mental Well-Being
- Sexual Health
- Vitamins and Supplements
- Women's Wellness
Product Reviews
- At-Home Testing
- Men's Health
- Women's Health
Featured Programs
- Video Series
- Pill Identifier
- Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis Essentials
- Diabetes Nutrition
- High Cholesterol
- Taming Inflammation in Psoriasis
- Taming Inflammation in Psoriatic Arthritis
Newsletters
- Anxiety and Depression
- Nutrition Edition
- Wellness Wire
Lifestyle Quizzes
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Are You a Workaholic?
Find Your Bezzy Community
Bezzy communities provide meaningful connections with others living with chronic conditions. Join Bezzy on the web or mobile app.

Follow us on social media
Can't get enough? Connect with us for all things health.

What to Know About Speech Disorders

Speech disorders can affect the way a person creates sounds to form words. Certain voice disorders may also be considered speech disorders.
Some people with speech disorders are aware of what they would like to say but unable to articulate their thoughts. This may lead to self-esteem issues and the development of depression .
Speech disorders can affect adults and children. Early treatment can correct these conditions.
Types of speech disorders
One of the most commonly experienced speech disorders is stuttering. Other speech disorders include apraxia and dysarthria .
- Apraxia: a motor speech disorder caused by damage to the parts of the brain related to speaking.
- Dysarthria: a motor speech disorder in which the muscles of the mouth, face, or respiratory system may become weak or have difficulty moving.
People who stutter can experience the following types of disruption:
- Repetitions : involuntarily repeat sounds, vowels, or words.
- Blocks : difficulty making the necessary speech sounds despite knowing what you want to say
- Prolongations : stretching or drawing out of particular sounds or words
Apraxia may present itself in the following ways:
- long pauses between syllables
- having to move the lips, jaw, or tongue a few times before speaking
- slower rate of speech
- distorted sounds in speech, such as sound substitutions or difficulty saying long words
People who live with dysarthria may experience the following symptoms:
- slurred speech
- speaking too slowly or too quickly
- soft or quiet speech
- difficulty moving the mouth or tongue
What causes speech disorders?
Speech disorders affect the vocal cords, muscles, nerves, and other structures within the throat.
Causes may include:
- vocal cord damage
- brain damage
- muscle weakness
- respiratory weakness
- polyps or nodules on the vocal cords
- vocal cord paralysis
People who have certain medical or developmental conditions may also have speech disorders. Common conditions that can lead to speech disorders are:
- attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- oral cancer
- laryngeal cancer
- Huntington’s disease
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) , also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease
Speech disorders may be hereditary, and they can develop over time.
What are the symptoms of a speech disorder?
Several symptoms may be present depending on the cause of the speech disorder. Common symptoms experienced by people with speech disorders are:
- repeating sounds , which is most often seen in people who stutter
- adding extra sounds and words
- elongating words
- making jerky movements while talking, usually involving the head
- blinking several times while talking
- visible frustration when trying to communicate
- taking frequent pauses when talking
- distorting sounds when talking
- hoarseness , or speaking with a raspy or gravelly-sounding voice
How are speech disorders diagnosed?
Many tests are available to diagnose speech disorders.
Denver articulation screening exam
The Denver articulation screening examination (DASE) is a commonly used testing system to diagnose articulation disorders. This test evaluates the clarity in pronunciation in children between the ages of 2 and 7. This five-minute test uses various exercises to assess the child’s speech.
Early language milestones scale 2
This test , created by neurodevelopmental pediatrician James Coplan, determines a child’s language development. This test can quickly identify delayed speech or language disorders.
Peabody picture vocabulary test, revised
This test measures a person’s vocabulary and ability to speak. The person will listen to various words and choose pictures that describe the words. People who have severe intellectual disabilities and those who are blind won’t able to take this assessment. The Peabody picture vocabulary test has been revised many times since its first version was administered in 1959.
How are speech disorders treated?
Mild speech disorders may not require any treatment. Some speech disorders may simply go away. Others can improve with speech therapy.
Treatment varies and depends on the type of disorder. In speech therapy, a professional therapist will guide you through exercises that work to strengthen the muscles in your face and throat.
You’ll learn to control your breathing while speaking. Muscle-strengthening exercises and controlled breathing help improve the way your words sound. You’ll also learn ways to practice smoother, more fluent speech.
Some people with speech disorders experience nervousness, embarrassment, or depression. Talk therapy may be helpful in these situations. A therapist will discuss ways to cope with the condition and ways to improve the outlook of your condition.
If your depression is severe, antidepressant medications can help.
What are the potential complications of speech disorders?
Untreated speech disorders may cause a person to experience a great deal of anxiety . Over time, this anxiety can trigger anxiety disorders or a phobia of speaking in public . Early treatment for anxiety can help prevent the development of anxiety disorders or phobias.
Treatment options include talk therapy and anti-anxiety medications .
What is the long-term outlook?
The outlook improves for people who seek early treatment. Early treatment helps prevent a speech disorder from worsening. The outlook for those with permanent disabilities depends upon the severity of the disability.
How we reviewed this article:
- Apraxiaof speech in adults. (n.d.). http://www.asha.org/public/speech/disorders/Apraxia-of-Speech-in-Adults/
- Childhoodapraxia of speech. (n.d.). http://www.asha.org/public/speech/disorders/ChildhoodApraxia/
- CoplanJ. (n.d.). Early language milestone scale - 2 [Video]. http://www.drcoplan.com/early-language-milestone-scale-2
- Peabodypicture vocabulary test: Revised. (n.d.). https://www.nlsinfo.org/content/cohorts/nlsy79-children/topical-guide/assessments/peabody-picture-vocabulary-test-revised
- Screening and assessment. (n.d.). https://www.elcbigbend.org/site/Providers/Early-Care-and-Education/Professional-Development/Screening-and-Assessment
Share this article
More in Managing Friedreich’s Ataxia
- Friedreich’s Ataxia
- What Is Ataxia?
- What Is Episodic Ataxia?
- Acute Cerebellar Ataxia (ACA)
Read this next
Friedreich’s ataxia is a rare genetic disease that causes difficulty walking, a loss of sensation in the arms and legs, and impaired speech.
Ataxia involves a lack of muscle coordination and control. There are many types. Learn more about ataxia's causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Episodic ataxia (EA) is a rare neurological condition that impairs movement. We'll look at the different types, symptoms, and treatments.
Acute cerebellar ataxia (ACA) is a disorder that occurs when the cerebellum becomes inflamed or damaged. The cerebellum is the area of the brain…
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Forums Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Speaking Skills
How to Get Rid of a Speech Disorder
Last Updated: December 8, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Devin Fisher, CCC-SLP . Devin Fisher is a Speech-Language Pathologist based in Las Vegas, Nevada. Devin specializes in speech and language therapy for individuals with aphasia, swallowing, voice, articulation, phonological social-pragmatic, motor speech, and fluency disorders. Furthermore, Devin treats cognitive-communication impairment, language delay, and Parkinson's Disease. He holds a BS and MS in Speech-Language Pathology from Fontbonne University. Devin also runs a related website and blog that offers speech-language therapy resources and information for clinicians and clients. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, several readers have written to tell us that this article was helpful to them, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 333,221 times.
Many people feel insecure about their speech impediments, whether they're dealing with a lisp or an inability to articulate words. Although it may not seem like it—particularly if you have been dealing with this problem for years—you may be able to get rid of or improve your speech impediment with a few speech-training practices and some major confidence-boosters. And don't forget to seek out the professional opinion of a speech and language therapist/pathologist for more information.
Helping Yourself with a Speech Disorder

- One modern approach is to use technology. There are apps that can run on smartphones and tablets that listen to what you say and then give you feedback. For example, on Android there is the free app "Talking English." You can also find similar apps in the Apple App Store.

Stephanie Jeret
Cues and picture boards can help those with aphasia find words and express thoughts. For aphasia or trouble finding words, cues like the first sound can help jog your memory. Picture boards are great too, especially if speaking is very difficult. These tools allow people to communicate their needs and thoughts through other means.
Using Your Body to Improve Speech

- Shoulders relaxed
- Back straight
- Feet steady

- Sit comfortably and with an erect posture. Breathe in deeply through your nose. You should use your hand to feel your stomach expanding like a balloon being inflated. Hold the breath and then release it slowly, feeling your stomach deflating beneath your hand. Repeat this exercise before you have to speak publicly to relieve stress.

Getting Professional Help

- Speech therapy is helpful for correcting your impediment. The therapist will point out the part of speech where you're having problems, and will work with you to correct it. Private speech therapy sessions do not come cheap, although most insurance policies will fund services needed to treat speech disorders.
- There's no substitute for learning and practice when it comes to the proper and effective use of language. Take every opportunity to speak, to practice and brush up on the correct pronunciation and enunciation provided to you by a professional.

- Every time the dentist adjusts your braces (or even dentures), you need to train yourself to talk and to eat properly. It may be quite painful at first, but remember not to go too far, lest you end up with a mouth injury.
- Most braces are used for orthodontic purposes, although some braces can be used as decorations. Braces are rather expensive, and you may need to take out a dental plan or cash in on dental insurance to pay for them.
- Kids and teenagers don't like to wear braces because they're often teased as “metal mouths” or “railroad faces.” The fact is that braces are still the best way to correct a lisp caused by misaligned teeth.
Assessing Your Speech Disorder

- Cleft lips and palates were a major cause of speech impediments until surgery became affordable. Now, children born with clefts can have reconstructive surgery and a multidisciplinary team of providers that help with feeding and speech and language development. [14] X Research source
- Malocclusion is when the teeth do not have the proper normal bite. Malocclusions are usually corrected through braces, although orthodontic surgery is necessary in some cases. Individuals with this condition may talk with a lisp, make a whistle sound when certain words are spoken, or mumble.
- Neurological disorders caused by accidents or brain and nerve tumors can cause a speech disorder called dysprosody. Dysprosody involves difficulty in expressing the tonal and emotional qualities of speech such as inflection and emphasis.

Expert Q&A

- Welcome good speech. Look forward to it, and accept and celebrate even little improvements. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Try to slow down and pronounce each word properly, as this can also help when trying to overcome a speech problem. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- See a Speech Pathologist who maintains their Certification of Clinical Competence from the American Speech and Hearing Association. These professionals are able to evaluate, diagnose and treat speech impairments. Nothing replaces sound medical advice from a specialist. Thanks Helpful 11 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.uts.edu.au/sites/default/files/2018-10/Camperdown%20Program%20Treatment%20Guide%20June%202018.pdf
- ↑ Devin Fisher, CCC-SLP. Speech Language Pathologist. Expert Interview. 15 January 2021.
- ↑ https://www.stutteringhelp.org/sites/default/files/Migrate/Book_0012_tenth_ed.pdf
- ↑ http://www.coli.uni-saarland.de/~steiner/publications/ISSP2014.pdf
- ↑ https://sps.columbia.edu/news/five-ways-improve-your-body-language-during-speech
- ↑ https://www.nhs.uk/mental-health/self-help/guides-tools-and-activities/breathing-exercises-for-stress/
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/speech-disorders.html
- ↑ https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/stuttering
- ↑ https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001058.htm
- ↑ https://www.asha.org/public/speech/disorders/CleftLip
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/hearing-loss-children-guide/parents-guide/building-languages.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/developmentaldisabilities/language-disorders.html
- ↑ https://raisingchildren.net.au/preschoolers/development/language-development/stuttering
About This Article

Medical Disclaimer
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, examination, diagnosis, or treatment. You should always contact your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional before starting, changing, or stopping any kind of health treatment.
Read More...
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Bikash Pokharel
Apr 23, 2017
Did this article help you?

Mar 28, 2016
Manisha Singh
Feb 22, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Call Us Today: (224) 219-1924
Grow with us in a FUN & functional way!
e-mail: [email protected]

Speech Impediment: Definition, Causes, Types and Treatment
02 may speech impediment: definition, causes, types and treatment.
One of life’s joys as a parent is watching your kids grow and change. You see them learn new things, meet new friends, and explore the world around them. But sometimes, you also witness them struggle – like when they have their first fight with a friend or don’t do as well as they wanted to on a test. And while it’s never easy to see your child suffer, one of the hardest things to watch is when your child has difficulty communicating. If your child has a speech impediment, you know that feeling all too well. It can be frustrating and heartbreaking to see your little one struggling to be understood. But take heart – you’re not alone. Many children have difficulties with speech, and with the right pediatric speech therapist in Chicago , your child can learn to overcome their impediment. This blog post will define a speech impediment, discuss some of the most common types and causes, and provide information on treatment options.
What is a speech impediment?
A speech impediment is a condition that affects a person’s ability to produce sound correctly. The term can refer to any difficulties that impede a person’s speech, from mild sound errors to severe problems with articulation. All individuals with speech impediments have difficulty producing certain sounds, depending on one sound. Some people may only have trouble with one sound, while others may have difficulty producing multiple sounds.
What causes speech impediments?
Some people are born with speech impediments, while others develop them later in life. There are many different causes of speech impediment, as you will see below.
1. Congenital defects Congenital defects are abnormalities that are present at birth. They can affect any part of the body, including the mouth and vocal cords. In some cases, congenital defects can cause problems with the tongue moving or the formation of teeth. Many different types of congenital defects can cause a speech impediment, including : Cleft lip and palate is a condition where there is an opening in the lip and/or roof of the mouth. This opening can cause problems with the way the mouth forms words, as well as with eating and drinking. Cleft lip and palate can also cause hearing problems. Vocal cord paralysis is a condition where the vocal cords are unable to move correctly. This can make it difficult to produce sound, as well as to breathe properly. Tongue-tie is a condition where the tongue is tethered to the floor of the mouth. This can make it difficult to move the tongue and can cause problems with eating, drinking, and speaking.
2. Neurological disorders Neurological disorders are conditions that affect the nervous system. These disorders can cause problems with the way the brain sends signals to the muscles, which can lead to difficulties with movement and speech. Some of the more common neurological disorders include: Cerebral palsy is a condition that affects movement and muscle coordination. It is caused by damage to the brain, usually before or during birth. Cerebral palsy can cause problems with the way a person walks, talks, and eats. Multiple sclerosis is a disease of the nervous system that causes the immune system to attack the nerves. This can lead to problems with muscle control and vision, hearing, and speech.
3. Hearing loss Hearing loss can be caused by many different things, including exposure to loud noise, certain medications, and aging. Hearing loss can make it difficult to understand what other people are saying, which can lead to problems with speech. There are many different types of hearing loss, and the severity can vary from person to person. Some people with hearing loss may only have trouble hearing certain sounds, while others may not be able to hear anything at all. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. Temporary hearing loss can be caused by things like earwax buildup or infection. Permanent hearing loss can be caused by things like damage to the inner ear or a genetic disorder.
4. Language disorders Language disorders are conditions that affect a person’s ability to understand or use language. These disorders can make it difficult to produce or comprehend speech. Some of the more common language disorders include dyslexia and aphasia.
5. Emotional disorders Emotional disorders are conditions that affect a person’s emotions or mood. These disorders can cause problems with speech due to anxiety or stress. Some of the more common emotional disorders include anxiety disorders and depression. lip
Types of speech disorder
There are many different types of speech disorders, and the symptoms can vary from person to person. Some of the more common types of speech disorders include:
1. Articulation disorder An articulation disorder is a problem with the way the mouth, teeth, or tongue move to make sounds. This can make it difficult to produce certain sounds correctly. People with articulation disorders may have trouble saying certain words correctly, or they may leave out parts of words when they speak.
2. Fluency disorder A fluency disorder is a problem with the flow of speech. People with fluency disorders may have trouble putting their thoughts into words, and they may stutter when they speak. Stuttering is a type of fluency disorder that is characterized by pauses, repetitions, or prolongations of sounds.
3. Resonance disorder A resonance disorder is a problem with the way sound resonates in the mouth and throat. This can make it difficult to produce certain sounds correctly. People with resonance disorders may have trouble producing vowel sounds, or they may speak with a nasal tone.
4. Voice disorder A voice disorder is a problem with the way the voice sounds. This can be caused by things like vocal cord damage or misuse of the voice. People with voice disorders may have trouble speaking loudly or speaking in a hoarse or breathy voice.
Treatment of speech impediments
There are many different treatments for speech disorders, and the best treatment will depend on the individual and the cause of the disorder. Some of the more common treatments include:
1. Speech therapy Speech therapy is a type of treatment that helps people with speech disorders improve their abilities. Speech therapists can help people with articulation disorders learn to produce sounds correctly, people with fluency disorders reduce their stuttering, and people with resonance disorders improve their vowel production.
2. Surgery Surgery can be used to correct some anatomical defects that cause speech disorders. For example, surgery can be used to correct cleft lip and palate, vocal cord paralysis, and tongue tie.
3. Medication Medication can be used to treat some neurological disorders that cause speech disorders. For example, medication can be used to treat conditions like cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis.
4. Hearing aids Hearing aids can be used to treat hearing loss that causes speech disorders. Hearing aids amplify sound so that people with hearing loss can better understand what other people are saying.
5. Communication devices Communication devices can be used to help people with language disorders or severe speech disorders communicate. These devices can include things like picture boards and computer software that helps people generate speech.
6. Counseling Counseling can be used to treat emotional disorders that cause speech disorders. Counseling can help people manage their anxiety and stress and learn coping mechanisms to deal with their disorders.
7. Alternative treatments There are many different alternative treatments for speech disorders. Some of these treatments include acupuncture, aromatherapy, and massage therapy. It is important to speak with a doctor before starting any alternative treatment.
Speech disorders can cause a variety of problems for people, ranging from difficulty understanding what other people are saying to difficulty producing speech. There are many different causes of speech disorders, and the best treatment will depend on the individual and the cause of the disorder. Visit https://functionalspeechtherapy.com/ to learn more about pediatric speech disorders and treatment options.
Functional Speech Therapy Co., 960 Route 22, Unit 216 Fox River Grove Illinois 60021, (224) 219-1924
Find us on Social Media https://www.facebook.com/FUNctionalSpeechClinic/ https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCJyXslNcwUw-ABZ5myhERTQ https://www.instagram.com/functional\_speechtherapy
No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Speech Impediment Guide: Definition, Causes, and Resources
December 8, 2020

Tables of Contents
What Is a Speech Impediment?
Types of speech disorders, speech impediment causes, how to fix a speech impediment, making a difference in speech disorders.
Communication is a cornerstone of human relationships. When an individual struggles to verbalize information, thoughts, and feelings, it can cause major barriers in personal, learning, and business interactions.
Speech impediments, or speech disorders, can lead to feelings of insecurity and frustration. They can also cause worry for family members and friends who don’t know how to help their loved ones express themselves.
Fortunately, there are a number of ways that speech disorders can be treated, and in many cases, cured. Health professionals in fields including speech-language pathology and audiology can work with patients to overcome communication disorders, and individuals and families can learn techniques to help.

Commonly referred to as a speech disorder, a speech impediment is a condition that impacts an individual’s ability to speak fluently, correctly, or with clear resonance or tone. Individuals with speech disorders have problems creating understandable sounds or forming words, leading to communication difficulties.
Some 7.7% of U.S. children — or 1 in 12 youths between the ages of 3 and 17 — have speech, voice, language, or swallowing disorders, according to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). About 70 million people worldwide, including some 3 million Americans, experience stuttering difficulties, according to the Stuttering Foundation.
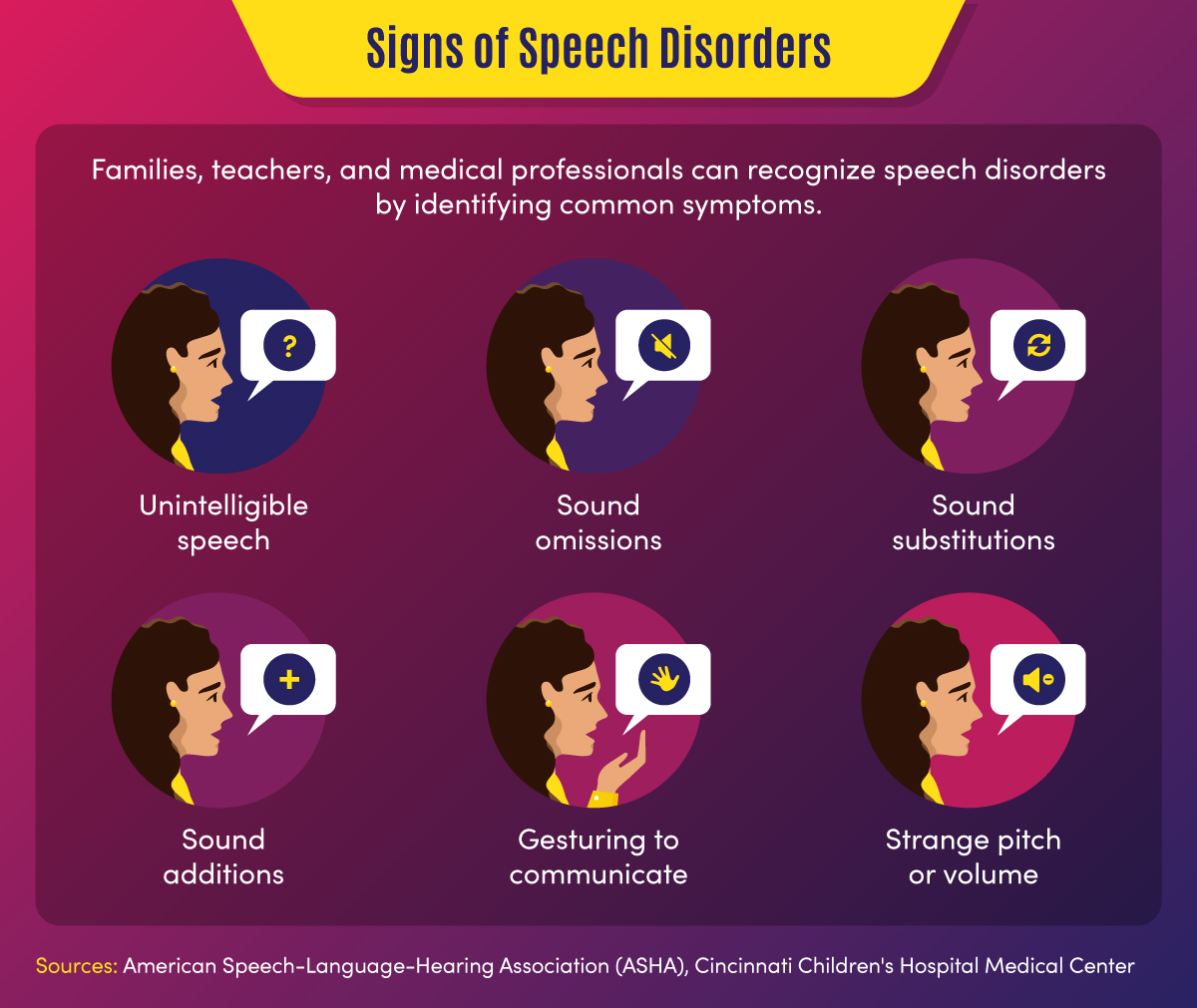
Common signs of a speech disorder
There are several symptoms and indicators that can point to a speech disorder.
- Unintelligible speech — A speech disorder may be present when others have difficulty understanding a person’s verbalizations.
- Omitted sounds — This symptom can include the omission of part of a word, such as saying “bo” instead of “boat,” and may include omission of consonants or syllables.
- Added sounds — This can involve adding extra sounds in a word, such as “buhlack” instead of “black,” or repeating sounds like “b-b-b-ball.”
- Substituted sounds — When sounds are substituted or distorted, such as saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit,” it may indicate a speech disorder.
- Use of gestures — When individuals use gestures to communicate instead of words, a speech impediment may be the cause.
- Inappropriate pitch — This symptom is characterized by speaking with a strange pitch or volume.
In children, signs might also include a lack of babbling or making limited sounds. Symptoms may also include the incorrect use of specific sounds in words, according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA). This may include the sounds p, m, b, w, and h among children aged 1-2, and k, f, g, d, n, and t for children aged 2-3.
Back To Top
Categories of Speech Impediments
Speech impediments can range from speech sound disorders (articulation and phonological disorders) to voice disorders. Speech sound disorders may be organic — resulting from a motor or sensory cause — or may be functional with no known cause. Voice disorders deal with physical problems that limit speech. The main categories of speech impediments include the following:
Fluency disorders occur when a patient has trouble with speech timing or rhythms. This can lead to hesitations, repetitions, or prolonged sounds. Fluency disorders include stuttering (repetition of sounds) or (rapid or irregular rate of speech).
Resonance disorders are related to voice quality that is impacted by the shape of the nose, throat, and/or mouth. Examples of resonance disorders include hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance.
Articulation disorders occur when a patient has difficulty producing speech sounds. These disorders may stem from physical or anatomical limitations such as muscular, neuromuscular, or skeletal support. Examples of articulation speech impairments include sound omissions, substitutions, and distortions.
Phonological disorders result in the misuse of certain speech sounds to form words. Conditions include fronting, stopping, and the omission of final consonants.
Voice disorders are the result of problems in the larynx that harm the quality or use of an individual’s voice. This can impact pitch, resonance, and loudness.
Impact of Speech Disorders
Some speech disorders have little impact on socialization and daily activities, but other conditions can make some tasks difficult for individuals. Following are a few of the impacts of speech impediments.
- Poor communication — Children may be unable to participate in certain learning activities, such as answering questions or reading out loud, due to communication difficulties. Adults may avoid work or social activities such as giving speeches or attending parties.
- Mental health and confidence — Speech disorders may cause children or adults to feel different from peers, leading to a lack of self-confidence and, potentially, self-isolation.
Resources on Speech Disorders
The following resources may help those who are seeking more information about speech impediments.
Health Information : Information and statistics on common voice and speech disorders from the NIDCD
Speech Disorders : Information on childhood speech disorders from Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center
Speech, Language, and Swallowing : Resources about speech and language development from the ASHA
Children and adults can suffer from a variety of speech impairments that may have mild to severe impacts on their ability to communicate. The following 10 conditions are examples of specific types of speech disorders and voice disorders.
1. Stuttering
This condition is one of the most common speech disorders. Stuttering is the repetition of syllables or words, interruptions in speech, or prolonged use of a sound.
This organic speech disorder is a result of damage to the neural pathways that connect the brain to speech-producing muscles. This results in a person knowing what they want to say, but being unable to speak the words.
This consists of the lost ability to speak, understand, or write languages. It is common in stroke, brain tumor, or traumatic brain injury patients.
4. Dysarthria
This condition is an organic speech sound disorder that involves difficulty expressing certain noises. This may involve slurring, or poor pronunciation, and rhythm differences related to nerve or brain disorders.
The condition of lisping is the replacing of sounds in words, including “th” for “s.” Lisping is a functional speech impediment.
6. Hyponasality
This condition is a resonance disorder related to limited sound coming through the nose, causing a “stopped up” quality to speech.
7. Cul-de-sac resonance
This speech disorder is the result of blockage in the mouth, throat, or nose that results in quiet or muffled speech.
8. Orofacial myofunctional disorders
These conditions involve abnormal patterns of mouth and face movement. Conditions include tongue thrusting (fronting), where individuals push out their tongue while eating or talking.
9. Spasmodic Dysphonia
This condition is a voice disorder in which spasms in the vocal cords produce speech that is hoarse, strained, or jittery.
10. Other voice disorders
These conditions can include having a voice that sounds breathy, hoarse, or scratchy. Some disorders deal with vocal folds closing when they should open (paradoxical vocal fold movement) or the presence of polyps or nodules in the vocal folds.
Speech Disorders vs. Language Disorders
Speech disorders deal with difficulty in creating sounds due to articulation, fluency, phonology, and voice problems. These problems are typically related to physical, motor, sensory, neurological, or mental health issues.
Language disorders, on the other hand, occur when individuals have difficulty communicating the meaning of what they want to express. Common in children, these disorders may result in low vocabulary and difficulty saying complex sentences. Such a disorder may reflect difficulty in comprehending school lessons or adopting new words, or it may be related to a learning disability such as dyslexia. Language disorders can also involve receptive language difficulties, where individuals have trouble understanding the messages that others are trying to convey.

Resources on Types of Speech Disorders
The following resources may provide additional information on the types of speech impediments.
Common Speech Disorders: A guide to the most common speech impediments from GreatSpeech
Speech impairment in adults: Descriptions of common adult speech issues from MedlinePlus
Stuttering Facts: Information on stuttering indications and causes from the Stuttering Foundation
Speech disorders may be caused by a variety of factors related to physical features, neurological ailments, or mental health conditions. In children, they may be related to developmental issues or unknown causes and may go away naturally over time.
Physical and neurological issues. Speech impediment causes related to physical characteristics may include:
- Brain damage
- Nervous system damage
- Respiratory system damage
- Hearing difficulties
- Cancerous or noncancerous growths
- Muscle and bone problems such as dental issues or cleft palate
Mental health issues. Some speech disorders are related to clinical conditions such as:
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Down syndrome or other genetic syndromes
- Cerebral palsy or other neurological disorders
- Multiple sclerosis
Some speech impairments may also have to do with family history, such as when parents or siblings have experienced language or speech difficulties. Other causes may include premature birth, pregnancy complications, or delivery difficulties. Voice overuse and chronic coughs can also cause speech issues.
The most common way that speech disorders are treated involves seeking professional help. If patients and families feel that symptoms warrant therapy, health professionals can help determine how to fix a speech impediment. Early treatment is best to curb speech disorders, but impairments can also be treated later in life.
Professionals in the speech therapy field include speech-language pathologists (SLPs) . These practitioners assess, diagnose, and treat communication disorders including speech, language, social, cognitive, and swallowing disorders in both adults and children. They may have an SLP assistant to help with diagnostic and therapy activities.
Speech-language pathologists may also share a practice with audiologists and audiology assistants. Audiologists help identify and treat hearing, balance, and other auditory disorders.
How Are Speech Disorders Diagnosed?
Typically, a pediatrician, social worker, teacher, or other concerned party will recognize the symptoms of a speech disorder in children. These individuals, who frequently deal with speech and language conditions and are more familiar with symptoms, will recommend that parents have their child evaluated. Adults who struggle with speech problems may seek direct guidance from a physician or speech evaluation specialist.
When evaluating a patient for a potential speech impediment, a physician will:
- Conduct hearing and vision tests
- Evaluate patient records
- Observe patient symptoms
A speech-language pathologist will conduct an initial screening that might include:
- An evaluation of speech sounds in words and sentences
- An evaluation of oral motor function
- An orofacial examination
- An assessment of language comprehension
The initial screening might result in no action if speech symptoms are determined to be developmentally appropriate. If a disorder is suspected, the initial screening might result in a referral for a comprehensive speech sound assessment, comprehensive language assessment, audiology evaluation, or other medical services.
Initial assessments and more in-depth screenings might occur in a private speech therapy practice, rehabilitation center, school, childcare program, or early intervention center. For older adults, skilled nursing centers and nursing homes may assess patients for speech, hearing, and language disorders.
How Are Speech Impediments Treated?
Once an evaluation determines precisely what type of speech sound disorder is present, patients can begin treatment. Speech-language pathologists use a combination of therapy, exercise, and assistive devices to treat speech disorders.
Speech therapy might focus on motor production (articulation) or linguistic (phonological or language-based) elements of speech, according to ASHA. There are various types of speech therapy available to patients.
Contextual Utilization — This therapeutic approach teaches methods for producing sounds consistently in different syllable-based contexts, such as phonemic or phonetic contexts. These methods are helpful for patients who produce sounds inconsistently.
Phonological Contrast — This approach focuses on improving speech through emphasis of phonemic contrasts that serve to differentiate words. Examples might include minimal opposition words (pot vs. spot) or maximal oppositions (mall vs. call). These therapy methods can help patients who use phonological error patterns.
Distinctive Feature — In this category of therapy, SLPs focus on elements that are missing in speech, such as articulation or nasality. This helps patients who substitute sounds by teaching them to distinguish target sounds from substituted sounds.
Core Vocabulary — This therapeutic approach involves practicing whole words that are commonly used in a specific patient’s communications. It is effective for patients with inconsistent sound production.
Metaphon — In this type of therapy, patients are taught to identify phonological language structures. The technique focuses on contrasting sound elements, such as loud vs. quiet, and helps patients with unintelligible speech issues.
Oral-Motor — This approach uses non-speech exercises to supplement sound therapies. This helps patients gain oral-motor strength and control to improve articulation.
Other methods professionals may use to help fix speech impediments include relaxation, breathing, muscle strengthening, and voice exercises. They may also recommend assistive devices, which may include:
- Radio transmission systems
- Personal amplifiers
- Picture boards
- Touch screens
- Text displays
- Speech-generating devices
- Hearing aids
- Cochlear implants
Resources for Professionals on How to Fix a Speech Impediment
The following resources provide information for speech therapists and other health professionals.
Assistive Devices: Information on hearing and speech aids from the NIDCD
Information for Audiologists: Publications, news, and practice aids for audiologists from ASHA
Information for Speech-Language Pathologists: Publications, news, and practice aids for SLPs from ASHA
Speech Disorder Tips for Families
For parents who are concerned that their child might have a speech disorder — or who want to prevent the development of a disorder — there are a number of activities that can help. The following are tasks that parents can engage in on a regular basis to develop literacy and speech skills.
- Introducing new vocabulary words
- Reading picture and story books with various sounds and patterns
- Talking to children about objects and events
- Answering children’s questions during routine activities
- Encouraging drawing and scribbling
- Pointing to words while reading books
- Pointing out words and sentences in objects and signs
Parents can take the following steps to make sure that potential speech impediments are identified early on.
- Discussing concerns with physicians
- Asking for hearing, vision, and speech screenings from doctors
- Requesting special education assessments from school officials
- Requesting a referral to a speech-language pathologist, audiologist, or other specialist
When a child is engaged in speech therapy, speech-language pathologists will typically establish collaborative relationships with families, sharing information and encouraging parents to participate in therapy decisions and practices.
SLPs will work with patients and their families to set goals for therapy outcomes. In addition to therapy sessions, they may develop activities and exercises for families to work on at home. It is important that caregivers are encouraging and patient with children during therapy.
Resources for Parents on How to Fix a Speech Impediment
The following resources provide additional information on treatment options for speech disorders.
Speech, Language, and Swallowing Disorders Groups: Listing of self-help groups from ASHA
ProFind: Search tool for finding certified SLPs and audiologists from ASHA
Baby’s Hearing and Communication Development Checklist: Listing of milestones that children should meet by certain ages from the NIDCD
If identified during childhood, speech disorders can be corrected efficiently, giving children greater communication opportunities. If left untreated, speech impediments can cause a variety of problems in adulthood, and may be more difficult to diagnose and treat.
Parents, teachers, doctors, speech and language professionals, and other concerned parties all have unique responsibilities in recognizing and treating speech disorders. Through professional therapy, family engagement, positive encouragement and a strong support network, individuals with speech impediments can overcome their challenges and develop essential communication skills.
Additional Sources
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, Speech Sound Disorders
Identify the Signs, Signs of Speech and Language Disorders
Intermountain Healthcare, Phonological Disorders
MedlinePlus, Speech disorders – children
National Institutes of Health, National Institutes on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, “Quick Statistics About Voice, Speech, Language”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jan 26, 2024 · A speech impediment describes speaking difficulties, such as stuttering and child apraxia. Learn how therapy, games, and guided treatment can help.
Aug 15, 2024 · What are treatments for speech impairments? Treatment varies depending on your situation. For example, speech therapy is a common treatment for many speech impairments (speech disorders). If you have a voice disorder that affects your speech, your provider may refer you to specialists for voice therapy. Can you fix a speech impairment?
Oct 3, 2019 · Adult speech impairments involve difficulty with verbal communication, including slurred, stuttered, rapid, and slowed speech. Sudden unusual vocal symptoms require prompt medical attention.
Feb 8, 2023 · The type of treatment will typically depend on the severity of the speech disorder and its underlying cause. Treatment options can include: speech therapy exercises that focus on building ...
Jul 27, 2024 · When it comes to treatment options for speech impediments, early intervention is crucial for improving outcomes. Speech therapy, which involves working with a trained professional to practice and refine communication skills, is often recommended.
Mar 23, 2024 · Speech disorders can affect adults and children. Early treatment can correct these conditions. One of the most commonly experienced speech disorders is stuttering. Other speech disorders...
Jun 9, 2022 · Treatment typically includes training to compensate for deficiencies; patient and family education; at-home exercises; or neurological rehabilitation to address impairments due to medical conditions, illnesses or injury. Treatment options are extensive and not limited by age. Children and adults can experience the benefits of treatment.
Dec 8, 2024 · Although it may not seem like it—particularly if you have been dealing with this problem for years—you may be able to get rid of or improve your speech impediment with a few speech-training practices and some major confidence-boosters.
May 2, 2024 · Many children have difficulties with speech, and with the right pediatric speech therapist in Chicago, your child can learn to overcome their impediment. This blog post will define a speech impediment, discuss some of the most common types and causes, and provide information on treatment options.
Dec 8, 2020 · Speech impediments, or speech disorders, can lead to feelings of insecurity and frustration. They can also cause worry for family members and friends who don’t know how to help their loved ones express themselves. Fortunately, there are a number of ways that speech disorders can be treated, and in many cases, cured.