The Study Blog :
5 examples of thesis statements about racism for your next paper.
By Evans Apr 28 2021
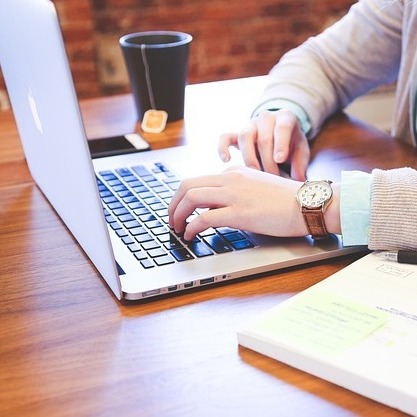
Racism is a hot topic worldwide. It is one of the topics that never lack an audience. As expected, racism is also one of the most loved topics by teachers and even students. Therefore, it is not a surprise to be told to write an essay or a research paper on racism. You need to come up with several things within an incredible paper on racism, the most important one being a thesis statement. The term thesis statement sends shivers down the spine of many students. Most do not understand its importance or how to come up with a good thesis statement. Lucky for you, you have come to the right place. Here, you will learn all about thesis statement and get to sample a few racist thesis statements.

Are tight deadlines, clashing assignments, and unclear tasks giving you sleepless nights?
Do not panic, hire a professional essay writer today.
Tips to writing a strong racism thesis statement
Keep it short.
A thesis statement is supposed to appear in the first paragraph of your essay. However, this does not mean that it should be the entire paragraph! A strong thesis statement should be one sentence (not an annoyingly long sentence), usually placed as the last sentence in the first paragraph.
Have a stand
A thesis statement should show what you aim to do with your paper. It should show that you are aware of what you are talking about. The thesis statement prepares the reader for what he or she is about to read. A wrong thesis statement will leave the reader of your paper unsure about your topic choice and your arguments.
Answer your research question
If you have been tasked with writing a research paper on why the Black Lives Matter movement has successfully dealt with racism, do not write a thesis statement giving the movement's history. Your thesis statement should respond to the research question, not any story you feel like telling. Additionally, the thesis statement is the summary of your sand and answer to the question at hand.
Express the main idea
A confused thesis statement expresses too many ideas while a strong, suitable one expresses the main idea. The thesis statement should tell the reader what your paper is all about. It should not leave the reader confused about whether you are talking about one thing or the other.
Earn Good Grades Without Breaking a Sweat
✔ We've helped over 1000 students earn better grades since 2017. ✔ 98% of our customers are happy with our service

Thesis Statements About Racism Samples
Racism in workplace thesis statement examples.
Racism is so rampant in the workplace. Thousands face discrimination daily in their workplaces. While this is definitely bad news, it gives us more data to choose from when working on an essay or research paper on racism in the workplace. Here are a few examples of thesis statements about racism in the workplace:
1. Despite being in the The 21st century, racial discrimination is still rampant in the workplace. The efforts made by governments and world organizations have not helped to do away with this discrimination completely.
2. Even with the unity that comes with digitalism, colour remains the one aspect of life that has continually caused a rift in this life. A lot of efforts have turned futile in the war against racism. The workplace is no exception. It is infiltrated with racial ideologies that remain within man's scope despite the professionalism within the workplace.
3. Systemic racism is no new concept. It remains the favoured term with the tongues of many after food and rent. This is an indicator of how rooted the world is when it comes to the issue of racism. The now world has been configured to recognize racial differences and be blind to human similarity. Organizations have been established upon this social construct, and more often than it has led them into a ditch of failure. The loot that comes with racism is of great magnitude to bear.
Thesis statement about Racism in schools
Many academic institutions have been recognized for producing students who have passed with distinctions. Unfortunately, behind these overwhelming results lies a trail of many students who have suffered racism and have missed the honors board because of the color differences. Let's look at some of the examples of thesis statements on racism in schools:
1. Merit should be the S.I unit upon which humanity is graded. Unfortunately, this is not the case, especially in schools, for the new merit score is the person's color. Many have found their way to the honour's board not because of merit but because they of the same color affiliation as the teacher.
2. Enlightenment and civilization have found their way to the world through one important institution called schools. We owe that to it. Unfortunately, even with the height to which the world has reached civilization and enlightenment, one area has been left out and remains unaddressed- the world view of color. Despite the light and glamour, we see globally, one predominant view is called race. We continue to paint the world based on human color, even in schools.
3. Bullying falls among the vices that have dire consequences to the victim. One of the spheres to which bullying exists is the sphere of color and race within the context of schools. Many student's confidence and esteem have been shuttered only because they are black or white. Many have receded to depression because they feel unwanted in the schools. One of the prominent times within American History is the Jim Crow Era, where racial segregation in schools within North Carolina was rampant. We saw schools have a section for white students and a separate section for black students within this era. The prevailing flag was black and white, and racism was the order of the day.
Final Thought
Coming up with a thesis statement does not have to difficult. No, not at all. Evaluate the topic or question and express yourself through the thesis statement from your stance or the answer. Mastering this one key in writing exams or assignments is one of the keys to scaling up the ladder of lucrative grades. However, practice is a discipline that will see you become a pro in writing a prolific strong, and catchy thesis statement. Henceforth, regard yourself as a pro, regard yourself as the best in thesis statement writing. If you are still having trouble with coming up with an excellent thesis statement, do not beat yourself up because of it. Paper per hour has the best writers who can help you with all your racism thesis statement needs.
Popular services
The little secret why your friends are earning better grades.
Hire an Expert from our write my essay service and start earning good grades.
Can Someone Write My Paper for Me Online? Yes, We Can!
Research topics
Essay Topics
Popular articles
Six Proven ways to cheat Turnitin with Infographic
Understanding Philosophy of Nursing: Complete Guide With Examples
50+ Collection of the Most Controversial Argumentative Essay Topics
50+ Economics research Topics and Topic Ideas for dissertation
20+ Interesting Sociology research topics and Ideas for Your Next Project
RAISE YOUR HAND IF YOU ARE TIRED OF WRITING COLLEGE PAPERS!
Hire a professional academic writer today.
Each paper you order from us is of IMPECCABLE QUALITY and PLAGIARISM FREE
Use code PPH10 to get 10% discount. Terms and condition apply.

Ready to hire a professional essay writer?
Each paper you receive from us is plagiarism-free and will fetch you a good grade. We are proud to have helped 10,000+ students achieve their academic dreams. Enjoy our services by placing your order today.

Write my paper
Do my assignment
Essay writing help
Research paper help
College homework help
Essay writing guide
College admission essay
Writing a research paper
Paper format for writing
Terms & conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Policy
Money-Back Guarantee
Our services

Copyright © 2017 Paper Per Hour. All rights reserved.
354 Racism Essay Titles, Thesis Statement Examples, & More
🔝 top-10 racism essay topics, 🏆 best racism topic ideas & essay examples, ✍️ thesis statement about racism: best examples, 🥇 most interesting racism topics to write about, 🔥 hottest titles for racism essays, 🎓 simple & easy racism essay titles, ⚡ shocking essay topics on racism, 👍 good essay topics on racism, 💡 interesting essay titles about racism, ❓ racism questions for essay.
- 🔖 Secrets of Powerful Racism Essay
Looking for powerful racism essay topics? You will find them here! This list contains a great variety of titles for racism-themed papers. We’ve also included useful tips and plenty of racism essay examples to help you write an outstanding paper.
- Racism in “The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn” by Mark Twain
- Racism in The Paper Menagerie Essay
- The Challenges of Racism Influential for the Life of Frederick Douglass and Barack Obama
- Racism in Music: “(What Did I Do to Be So) Black and Blue”
- Imperialism and Racism in Joseph Conrad’s Heart of Darkness
- Racism in the “Dutchman” by Amiri Baraka
- Issue of Racism in Healthcare
- The Problem of Racism in Brazilian Football
- Nikki Giovanni: Challenging Racism and Patriarchy
- Contrast Between Tituba and John Indian and Countering Racism
- Racism and Motherhood Themes in Grimke’s “Rachel” In addition, her mother kept the cause of the deaths of Rachel’s father and brother secret. In essence, the play Rachel is educative and addresses some of the challenges people face in society.
- Rasism in “No Telephone to Heaven” by Michelle Cliff This complexity comes even more difficult when the topic of race and identity is involved in literature.”No Telephone to Heaven” by Michelle Cliff is the piece of literature dealing with this topic, and the present […]
- Racism in “The Black Table Is Still There” by Graham The black table, as he calls it, is a table, that was and still is, present in his school’s cafeteria, that accommodated the black students only depicting no more than racism in schools.
- “A Genealogy of Modern Racism” by C. West As noted by West, the change in the role of science was key to the consequent promotion of the Western norms of beauty and civility.
- Racial Discrimination in “A Raisin in the Sun” Racial discrimination is the main theme of the book, strongly reflecting the situation that prevailed during the 1950s in the United States, a time when the story’s Younger family lived in Chicago’s South Side ghetto.
- Racism and Discrimination as Social Constructs This is because the concept of race has a negative connotation in the society. For example in some societies, especially the western society; the concept of race implies un-fair treatment and discrimination of a particular […]
- Racial Discrimination in Dormitory Discrimination is considered to be behavior that restricts the rights and freedoms of the individual. Therefore, it is essential to investigate discrimination in dormitories and propose solutions to this problem, such as disseminating knowledge about […]
- Racism: US v. The Amistad and Dred Scott v. Sandford In legal terms, the key difference between the two was that the Africans from Amistad were freeborn and enslaved in violation of the international agreements, while Dred Scott, despite his sojourn in Illinois, was born […]
- The Problem of Racism and Injustice in To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee In the novel, Harper Lee demonstrates her vision of the question of the social inequality with references to the problem of racism in the society based on prejudice and absence of actual principles of tolerance […]
- Racial Discrimination Effects in Coming of Age in Mississippi by Anne Moody The vivid description of events from the beginning gives the reader a clear picture of a girl who was born in problems and in spite of her intelligence she always became a victim of circumstances.
- Racism in Play “Othello” by William Shakespeare Since Othello is dark-skinned, the society is against his marriage to the daughter of the senator of Venice. In summary, the play Othello is captivating and presents racism as it was.
- Root Causes and Solutions to Racism Media is meant to eradicate racism and maintain unity among people but the case is different in some situations. Also, it is vital to make children understand nothing is amusing in the use of stereotypes […]
- Gonzalez v. Abercrombie & Fitch Discrimination Racism Lawsuit: An Analysis The case was filed in June 2003, and the claim was that this company has grossly violated the rights of the citizens as provided for in the constitution of the country.
- Racism in Ralph Ellison’s “Battle Royal” The main focus of the story is the problem of racism, particularly to African-American people in the United States. In terms of other issues that “Battle Royal” demonstrates and that are further developed in the […]
- Maya Angelou: Racism and Segregation in “I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings” An example is that, as she fails to recite her poem in church, she notes that her dress is probably a handout from a white woman.
- Systemic Racism in Education Theoretical perspectives suggest that this is due in part to the ways in which racism operates within educational institutions, including biased testing practices and the overrepresentation of students of color in disciplinary actions.
- Racism and Sexism as a Threat Women suffer from sexism, people of color are affected by racism, and women of color are victims of both phenomena. Prejudices spread in families, communities, and are difficult to break down as they become part […]
- Racism and Gender in Beyoncé’s Lemonade The album Lemonade by an American singer Beyonce is one of the brightest examples when an artist portrays the elements of her culture in her music. Along with music videos, the album features a number […]
- Racism in Shakespeare’s “Othello” and Dick’s “Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?” The formalist analysis of Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep repeats the same mistake, as it focuses on the plot devices and tropes presented in the story.
- Society Moral Standards: Racism and Its Harmful Effects The belief in the superiority of one race over the other is normally used to justify the unequal treatment of different races.
- Is Troy Maxson (Wilson’s Fences) a Victim of Racism? As a black American, Troy’s childhood experiences have been passed on to his children, making him a victim of an oppressive culture. Therefore, this makes Troy a victim of racism and culture, contributing to his […]
- Colonialism and Racism in Foe by J. M. Coetzee and Small Island by Andrea Levy This paper will try to expound on the relevance of real-life politics, of colonialism and racism, with regards to two popular works of fiction that used as themes or backdrop colonialism and racism.
- English Literature Impact on Racism Among Africans Examining the topic of race and racism in language has not been a grave issue in the recent years, particularly because most of the discourse experts are whites.
- Empathy and Racism in Stockett’s The Help and Li’s To Kill a Mockingbird To start with, the first approach to racism and promoting empathy is to confront prevalent discrimination and racism, which was often shown in The Help. Another solution to racism and the possibility of promoting empathy […]
- Anti-Racism in Shakespeare’s Othello For Shakespeare, Brabantio’s views are representative of the racial prejudice of the society in general, rather than of his personal feelings towards the protagonist. On the other hand, Othello’s story is cohesive and believable; he […]
- Racism in the United States of the 21st Century The purpose of this paper is to present convincing reasons to support the argument that racial discrimination is still common in the United States today.
- Racial Discrimination at the Workplace The main change that is discussed in this essay is the introduction of legislation that will see the creation of a special authority that is aimed at guaranteeing the freedom of all workers at the […]
- Racial Discrimination and Color Blindness Of the three ideologies, racial harmony is considered the most appropriate for coping with problems of racism and racial injustice due to various reasons.
- Racism and Prejudice: “Gone With the Wind“ and “The Help” The current paper will discuss the issues of racism and prejudice in two brilliant pieces of art: Kathryn Stockett’s novel “The Help” and the movie “Gone with the Wind” directed by Victor Fleming.
- Racial Stereotypes in Movie Industry The character of Tom Hanson in the movie thought he was not racist but at a subconscious level he too was affected by the racial stereotypes just as many of us are unaware of how […]
- The Issue of Racism: One of Social Evils In conclusion, racism is among the social evils that have been so engraved in society to the extent of being considered a healthy and natural existence.
- Racial Discrimination in American Literature In this way, the author denies the difference between people of color and whites and, therefore, the concept of racism in general.
- Summary of the Issue About Racism In schools in the United States, with the advent of the new president, a critical racial theory began to be taught.
- The Reflection of Twain’s Views on Racism in Huck Finn One of the most problematic aspects in the novel that potentially can make readers think that Twain’s attitude toward slavery and racism is not laudable is the excessive usage of the n-word by all sorts […]
- Racism in Movies: Stereotypes and Prejudices I believe that, despite the legal manifestation of validity and equality of the law, there are still some restrictions that hinge the normal way of living of national minorities and Afro-Americans in particular.
- Scientific Racism: the Eugenics of Social Darwinism I think that the development of Scientific Racism and further Eugenics became the result of people’s attempts to justify their unethical behavior toward other individuals and to support their material goals to develop slavery, and […]
- Comparison of Ethnicity and Racism in “Country Lovers” and “The Welcome Table” In both cases, the texts have devoted their concerns to the plight of a black female who is deposed off her meaning within the realms of the society.
- America: Racism, Terrorism, and Ethno-Culturalism The myth of the frontier is one of the strongest and long-lived myths of America that animates the imagination of the Americans even to this day.
- Racism Themes in Twain, Washington, and DuBois Works It is evident that Huck and his kids did not view Jim as a person in the first few chapters of the book.
- Racial Discrimination in the US Criminal Justice System: Hickey’s Article The purpose of this article is to expose the realities of racism toward African Americans. Following the analysis of the article, I feel more at ease clinging to previous views and understandings, whether they are […]
Creating the best thesis statement for your research or essay can be hard work. If you need some examples, look through the list of thesis statements on racism together with corresponding topics:
- Topic: Ethnic cuisine meets racism: where is the hate coming from? Thesis: Western culture often finds ethnic dishes inferior to Western ones, which spikes a new debate about racism.
- Topic: Racism in sports: how Jackie Robinson changed baseball. Thesis: Jackie Robinson became the first baseball player of color who got into Major League Baseball, breaking the racist baseball rules forever.
- Topic: Why Critical Race Theory is integral to the school curriculum. Thesis: Despite the significant debate, Critical Race Theory should be presented in schools and colleges to teach students diverse perspectives.
- Topic: Racial barriers in Hollywood: intersectionality and the Oscars. Thesis: Hollywood should work better on inclusivity to increase the number of women of color nominated for Oscars, which is currently at less than two percent.
- Topic: Extreme cases of racism labeled as a mental disorder. Thesis: Showing signs of extreme hate towards other races should be seen as a mental illness and treated accordingly.
- Topic: Social media hate crime: what to do with racist comments across media platforms? Thesis: The administration of the major social media platforms has started taking measures against racism by using AI to warn against hate speech.
- Discussion: The Film Green Book and Racism The problem of inequality between black and white people, racism, and the injustice of dividing people into categories has been an important issue of social justice.
- Racial Discrimination: Diann “Sally” Case They would swim in the canal by the family home or play a game they called “Handy,” wherein they would split up into two teams, one team at the front of the house, the other […]
- Racism as a Dragging Factor for Children’s Education, Health and General Welfare The future of accommodating equality for all students in the US is uncertain due to the statistics of teaching staff in the country.
- Systematic Racism and Open Bias Against the Black Population The relevance of this research topic is due to the fact that the problems of race relations and systemic discrimination against the black population in the United States is a complicated topic.
- Roy’s and Hooks’s Ideologies About Racism The cross-examination of the main ideas in Hooks and Roy’s texts simplify the understanding of the terminology and the practice of racism in the community today.
- Systemic Racism in Education and Society Sharma examines the theme of racism in the state of Hawaii, a state that is home to people from different geographical backgrounds.
- Systemic Racism in Harris’ The Other Black Girl and Baraka’s Dutchman One unique thing in the novel The Other Black Girl is that the author expresses systemic racism through dark humor and a real chat about the topic.
- Wrongful Convictions, Racism, and Injustice in Law Enforcement The case of Ricky Jackson and the concepts featured in Cretton’s film are similar because, in both instances, black men face losing their lives because of racism, injustice, inequality, and discrimination.
- Criminal Justice Reform and Racism in America Millions of Americans, especially the young and marginalized communities, had their lives wrecked as a consequence of the way the legal system and the drug trade have been exploited as a form of social control, […]
- Training to Prevent Racial Discrimination in Education The findings of the article identify “the multidimensional, quotidian, and impactful nature of racial discrimination in the lives of Black adolescents in the U.S”.
- Effects of Racism on Mental Health Article by Kwate and Goodman In terms of alignment, the problem and the purpose are thematically related to the theory of racism as a barrier to health and the correlational design, and the implied research questions/hypotheses also cover racism and […]
- Racism: De Brahm’s Map and the Casta Paintings However, De Brahm’s map is one of the most striking pieces of evidence of the conquest of space and the entrenchment of the idea of land and people as titular property.
- Racism and Inequality in Society The idea of race as a social construct is examined in the first episode of the documentary series “The Power of an Illusion”.
- Anti-Racism: Marginalization and Exclusion in Healthcare This essay examines the course’s impact and the concepts of marginalization and exclusion in healthcare. Marginalization is a concept that has profoundly influenced the understanding of race and racism in healthcare.
- The Issue of Racism in the United States The entire history of the United States is permeated with the evolution of the ideas of racism. Turning to history, we can see that the U.S.moved from slavery to using the Black population to solve […]
- History of Racial Discrimination in Haiti and America The choice of topic, racial discrimination in Haiti and America, was influenced by beliefs, values, and assumptions emphasizing the importance of equality and justice for all races.
- Racism and History of Discrimination As a result, advocacy should be aimed at creating new models in criminal justice that will ensure the protection of all minority groups and due process.
- Race, Racism, and Dangers of Race Thinking While it is true that some forms of race thinking can be used to justify and perpetuate racism, it is not necessarily the case that all forms of race thinking are inherently racist. Race thinking […]
- Racism in the US: Settler Imperialism They prove that colonial imperialism is a structure, not a contextual phenomenon and that, as such, it propagates the marginalization of native people.
- Why Empathy in Racism Should Be Avoided Empathy is the capacity to comprehend and experience the emotions and ideas of others. Moreover, empathic emotions are essential to social and interpersonal life since they allow individuals to adapt their cognitive processes to their […]
- Racial Discrimination in High Education This peer-reviewed scholar article was found in the JSTOR database through entering key words “race affirmative action” and marking the publication period between 2017 and 2022.
- Social Sciences: Racism Through Different Lenses A thorough analysis of diversity adds value to social interactions by informing human behavior through a deeper understanding of racism and its impacts on society. Using the humanities lens leads to a better understanding of […]
- Racism and Its Impact on Populations and Society The ignorance of many individuals about other people’s cultures and ethnicities is one of the causes of racism. One can examine the various components of society and how they relate to the issue of racism […]
- Institutionalized Racism and Individualistic Racism Excellent examples of individualistic racism include the belief in white supremacy, racial jokes, employment discrimination, and personal prejudices against black people. Overall, institutionalized and individualistic racism is a perversive issue that affects racial relations in […]
- Community Engagement with Racism To enhance the population’s degree of involvement in racism, the study calls for collaboration; this can be seen as a community effort to foster a sense of teamwork.
- Racism Detection with Implicit Association Test Racial bias is deeply rooted in human society and propelled by norms and stereotypic ideologies that lead to implicit bias and the unfair treatment of minority groups.
- Identity and Belonging: Racism and Ethnicity In the documentary Afro Germany – Being Black and German, several individuals share their stories of feeling mistreated and excluded because of their skin color.
- Policies to Eliminate Racial Disparities and Discrimination The solution to exclusion is to build social inclusion in the classroom and within the school by encouraging peer acceptance, cross-group friendships, and built-in prevention.
- Racial Discrimination and Justice in Education An example is the complaint of the parents of one of the black students that, during the passage of civilizations, the Greeks, Romans, and Incas were discussed in the lessons, but nothing was said about […]
- Racism in the Healthcare Sector In 2020, the cases and instances of racism in healthcare rose by 16% from 2018; there were notable instances of racism in various spheres of health. 9% of blacks have been protected from discrimination and […]
- Racism in Healthcare and Education The mission should emphasize that it promotes diversity and equality of all students and seeks to eliminate racial bias. It is necessary to modify the mission to include the concept of inclusiveness and equality.
- Institutional Racism in the Workplace Despite countless efforts to offer African-Americans the same rights and opportunities as Whites, the situation cannot be resolved due to the emergence of new factors and challenges.
- Racism in Education in the United States Such racial disparities in the educational workforce confirm the problem of structural racism and barrier to implementing diversity in higher medical education. Structural racism has a long history and continues to affect the growth of […]
- Rhetoric in Obama’s 2008 Speech on Racism When the audience became excited, it was Obama’s responsibility to convey his message in a more accessible form. To conclude, Obama’s speech in 2008 facilitated his election as the first African American President in history.
- How to Talk to Children About Racism The text begins by referring to recent events that were related to race-based discrimination and hatred, such as the murder of George Floyd and the protests dedicated to the matter.
- Care for Real: Racism and Food Insecurity Care for Real relies on the generosity of residents, donation campaigns, and business owners to collect and deliver these supplies. The research article discusses some of the factors that contribute to the creation of racism […]
- Racism Towards Just and Holistic Health Therefore, the critical content of the event was to determine the steps covered so far in the fight for racial equality in the provision of care and what can be done to improve the status […]
- Systemic Racism and Discrimination Thus, exploring the concept of race from a sociological perspective emphasizes the initial aspect of inequality in the foundation of the concept and provides valuable insight into the reasons of racial discrimination in modern society.
- The Racism Problem and Its Relevance The images demonstrate how deeply racism is rooted in our society and the role the media plays in spreading and combating racism.
- Aspects of Socio-Economic Sides of Racism And the answer is given in Dorothy Brown’s article for CNN “Whites who escape the attention of the police benefit because of slavery’s long reach”.. This shows that the problem of racism is actual in […]
Looking for the most discussed topics about racism? Here are the top 5 ideas:
- Reasons to introduce zero-tolerance policy against police violence towards minorities. Racism causes too many cases of police brutality. Do you think it can be stopped by implementing zero-tolerance rules? Share your thoughts.
- India as the most racist country in the world. Indians show racism towards their own people due to their preference for lighter skin. This phenomenon is called colorism, which is discrimination based on skin tone. Discuss this issue from the perspective of modern inclusivity movements.
- The results of racism against the Aboriginal population of Australia. Racial discrimination has become an essential aspect of the Australian Aboriginals’ health and lives. Discuss this issue and include reliable sources.
- Cannes guard: racism on the red carpet or following the rules? The action of the red-carpet security guard at Cannes has sparked lots of criticism. The guard appeared to have mistreated only the guests of color. What are your thoughts on it?
- The progress of the fight against racism since George Floyd’s murder. The crisis seems to have passed, but the progress is slow. The fight against racism in the US is still ongoing. Analyze the current trends and news to write an essay about this issue.
- Tackling Racism in the Workplace It means that reporting racism to HR does not have the expected positive effect on workplace relations, and employees may not feel secure to notify HR about the incidences of racism.
- Issue of Racism Around the World One of the instances of racism around the world is the manifestations of violence against indigenous women, which threatens the safety of this vulnerable group and should be mitigated.
- The “Racism and Discrimination” Documentary The documentary “Racism and Discrimination” is about an anti-racist teacher Jane Elliot who attempts to show the white people the feeling of discrimination. The central argument of the documentary is diversity training to seize the […]
- Abortion-Related Racial Discrimination in the US In spite of being a numerical minority, Black women in the U.S.resort to abortion services rather often compared to the White population.
- Social Problems Surrounding Racism, Prejudice and Discrimination This kind of discrimination makes the students lose their self-esteem and the traumas experienced affects the mental health of these students in the long term.
- Racism and Intolerance: The 1921 Tulsa Race Massacre The 1921 Tulsa Race Massacre: Crafting a Legacy by Messer elaborates on the legacy of the event and its repercussions and offers a profound analysis of the issue, which strengthened my focus of the research.
- The Unethical Practice of Racism in a Doctor’s Case The involvement of Barrett in the protest is both unethical for the university’s image and immoral for the community. However, the school would likely face tougher court fines and a direct order to reinstate Barrett’s […]
- The Problem of Racism in America One explanation of racism by feminist thinkers is that racism is a manifestation of the agency and power of people of a particular racial identity over others.
- Racism: “The Sum of Us” Article by McGhee The economic analysis and sociological findings in America have drawn a detailed picture of the cost of racism in America and how to overcome it together.
- Contemporary Sociological Theories and American Racism The central intention of this theory paper is to apply modern theoretical concepts from the humanities discipline of sociology to the topic of racism in the United States.
- A Cause-and-Effect Analysis of Racism and Discrimination As a result, it is vital to conduct a cause-and-effect analysis to determine the key immediate and hidden causes of racism to be able to address them in a proper manner.
- Cause and Effect of Racial Discrimination Irrespective of massive efforts to emphasize the role of diversity and equality in society, it is still impossible to state that the United States is free from racial discrimination.
- Institutional Racism Through the Lenses of Housing Policy While not being allowed to buy property because of the racial covenants, the discriminated people had to house in other areas.
- Role of Racism in Contemporary US Public Opinion This source is useful because it defines racism, describes its forms, and presents the survey results about the prevalence of five types of racial bias.
- The Mutation of Racism into New Subtle Forms The trend reflects the ability of racism to respond to the rising sensitivity of the people and the widespread rejection of prejudice.
- Racism: Healthcare Crisis and the Nurses Role The diminished admittance to mind is because of the impacts of fundamental bigotry, going from doubt of the medical care framework to coordinate racial segregation by medical care suppliers.
- Origins of Racial Discrimination Despite such limitations as statistical data being left out, I will use this article to support the historical evaluation of racism in the United States and add ineffective policing to the origins of racism.
- Historical Racism in South Africa and the US One of the major differences between the US and South Africa is the fact that in the case of the former, an African American minority was brought to the continent to serve the White majority.
- Minstrels’ Influence on the Spread of Racism The negative caricatures and disturbing artifacts developed to portray Black people within the museum were crucial in raising awareness on the existence of racism.
- How Parents of Color Transcend Nightmare of Racism Even after President Abraham Lincoln outlawed enslavement and won the American Civil War in 1965, prejudice toward black people remained engrained in both the northern and southern cultural structures of the United States.
- A Problem of Racial Discrimination in the Modern World This minor case suggests the greater problem that is unjustly treating people in the context of the criminal justice system. In the book, Stevenson writes about groups of people who are vulnerable to being victimized […]
- Issue of Institutional Racism Systemic and structural racisms are a form of prejudice that is prevalent and deeply ingrained in structures, legislation, documented or unpublished guidelines, and entrenched customs and rituals.
- Racism in America Today: Problems of Today Even though racism and practices of racial discrimination had been banned in the 1960s after the mass protests and the changes to the laws that banned racial discrimination institutionally.
- Evidence of Existence of Modern Racism It would be wrong to claim that currently, the prevalence and extent of manifestations of racism are at the same level as in the middle of the last century.
- Culture Play in Prejudices, Stereotyping, and Racism However, cognitive and social aspects are significant dimensions that determine in-group members and the constituents of a threat in a global religious view hence the relationship between religion and prejudices.
- Latin-African Philosophical Wars on Racism in US Hooker juxtaposition Vasconcelos’ ‘Cosmic Race’ theory to Douglass’s account of ethnicity-based segregation in the U.S.as a way of showing the similarities between the racial versions of the two Americas.
- Confronting Stereotypes, Racism and Microaggression Stereotypes are established thought forms rooted in the minds of particular groups of people, in the social environment, and in the perception of other nations.
- Racial Discrimination in Dallas-Fort Worth Region Thus, there is a historical imbalance in the political representation of racial minorities in the Dallas-Fort Worth area. Nonetheless, the Black population is reported to thrive best in the suburban areas of DFW, where this […]
- Healthcare Call to Action: Racism in Medicine To start the fight, it is necessary to identify the main manifestations of discrimination in health care, the reasons for the emergence of the location of social superiority and discrimination, and the scale.
- White Counselors Broaching Race and Racism Study The essence of the verbal behavior of the consultants is the ways of their reaction in the process of interaction with the client – the basic skills of counseling, accessibly including race and racism topics.
- British Colonial Racism for Aboriginal Australians Precisely this colonial racism and genocide can be considered to be the cruelest in the history of the world and may have influenced the ideas and plans of Adolf Hitler, who got inspired by the […]
- The Black People: Sexuality and Racial Discrimination Interview Review Nevertheless, the author does not provide practical solutions to the issue of racism and discrimination of the LGBTQ community. The purpose of this interview is to demonstrate the author’s attitude to the sexuality of black […]
- Racial Discrimination Through the Cosmetics Industry The variety of preconceptions such as the hypersexuality of black women and the perception of their beauty as an unideal version of whites’ one also indicates racism.
- Racism Evolution: Experience of African Diaspora As a result, distinct foundations fostered the necessity of inequality to establish effectiveness of inferiority and superiority complexes. To determine the effect of slavery and racism to modern society.
- Racial Discrimination and Residential Segregation Despite the end of segregation policies and the passing of Fair Housing laws and numerous subsidy measures, people of color cannot access wealthy areas, facing unofficial exclusion into poorer parts of the city.
- Significance of Perceived Racism:Ethnic Group Disparities in Health Coates points out that a sign of the gulf between blacks and whites manifests in the context where there is expectation for him to enlighten his opinions while in mind the essential indication lies in […]
- Racism as Origin of Enslavement Some ideas are mentioned in the video, for example, the enslavement of Black people and their children. The most shocking fact mentioned by the speaker of the video is that children of enslaved people were […]
- Colorblind Racism and Its Minimization Colorblind racism is a practice that people use to defend themselves against accusations of racism and deny the significance of the problem.
- The Bill H.R.666 Anti-Racism in Public Health Act of 2021 That is why the given paper will identify a current and health-related bill and comment on it. This information demonstrates that it is not reasonable to oppose passing the bill under consideration.
- How the Prison Industrial Complex Perpetuate Racism In the United States, the system is a normalization of various dynamics, such as historical, cultural, and interpersonal, that routinely benefit the whites while causing negative impacts for the people of color.
- Battling Racism in the Modern World Racism and racial discrimination undermine the foundations of the dignity of an individual, as they aim to divide the human family, to which all peoples and people belong, into different categories, marking some of them […]
- Indian Youth Against Racism: Photo Analysis The main cause of racism within American societies is the high superiority complex possessed by the white individuals living with the Asian American in the society.
- Racism: Do We Need More Stringent Laws? The Civil Rights Division of the Department of Justice is worried that national origin discrimination in the U.S.may go undetected because victims of prejudice are unaware of their legal rights or are hesitant to complain […]
- Problem of Racism in Schools Overview Racism should be discouraged by all means and the government should do its best to educate citizens on the importance of unity and the disadvantages of racism.
- US Immigration Policy and Its Correlation to Structural Racism That may create breaches in the immigration policy and cause social instability that could endanger the status of immigrants and even negatively affect the lives of the nationals.
- Solving Racial Discrimination in the US: The Best Strategies The Hollywood representation of a black woman is often a magical hero who “is a virtuous black character who serves to better the lives of white people…and asks nothing for herself”.
- Popular Music at the Times of Racism and Segregation The following work will compare and contrast the compositions of Louis Armstrong and Scott Joplin and examine the impact of racism on popular music.
- Temporary Aid Program: Racism in Child Welfare The purpose of this paper is to analyze the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families program in the context of child welfare disparities.
- Western Scientific Approach as a Cause of Racism This paper will highlight the main methods of refuting the works of racist anthropologists and how they influenced the emergence of stereotypes about people of color.
- How Does Racism Affect Health? Many people of color experience internalized racism, which can lead to anxiety and depression that can be the cause of physical issues.
- Black as a Label: Racial Discrimination People are so used to identifying African Americans as black that they refuse to accept the possibility of the artificiality of labeling.
- The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) and Racial Discrimination The author argues that despite increasing the overall prosperity of the local communities, the policies and projects of the Tennessee Valley Authority did not address the well-being of the white population and Afro-American citizens equally.
- Flint Water Crisis: Environmental Racism and Racial Capitalism The Flint crisis is a result of the neoliberal approach of the local state as opposed to the typical factors of environmental injustice; a polluter or a reckless emitter cutting costs. The two main factors […]
- Cancer Alley and Environmental Racism One of the sources under study is valuable, as it examines the current situation of the coronavirus and the impact of pollution on human health.
- American Healthcare in the Context of Racism According to the researchers, the fundamental issue of racism in health care is the practitioners and public health representatives’ lack of desire to recognize the health specifics of racial and ethnic minorities, which results in […]
- Origins of Modern Racism and Ancient Slavery The diversity of African kingdoms and the empires were engaged in the slave trade for hundreds of years prior to the beginnings of the Atlantic slave trade. The working and living condition of slaves were […]
- What Stories Can Teach Us About Racism On top of this before the establishment of the school there was no public education for the Negro children and this made it more difficult for the children to access education just like the other […]
- Racism in Canadian Medical System The difference in the treatment of indigenous and non-indigenous individuals in Canada is a result of racism in the medical facility.
- Profit and Racism in the Prisons of the United States As an argument for the work of prisoners, the prison of Angola makes the argument that work is a way of rehabilitation for the prisoner.
- Rio Tinto: Case Study About Racism and Discrimination The repercussions of this situation for the preservation of cultural heritage may be considerable, as the expert community was denied an opportunity to research the artifacts.
- Critical Social Problems Research: Racism and Racial Domination According to his opinion, which is proven today by many examples including the attitude of the authorities, people of color are treated as if they are worthless and not destined to achieve success.
- The History of Racial Discrimination and Its Effects on the American Races The saddest part of it all is that our Indian American brothers are discussed in public and used as examples in a manner that makes it seem like they exist only as a mere caricature […]
- Racial Discrimination in the US Criminal Justice System This report argues that when one studies the proportion of blacks in the Cincinnati community and the number of times that they have been stopped for traffic violations, one finds that there is a large […]
- Policing in America: The Issue of Violence and Racism While the former proposition has various negative aspects to be considered, the latter appears to be the appropriate reaction to the challenges posed for the United States’ society in 2020.
- Institutional and Interpersonal Racism, White Privilege One should be aware of the fact that issues such as institutional and interpersonal racism, privilege, power, and bias are complex problems, which need a thorough analysis and consideration of all the facts.
- The Development of a Measure to Assess Symbolic Racism The originators of the concept applied it only to the African-American race, while other scientists engaged in researching and applying the construct of symbolic racism to other races and cultures.
- Racism and Tokenism in Bon Appetit: Leadership and Ethical Perspective Leadership is defined as a set of actions and beliefs of a manager who directs and controls the followers to achieve a common goal.
- From “Scientific” Racism to Local Histories of Lynching Both chapters serve as a premise to the following arguments in the book, arguing that White power is still dominant in the contemporary world, and give context to the broader scale of oppression worldwide.
- Subjective Assumptions and Medicine: Racism The given supposition demonstrates that Allen believed in the superiority of white southerners over Black Americans because the latter ones were made responsible for the deteriorated health of the former.
- Racism Experiences in the Workplace in the UK This research paper provides the background of racism in the UK, particularly in the area of employment. The UK struggles against racial discrimination and paves the way to equity and inclusion in the area of […]
- The History of Immigration to the United States and the Nature of Racism The development of the idea of race and ethnicity along with the idea of racial antagonism has two main stages in the history of the United States.
- Race and Racism in the USA: The Origins and the Future In conclusion, the author suggests that the possible solution to the problem of racial conflicts is the amalgamation of different races and ethnics.
- Racially Insensitive Name-Calling in Classroom Probably, the teacher had to initiate the lesson devoted to the topic of racial discrimination and to think over all the stages of the discussion, to organize it in a polite and friendly manner.
- Environmental Racism in the United States: Concept, Solution to the Problem With regards to this definition, a row of issues connected to social justice and the equality in the rights of people which is firmly established in the Constitution of the United States are to be […]
- Protecting George Wallace’s Organized Racism Instead of claiming that segregation was a necessary evil or that it benefited the minorities, he claimed that it is the only way to protect the freedom of the white people.
- How Can the World Unite to Fight Racism? One of the highly discussed topics in the modern world is the question of racism. It all leads to the idea that racism could be fought due to the improved educational system, where the teachers […]
- Racism in America and Its Literature In the first part of this stanza, Hughes articulates his view that when an African American is finally sitting at the table, others will recognize the beauty of African Americans.
- Race, Class and Gender. Racism on Practice The separation and the segregation on an individual or group is what is based on the grounds of racism, and this has been well illustrated in the book the Ethics of Living Jim Crow where […]
- Racism: Term Definition and History of Display of Racism Remarks It is no wonder that this form of discrimination is known to have caused the worst wars in the world and led to nations being formed together with all forms of legal codes.
- Institutional Discrimination, Prejudice and Racism Racism that is in the society today is not evident like that of the early 19th and 20th century which was characterized by among other things separation based on color of the skin, religious differences […]
- Racism in Contemporary North America
- Racial and Gender Discrimination in the Workplace and Housing
- “Bluest Eye” by Toni Morrison: Themes of Racism and Unequal Opportunity
- Racism Without Racists in Patriarchal Society
- The Problem of Racism in Canada
- Exploring and Comparing Racism and Ethnocentrism
- Racism Cannot Be Unlearned Through Education
- Facing Racism: A Short Story
- White Supremacy as an Extreme Racism Group
- American Racism: So Why Isn’t Obama White?
- Social Construction of Race and Racism
- Racism Issues: Looking and Stereotype
- Anti-Racism Policy Statement in Australian Schools
- Racism, Minorities and Majorities Analysis
- Racism and Ethnicity in Latin America
- Racial Discrimination in Song ‘Strange Fruit’
- Racism Effects on the Premier League Players
- Social Psychology: Racism in Jury Behaviour
- Appiah’s Ideas of Racism, Equality, and Justice
- Sexism, Racism, Ableism, Ageism, Classism
- Racism in Media: Positive and Negative Impact
- Racism: Once Overt, but Now Covert
- Racism: “Get Out” Film and “Screams on Screens” Article
- How Racism Makes Us Sick: Public Talk That Matters
- Environmental Racism and Indigenous Knowledge
- Racism in the “Do the Right Thing” Movie
- Islam and Racism: Malcolm X’s Letter From Mecca
- Racism vs. “Love Thy Neighbor as Thyself”
- Racism in Lesbians, Gays, Bisexuals, Transgenders
- Racism in Australian Football League Sporting Clubs
- Thomas Jefferson on Civil Rights, Slavery, Racism
- Racial Discrimination Forms Against Afro-Americas
- White Privilege and Racism in American Society
- Racism, Privilege and Stereotyping Concepts
- Racism in Rankine’s “Citizen” and Whitehead’s “The Underground Railroad”
- Racism in the United States: Before and After World War II
- Baldwin’s and Coates’ Anti-Racism Communication
- Racism as the Epitome of Moral Bankruptcy
- Racism in “The Invisible Man” by Ralph Ellison
- Racism in Trump’s and Clinton’s Campaigns
- Colin Powell and the Fight Against Structural Racism
- Racism in “Passing” and “Uncle Tom’s Children” Novels
- Racism in “To Kill Mocking Bird” by Harper Lee
- Racism Elimination and Sociological Strategies
- Racism History in No Name on the Street by Baldwin
- “Nigger” as a Racially Directed Slur
- Racism and Discrimination in Religion Context
- Racism: Theoretical Perspectives and Research Methods
- Racism in the Setting the Rising Sun Postcard
- Does Racism and Discrimination Still Exist Today?
- Jerrell Shofner’s Views on the Racial Discrimination
- Asian American Communities and Racism in the USA
- Racial Discrimination and Its Effects on Employees
- Racial Discrimination in Social Institutions
- King’s and Obama’s Views on Racism in America
- Racism in USA: Virginia Laws on Slavery
- Racism as a Reality of Modern American Society
- Racism Issue and Solutions
- Intersectionality and Gendered Racism
- Racism and Education in the United States
- Racism as a Case of Ignorance and Prejudice
- Racism and Segregation in American History
- Humanism, Racism, and Speciesism
- Racism in American Schools
- Racist America: Current Realities and Future Prospects
- Racism Against Native Americans
- Obama’s First Election and Racism
- Adolf Hitler: From Patriotism to Racism
- “Globalization and the Unleashing of New Racism: an Introduction” by Macedo and Gounari
- Problems of Environmental Racism
- How Obama’s First Election Has Been Affected by Racism?
- How Different Young Australians Experience Racism?
- Racial Discrimination in Organizations
- In Australia, Are Cultural Rights a Form of Racism?
- Racism and Ethnicity in United States
- ‘Animal Rights’ Activists and Racism
- The Racial Discrimination Among Employers
- Multicultural Psychology: Cultural Identity and Racism
- How Fake News Use Satire as a Medium to Address Issues on Racism?
- Young Australians and Racism
- Relationship Between Institutionalized Racism and Marxism
- Democratic Racism in Canada
- Social Construction of “Race” and “Racism” and Its Relationship to Democratic Racism in Canada
- Black or White Racism
- Racism in Family Therapy by Laszloffy and Hardy
- The Roma Problems and the Causes of Racism
- Racial Discrimination in the US
- The ‘Peopling’ Process of Australia Since 1788 With Influence of Racism
- Globalization and Racism
- Racism in Native Son
- The Issue of Racial Segregation in the United States
- Racism and Male Dominance in Education
- Comparison of Racism in the United States and South Africa
- English Racism During World Cup
- The Historical Roots of Racism in Australia
- Racism Is Not All About Individual Attitude
- Discrimination, Prejudice and Racism in the United States
- Racial or Ethnical Discrimination
- The Role of Racism in American Art During the 1930s and 1940s
- Promotion of Racism in US Through Sports
- Racism in U.S. Criminal Justice System
- Racism, Colonialism and the Emergence of Third World
- Why the Philosophy of King is More Effective in Fighting Racism than Malcolm’s?
- Racism and Discrimination: White Privilege
- Racism and Segregation in the United States
- The Root Cause of Racism and Ethnic Stratification in the US
- Racism in the USA
- Analysis on Religion, Racism and Family Conflicts
- The Concept of Racism
- The Theme of Liberation From Racism in Two Plays by August Wilson
- The Policy Status Quo to Prevent Racism in American Schools
- Racial Profiling: Discrimination the People of Color
- Racism as a Central Factor in Representing Asian American History
- Reducing Racism in the University of Alberta and University of York
- Achebe’s Views on Racism
- Racism in the American Nation
- The Civil Rights Movement: Ending Racial Discrimination and Segregation in America
- Institutionalized Racism and Sexism
- The Anatomy of Scientific Racism: Racialist Responses to Black Athletic Achievement
- The Problem of Global Racism in Modern World
- Racial Discrimination at the World Bank
- Australian Identities: Indigenous and Multicultural
- Racial Discrimination in America
- Institutionalized Racism From John Brown Raid to Jim Crow Laws
- Racism in America After the Civil War up to 1900
- Have You Experienced Racism in Korea?
- Racism in the “Crash”
- Contemporary Racism in Australia: the Experience of Aborigines
- Racism By Thomas Jackson
- Addressing the Racism in Society
- Racism in the Penitentiary
- Different Challenges of Racial Discrimination
- Slavery, Racism, and the Trans-Atlantic Slave Trade
- Why it is Safe to Say that Northrop’s Book Exposes the Roots of Racism in America
- How Has Racism Changed Throughout History, Starting From the Emancipation Proclamation to Today?
- Do Racism and Discrimination Still Exist Today?
- How Did Ideas of Black Stereotypes and Racism Become Embedded in American Culture?
- How Does Racism Affect the Way of a Caste Like System?
- What Connection Is Between Globalization and Racism?
- Why Do Exist Discrimination and Racism?
- How Do Educational Institutions Perpetuate Racism, Sexism, and Patriarchy?
- How Do Racism and Exclusion Shape the Social Geography of Race and Ethnicity?
- What Ways Does Cultural Racism Manifest Itself?
- How the Media Maintains Racism?
- Why Slavery and Racism Issues Still Affect America Today?
- How Racism and Ethnicity Affect the Sector of Education?
- How Has Racism Impacted Immigrant Families and Children?
- When Did Racism Begin?
- Racism: Why It’s Bad for Society and the Greater Health Issues It Creates?
- How Have Evolutionary Ideas Shaped Racism?
- Why Is Racism Bad for Society?
- What Effect Does Color-Blind Racism Have On Minorities in Society Today?
- How Does Sports Helped Diminish Racism?
- How Does Both Individual and Institutional Racism Impact Service Provision and the Experiences of People Receiving Services?
- Did Slavery Cause Racism?
- When You Think About Racism, What Do You Think About?
- What Does Racism Mean?
- Does Affirmative Action Solve Racism?
- Did Racism Precede Slavery?
- How Does Racism Affect Society?
- Does Racism Still Occur Today and Why People Can’t a Change?
- Between Compassion and Racism: How the Biopolitics of Neoliberal Welfare Turns Citizens Into Affective ‘Idiots’?
- Does Racism Play a Role in Health Inequities?
🔖 Secrets of a Powerful Racism Essay
Writing an essay on racism may seem easy at first. However, because racism is such a popular subject in social sciences, politics, and history, your piece needs to be truly powerful to receive a high mark. Here are the best tips to help make your racism essay stand out:
- Consider the historical causes of racism. Papers on racism often focus on discrimination and equality in modern society. Digging a bit deeper and highlighting the origins of racism will make your essay more impressive. Check academic resources on the subject to see how racism was connected to the slave trade, politics, and social development in Europe. Explore these ideas in your paper to make it more compelling!
- Show critical thinking. Racism essay titles often focus on the effects of racism on the population. To make your essay more powerful, you will need to discuss the things that are often left out. Think about why racial discrimination is still prevalent in modern society and who benefits from racist policies. This will show your tutor that you understand the topic in great depth.
- Look for examples of racism in art. One of the reasons as to why racism spread so quickly is because artists and authors supported the narratives of race. If you explore paintings by European artists created in 17-18 centuries, you will find that they often highlighted the differences between black and white people to make the former seem less human. In various literary works, such as Conrad’s Heart of Darkness and Shakespeare’s Othello, racism plays a vital role. In contrast, more recent works of art consider racism from a critical viewpoint. Examining how racism is reflected in the art will help you to earn an excellent mark for your analysis of the subject.
- Discuss the influences of racism. Of course, one of the key racism essay topics is the impact of racism on black populations in various countries. It is true that discrimination plays an essential role in the lives of black people, and reflecting this in your paper will help you to make it influential. You can discuss various themes here, from police brutality to healthcare access. Support your claims with high-quality data from official sources. If appropriate, you can also show how racism affected your life or the lives of your friends and loved ones.
- Show the correlation between racism and other social issues. Racism is connected to many different types of discrimination, including sexism and homophobia. This allows you to expand your paper by showing these links and explaining them. For instance, you could write an essay on racism and xenophobia, or find other topics that interest you.
Finally, structure your essay well. Write an outline first to determine the sequence of key points. You can check out a racism essay example on this website to see how other people structure their work.
Racism Thesis Statement, Main Body, & Conclusion
A typical essay should have an introduction, the main body, and a conclusion. Each paragraph of the main body should start with a topic sentence. Here’s what a topic sentence for racism-themed essay can look like:
Racism continues to be a pervasive issue in society, with deep-rooted prejudices and discrimination that impact individuals and communities across the globe.
Don’t forget to include a racism essay thesis statement at the end of your introduction to identify the focus of the paper! Check out these racism thesis statements for inspiration:
Racism is pervasive social problem that manifests in various forms, perpetuating systemic inequalities and marginalizing minority groups. Through an examination of racism’s history and its psychological impact on individuals, it becomes evident that this pressing issue demands collective action for meaningful change.
In your essay’s conclusion, you can simply paraphrase the thesis and add a couple of additional remarks.
These guidelines will help you to ensure that your work is truly outstanding and deserving of a great mark! Be sure to visit our website for more racism example essays, topics, and other useful materials.
- Sexual Abuse Essay Titles
- Youth Violence Research Topics
- Black Lives Matter Topics
- Ethnocentrism Topics
- Fascism Questions
- Segregation Research Topics
- Genocide Essay Titles
- Workplace Discrimination Research Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, November 25). 354 Racism Essay Titles, Thesis Statement Examples, & More. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/racism-essay-examples/
"354 Racism Essay Titles, Thesis Statement Examples, & More." IvyPanda , 25 Nov. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/racism-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '354 Racism Essay Titles, Thesis Statement Examples, & More'. 25 November.
IvyPanda . 2024. "354 Racism Essay Titles, Thesis Statement Examples, & More." November 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/racism-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "354 Racism Essay Titles, Thesis Statement Examples, & More." November 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/racism-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "354 Racism Essay Titles, Thesis Statement Examples, & More." November 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/racism-essay-examples/.
150+ Racism Essay Topics: Comprehensive Guide for Students
Table of contents
- 1.1 Key Elements of an Effective Racism Essay
- 2 Choose the Perfect Racism Essay Topic
- 3 Historical Racism Essay Topics
- 4 Contemporary Issues in Racism
- 5 Analytical Approaches to Racism Essays
- 6 Argumentative Racism Essay Topics
- 7 The Impact of Racism in Various Sectors
- 8 Racism in Education
- 9 Racism in the Workplace
- 10 Racism in Healthcare
- 11 Tips for Crafting an Effective Racism Essay
Writing about racism can be challenging, but it is an important and impactful way to address a critical issue in society. This guide will help you choose compelling topics and craft essays that effectively communicate your arguments and insights.
Why Write About Racism?
Writing about racism is crucial because it addresses a persistent societal issue. Racism limits opportunities, fosters inequality, incites violence and creates social divides. Discussing this topic raises awareness, encourages self-reflection, and promotes empathy and understanding across different racial and ethnic groups.
Additionally, exploring racism helps:
- Understand its historical roots
- Dismantle harmful stereotypes
- Examine intersections with sexism, classism, and more
Writing about racism is not just academic; it educates, advocates, and drives social change.
Key Elements of an Effective Racism Essay
Choose the perfect racism essay topic.
The PapersOwl team has compiled a comprehensive list of topics to help you write an impactful essay on racism. These topics cover various aspects of racism, from historical roots to contemporary issues. Whether you need to explore the psychological effects of experiencing racism or examine the role of literature in addressing racial issues, this list offers a wide range of options. For more diverse writing ideas, you might also want to explore our opinion essay topics .
- The historical roots of racism in the United States
- How does institutional racism affect the education system?
- The impact of media representation on racial stereotypes
- How do hate crimes correlate with racism?
- What are the psychological effects of experiencing racism?
- The role of activism in combating racism
- How do immigration policies reflect racial biases?
- The influence of social media on racial attitudes
- Why do racial prejudices persist in modern society?
- How does economic inequality relate to racial discrimination?
- The effectiveness of diversity programs in workplaces
- How does racism manifest in the criminal justice system?
- The role of literature in addressing racism
- How does cultural appropriation affect racial relations?
- The effects of racism on mental health
- How do schools address issues of racial inequality?
- The impact of historical events on contemporary racism.
- How do different countries tackle the issue of racism?
- The relationship between race and identity.
- How can community programs reduce racial tensions?
Historical Racism Essay Topics
- The impact of slavery on American society
- How did the Jim Crow laws enforce racial segregation
- The role of Native Americans in early American conflicts
- The consequences of the Civil Rights Movement
- How did forced labor shape the economies of the Southern states
- The history of anti-blackness in American history
- The effects of colonialism on racial relations
- How did the abolitionist movement influence American history
- The role of black people in the American Revolution
- How did World War II impact racial dynamics in the United States
- The history of racial bias in the American legal system
- How did the Emancipation Proclamation change the lives of former slaves
- The impact of the Harlem Renaissance on racial identity
- 14 The significance of the Reconstruction era in US history
- How did the transatlantic slave trade affect global economies
- The role of women in the fight against racial discrimination
- The impact of historical immigration policies on racial diversity
- How did segregation in schools affect educational outcomes for black students
- The influence of historical literature on racial attitudes
- How did early American politics shape racial biases

Contemporary Issues in Racism
- What is the impact of structural racism on modern society
- How do African Americans experience racism in daily life
- In what ways does the Supreme Court address racial discrimination
- What are the effects of police brutality on community trust
- How can education and awareness combat racism
- To what extent does social media influence racial tensions
- How do immigration policies affect other ethnic groups
- What is the role of activism in the fight against racism
- How does economic inequality perpetuate racial disparities
- What is the effectiveness of diversity and inclusion programs
- How does racial profiling affect minority communities
- What is the relationship between racism and mental health
- How does media representation influence public perceptions of race
- In what ways does housing discrimination impact urban development
- How can workplace policies address racial bias
- What role do schools play in promoting racial equality
- How does environmental racism affect minority communities
- How do healthcare disparities reflect broader societal racism
- What influence does political rhetoric have on racial attitudes
- What are the challenges of achieving racial justice in a multicultural society
Analytical Approaches to Racism Essays
- How do race and racism intersect in contemporary society
- What is the significance of Black History Month in addressing racial issues
- How does less access to resources perpetuate racial disparities
- What does new research reveal about the causes of racism
- How does white supremacy manifest in modern institutions
- What impact did George Floyd’s death have on the racial justice movement
- What strategies are effective to end racism
- How can we understand and address racist behavior
- What are the root causes of racial inequities
- How does media portrayal of race influence public perception
- What role does education play in reducing racial prejudices
- How do economic factors contribute to systemic racism
- What are the psychological impacts of experiencing racism
- How does cultural representation affect racial identity
- What is the historical context of racial segregation policies
- How do laws and policies address racial discrimination
- What are the health implications of racial disparities
- How does socialization shape racial attitudes
- What impact do grassroots movements have on racial equality
- How do international perspectives on racism compare to those in the U.S.?

Argumentative Racism Essay Topics
- Should the Supreme Court play a more active role in combating racism
- How does racism affect children’s development and opportunities
- Are certain ethnicities more susceptible to systemic prejudice
- Should cultural practices be protected when they perpetuate racial biases
- Can the idea of colorblindness in society effectively reduce racism
- Should educational curriculums include more on the intersection of race and gender
- Is it possible for members of marginalized groups to hold racist views
- How do gender and race intersect to create unique forms of discrimination
- Should laws mandate diversity training to reduce workplace prejudice
- How does media representation of different ethnicities influence societal attitudes
- Can cross-cultural exchanges help mitigate racial prejudices
- Should schools teach children about the history and effects of racism
- Is it ethical to impose quotas for minority representation in institutions
- How do cultural norms perpetuate racial stereotypes
- Should hate speech be more heavily regulated to combat racism
- Can affirmative action effectively address racial inequities
- Is the concept of race scientifically valid or a social construct
- Should governments implement stricter penalties for racially motivated crimes
- Can community policing reduce racial tensions and improve trust
- Should cultural sensitivity be a mandatory part of professional training programs
The Impact of Racism in Various Sectors
- How does racism affect healthcare access and quality
- What is the impact of racial bias in the criminal justice system
- How do racial disparities manifest in educational outcomes
- What are the effects of racism on employment opportunities
- How does racial discrimination influence housing policies
- What is the role of racism in environmental justice issues
- How does racism affect mental health services and treatment
- What impact does racial prejudice have on political representation
- How do racial biases shape media and entertainment industries
- What are the consequences of racism in the tech industry
- How does racism affect immigration policies and practices
- What is the impact of racism on sports and athlete representation
- How do racial inequalities influence public transportation access
- What role does racism play in the allocation of social services
- How does racism affect consumer behavior and marketing strategies
- What are the impacts of racial bias in scientific research and academia
- How do racial prejudices influence the legal profession
- What is the effect of racism on financial services and banking
- How does racism impact the nonprofit and charitable sector
- What are the consequences of racism in the military and defense industries
Racism in Education
- How do racial biases affect student performance
- What impact does school segregation have on educational equality
- How does curriculum content perpetuate racial stereotypes
- What role do teachers’ attitudes play in racial disparities in education
- How do disciplinary practices in schools reflect racial biases
- What are the effects of underfunding schools in minority communities
- How does access to advanced courses differ by race
- What impact does racism have on college admissions processes
- How do racial biases affect students’ mental health in educational settings
- What role does racism play in the underrepresentation of minority faculty
Racism in the Workplace
- How does racial discrimination affect hiring practices
- What impact does workplace diversity training have on reducing racism
- How do racial biases influence promotion opportunities
- What are the effects of racism on employee morale and productivity
- How does racial discrimination manifest in workplace policies
- What role do corporate cultures play in perpetuating racial biases
- How do wage gaps reflect racial disparities
- What impact does racism have on workplace harassment and bullying
- How does racial prejudice affect job performance evaluations
- What are the legal implications of racial discrimination in the workplace

Racism in Healthcare
- How do racial biases affect patient treatment and outcomes
- What impact does racism have on access to healthcare services
- How does racial discrimination influence medical research and studies
- What role do healthcare providers’ attitudes play in racial disparities
- How do socioeconomic factors intersect with race to affect health
- What are the effects of racism on mental health care access
- How does racial bias manifest in maternal and infant healthcare
- What impact does racism have on the doctor-patient relationship
- How do public health policies reflect racial inequalities
- What are the consequences of racism in the training of healthcare professionals

Tips for Crafting an Effective Racism Essay
Writing an essay on racism can be challenging due to the emotional and sensitive nature of the topic. However, by following these tips, you can craft a thoughtful essay that will engage your readers and present a well-supported argument.
- Start with a Strong Thesis Statement
Begin your essay with a clear and debatable thesis statement. This central argument will guide the direction of your essay and provide a foundation for your discussion. For example, your thesis could be: “Systemic racism is a significant barrier to equality in the United States.”
- Conduct Thorough Research
Ensure that your essay is well-researched by consulting a variety of credible sources. Use data, expert analysis, case studies, and historical facts to support your argument. This not only strengthens your essay but also helps to present a balanced view of the topic.
- Show, Don’t Just Tell
Instead of simply stating that racism exists, show it through real-life examples and historical context. Use vivid descriptions and factual evidence to illustrate the impact of racism. This approach helps to make your argument more convincing and relatable to the reader.
- Anticipate Counterarguments
Consider the perspectives of those who might disagree with your argument. Address these counterarguments thoughtfully and respectfully, providing evidence to refute them. This demonstrates that you have considered multiple viewpoints and strengthens your overall argument.
- Personalize Your Argument
Incorporate personal anecdotes or stories to give a human dimension to your essay. Sharing personal experiences or narratives of those affected by racism can make your argument more compelling and emotionally resonant.
- Use Authoritative Sources
When citing facts and statistics, ensure that you reference authoritative sources. This includes academic journals, reputable news outlets, and respected experts in the field. Accurate citations enhance the credibility of your essay.
- Craft a Logical Structure
Organize your essay with a clear and logical structure. Typically, this includes an introduction, several body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each paragraph should focus on a single point that supports your thesis and transition smoothly to the next.
- Avoid Emotional Language
While it’s important to convey the emotional impact of racism, avoid using overly emotional or inflammatory language. Strive for a balanced tone that presents your argument objectively, making it more likely to resonate with a broader audience.
- End with a Strong Conclusion
Conclude your essay by reinforcing your thesis and summarizing your key points. Include a call to action or a thought-provoking statement that encourages the reader to consider the implications of your argument and reflect on their views.
- Edit and Revise
Lastly, thoroughly edit and revise your essay. Check for clarity, coherence, and grammatical correctness. Consider seeking feedback from peers or instructors to refine your argument and improve the overall quality of your writing.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

Thesis Statement For Racial Equality
Thesis Statement The fight for racial equality is a worldwide battle that will never end due to humans striving to become superior to all other races, genders, and religions; peace movements, and civil rights movements pushed to advance the world's mindset that all humans are equal and should be treated as such. However, political propaganda and other sources of media fuels the public into boosting the country's support for their military while degrading their opponents. Introduction “These are revolutionary times. All over the globe men are revolting against old systems of exploitation and oppression, and out of a frail world new systems of justice and equality are being born. The shirtless and barefoot people of the earth are rising up
The Main Obstacle Preventing Blacks From Achieving Equality Essay
To what extent can it be argued that De Jure (legal) segregation was the main obstacle preventing blacks from achieving equality in the 1920s – 1930s?
Essay On African American Equality
The history of the struggle for the advancement and progression of African Americans is a larger-than-life story. It reveals their endeavors for the initiation of change in political, financial, educational, and societal conditions. They did everything to shape their future and that of their country i.e. the United States of America. This struggle for the attainment of equal rights has helped them to determine the path and the pace of their improvement and development (Taylor & Mungazi, 2001, p. 1).
Essay On Race Disparities
U.S. There are more people of color, whether black, hispanic, Indian, or any other color other than white in our overcrowded prisons today. They are in there because of their street crimes and because they are minorities who get significantly higher rates of penalization. Because of their financial situation, they do not have the ability to get able attorneys to represent them. Since they don’t have able representation, they plead the way they are told and end up in prison and remain there until their sentence ends. Their plight is one that does not have much assurance because they live in high crime areas, have low income or no jobs at all, and little or no education. Living in these areas and having no form of income with little education has labeled them. This predicament unfortunately leads to crime. The punishment for the crimes of the minority races are most of the time more harsh than for the white person. If a black person harmed a white person, the penalty would be harsher than if the black person harmed another
Racial Inequality Research Paper
Johnson, H. B. (2014). The American dream and the power of wealth: Choosing schools and inheriting inequality in the land of opportunity. Routledge.
Racial Equality During The Civil Rights Movement
The civil rights movement was time when racial equality was prominent in America. In this essay it will address the ways in which people challenged the ways of life to one day achieve racial equality. Jim crows laws and segregation was a dominant factor in the way that the courts ruled in favour of racial inequality.
Essay On Race Relations
Race in the United States has always been a problem in the past and still remains the same in the present society. Race relations is defined by relations between members or communities of different races within one country (en.oxforddictionairies.com). Minorities have been denied legally and socially rights in the past by the dominant race, White Americans. Now in modern society minorities are the majority of the United States, but are still being racial targeted, profiled and killed by White Americans.
The Racial Contract Essay
In The Racial Contract, it is argued that contemporary structures of white domination in the United States operate by means of an epistemology of ignorance for white people. White people inadvertently suffer from cognitive dysfunctions such that they cannot understand the racially (and racistly) structured world in which they live and, indeed, helped create. For Mills, while no person of any race is self-transparent, becoming a white person entails a particularly extreme form of self-opacity regarding issues of race that corresponds with a conspicuously bad or offensive misunderstanding of the world. Recently with the invasion of Iraq, the president has proven that white people believe that they are correct when that in any given conflict
Racial Inequality Of African Americans Essay
As it talks about racial inequality in chapter 10, the definition of racism is the belief that one race is supreme and all others are innately inferior. White people are actually at the top while the others (the minority groups) are at the bottom. Considering that the laws of the USA revolved around white men in the beginning of this country, it’s not surprising to see how little people are not aware that racism still exists. They claim that it’s the 21st century, slavery happened in the past and it should stay in the past where it belongs. No. We’re going to recognize what white people did to African Americans. We are going to see how white supremacy is ugly and not needed.
racial injustice Essay
“Racism is a bad thing, you find it everywhere in the schools, the clubs and also in the streets.”
Essay about racial inequality
- 9 Works Cited
Some people define race as if it is something solid or concrete, but what they don’t see is that it is a “social fabrication”(Mathew Desmond, Mustafa Emibayer,2009;2). Race is based on the difference in physical appearance which is determined, for example, by the most apparent trait; skin color. Inequality emerges when people living, whether on the same sovereign terrain or across continents, are not treated with the same amount of respect and not given the chance to engage their rights in a free and fair manner. Race and inequality are often linked together because of the “issues that began in the 1800s”(NFB;Journey to Justice;2000) such as racial segregation. Over the years issues of race and inequality have
Essay about Racial Equality in the United States
Throughout the history of the country, America has been considered a fairly racist union. From the workplaces to the society, as an Asian, I felt there's a strong barrier between white and black people, although I felt a little bit of racial among us. In this essay, I will talk about the major racial issue of this country through out my experiences.
Racial Oppression Essay
- 3 Works Cited
Today, a serious problem exists all over the world. Racial oppression takes place in the poorest and the richest countries, including America. Racial oppression is characterized by the majority, or the ruling race, imposing its beliefs, values, and laws on the minority, or the ruled race. In most areas, the ruling race is upper class whites that run the “system”, and have a disproportionate amount of power. In other areas, it may not be the white race, but it is still the race that is comprised of the majority, makes the laws, or has the most money. These are the keys to domination over the weaker minorities that don’t have the power to thrive under the majority’s system according to their own cultural beliefs,
Civil Rights Movement Thesis Statement
Thesis Statement: In this paper, I’m going to explore how the Civil Rights Movement first started, and the brutal events and forms of protest during this monumental moment in history. Looking at first-hand accounts from pivotal figures such as the leaders of the social movement organizations, I can properly recount the conditions and struggles in the fight for equality for African Americans. Covering these topics, I can properly describe the effects that came from each movement and the change that subsequently followed. Brown v. Board:
Essay on Racial Inequality in America
- 4 Works Cited
In today’s world, the American still has barriers to overcome in the matter of racial equality. Whether it is being passed over for a promotion at the job or being underpaid, some people have to deal with unfair practice that would prevent someone of color or the opposite sex from having equal opportunity at the job. In 2004, Dukes vs. Wal-Mart Stores Incorporation was a civil rights class-action suite that ruled in favor of the women who worked and did not received promotions, pay and certain job assignments. This proves that some corporations ignore the 1964 Civil Rights Act, which protects workers from discrimination based on sex, race, religion or national origin.
Racism Is An Ongoing Social Justice Issue Essay
Racism has been an ongoing social justice issue for decades, and we seem to always fail to make it stop. According to Dummett (as cited in Fernando, 1984), racism is the behaviour and attitude that emerges from our beliefs that certain people are different from us. These differences are mainly based on race, where people come from, physical characteristics, such as colour and hair type or behavioural characteristics, and that people categorized must be treated differently based on their needs, capabilities and rights. Usually there is one dominant and superior group and a few inferior groups (Dummett, as cited in Fernando, 1984). Coates and Morrison (2011) suggests that what we distinguish as real and true may not always be real and that things may not always be as it seems. Coates and Morrison (2011) also states that we live in a racial matrix, where we have this illusion of reality and that differences associated with racial status and hierarchies are perceived as the norm in society and this perception of reality is not easy to get rid of. There are four types of racism; subtle racism, colorism, internalized racism and reverse racism (Nittle, 2016). Racism can be explicit, but it can also be very subtle and covert, which is a huge problem, as most people do not even notice it and they do not realize that it happens on a day-to-day basis (Coates and Morrison, 2011). Racism is not only one problem or concern, as it is brings along a variety of other problems and is compiled
Related Topics
- United States
- African American
- United States Declaration of Independence
- Black people
- American Civil War

Please wait while we process your request
Racism Essay Writing Guide
Published: 9th Dec 2016 | Last Updated: 31st Jul 2020 | Views: 105694
Essay paper writing
Academic writing

Racism essay
Being a student, you will have to complete a considerable amount of writing assignments, and essays will definitely be the most preferred type of academic work given by teachers and (a little later) by professors. It is beyond doubt that writing assignments help to develop good writing skills, but when you are wrapped up with work and the deadlines are pressing, the only things you probably can ‘develop’ are a headache and anxiety. If you need to write an essay on racism, firstly it might seem to be an easy task since the mighty Internet and numerous printed sources offer a good deal of information on this topic. At the same time, it will not always benefit you because you’ll have to spend a lot of time to find relevant and useful necessary materials, and then write something new. Thus, to avoid sleepless nights and to save time for other urgent work, you can order a paper on Pro-Papers.com and get a qualitative work within the given deadline.
Essay on racism
Racism is a long-lasting problem that bothers millions of people all over the world. That is why if you need to write an essay on racism, it shall not cause difficulties as you will find a vast amount of information on the Internet. The first thing you should do is to choose a topic, which you would like to devote your research to in your essay. It can be anything from the history of racism or causes and effects of racial bias up to anti-racist movements. You can also consider any country and study how intolerance emerged in it, or take any literature piece and investigate how an author has described the problem. To back up your words and ideas on the topic, search for facts and examples. Moreover, it is a rather controversial subject, and a student will have to watch his or her language and avoid offensive and rude words regarding different races.
Essay on racism and discrimination
When writing an essay on racism and discrimination, first of all, it is necessary to differentiate these two terms and give definitions to both. A student needs to indicate that discrimination is a much broader concept than racism. Discrimination deals with the unequal treatment of people belonging to the same race or ethnos. Another difficulty that can arise is that it may be hard to define what institutional racism is, how destructive it can be, and how it influences the whole population. Another important topic that has to be covered is discrimination prevention, especially at the workplace, or what has to be done when you become a victim of discrimination. Every employee should know his or her rights when applying for a job to avoid unfair treatment based on personal convictions of the hirer. It would be also a good idea to enumerate social programs that were designated to prevent prejudice and racial bias.
Types of essays on Racism
Does racism still exist today essay
To write a good essay on the topic “Does racism still exist today?”, one should find enough evidence to support his or her point of view on the issue. If you do agree that racial segregation remains a burning problem, then you can find various studies available on the Internet which prove that it is a significant issue. For example, it is proven that black people are more likely to be killed by police officers than white people. When Joshua Correll, researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder, designed the game in which every person can try himself as a police officer, the result reaffirmed this statement since people, regardless of their race, did not give much thought before killing black people and hesitated before killing whites even though they were armed. One more thing that proves that this type of intolerance exists is that professors favor white students over others. When looking for a mentor, students whose names sound less white will have hard times getting positive feedbacks. There are also many other researches and studies that can be considered while completing a paper.
Racism in the workplace essay
Discrimination in the workplace is a current issue since it takes place here and there. An essay on prejudice in the workplace, first of all, should include what types of prejudice exists in this sphere. Workers may face a denial from an employer based on race, skin color, origin, age and, of course, gender. Usually, females are subjected to gender discrimination, and different ethnical minorities are subject to racial and color discrimination. The problem arose due to the conviction that some whites are more superior in mental capacity while blacks, for example, can handle primarily physical work. One more reason why applicants may fail when trying to get a good job is a poor knowledge of English or a heavy accent. Fortunately, a number of laws, like the Civil Rights Act of 1964 in the U.S.A., have been issued to protect workers from unfair treatment in the workplace.
Anti-racism essay
Anti-racism is a set of beliefs, policies, and movements that emerged as a response to racism in order to create an egalitarian society where all people could be equal in their rights. When deciding what topic on anti-racism to choose, you will find much information on anti-racism movements, particularly anti-apartheid movement, and anti-racism activists. Among them you may mention, first of all, Nelson Mandela, Desmond Tutu and Walter Max Ulyate Sisulu. You can specify what each of them has done to fight prejudice in South Africa. One more interesting topic for an essay on the issue is the development of scientific anti-racism. Here you may concentrate on scientific investigations that disapproved the correctness of the cultural evolutionism paradigm and social Darwinism paradigm. You may consider, for instance, the doctrines of Friedrich Tiedemann, who was the first to use brain measurements of white and black people. As a result, he proved that black people have the same brain size as white people do, thus, they cannot be physiologically inferior.
Media and racism essay
When writing an essay on racial discrimination in media, one may start with a general statement saying that in the 21 st century, people have a regular access to different media sources: television, press, wireless and, of course, the Internet, which is the main stirrer of racial prejudice in the global community. Then it would be a good thing to search for examples in each media source. In case of television, it has been estimated that an average American watches TV approximately 4 hours a day. No wonder it has such a huge influence on its viewers. African Americans are primarily featured as criminals, drug dealers, members of ghetto groups, or hip hop musicians. Asian American students, for instance, are portrayed in media as nerdy individuals who lack social skills. If we take any primitive show on TV, the absolute majority of characters is white and people of other color always play inferior roles. A student may also write about positive and negative effects of racism in media.
Racism in advertising essay
Advertisement is something we can hardly imagine our lives without. Multiple surveys have shown that people of color are underrepresented in advertisements, be it television commercials or ads in magazines and newspapers, billboards and so on. According to the U.S. Census, 65 percent of Americans are white while the rest population consists of various minorities. The unequal ratio of representatives of different racial groups is obvious. Only 7 percent of all ads involve black people, and other racial minorities are represented more rarely. A student writing an essay on prejudice in advertising will be able to find numerous examples of prejudice, like “beauty whitewash” propaganda, despite the fact that advertisement should be free of any type of discrimination based on race, gender, ethnicity, religion and other factors. People daily absorb and, therefore, adopt so much information from ads that it is no wonder that the majority still has some preconceived opinions.

Causes and effects of racism essay
Racism has always been a delicate subject as it refers to the skin color. It tackles everyone who has ever experienced any type of prejudice. That is why practically everyone has developed his own viewpoint on the subject. No doubt, there many causes that engender racism, among them are, first of all, fear and the need of protection. Fear appears when we face something new and unfamiliar or when there is a threat to what we love and cherish most of all: family, identity, culture, territory, etc. Another significant cause is ignorance, which makes unaware or uneducated people condone prejudice. Evidently, writing a cause and effect essay is an important part of the education process. It is complicated to enumerate the effects of prejudice upon a victim: destroyed self-esteem, mental disorders, angry and violent attitude towards a group of people who assaulted this person. To write a good essay on causes and effects of racism, one has to do a significant research and nail all information down with examples.
Argumentative essays on racism
An argumentative essay differs from other types as you cannot rewrite what has already been said hundreds of times, but you will have to do a good research and start writing as soon as all additional information has been accumulated. When writing an argumentative essay on racism, it’s necessary to be logical and consistent. A student needs to take a particular theme on the subject and then provide proofs or arguments that suggest this or that standpoint. It should be taken into account that in an argumentative essay, one should refer to actual facts and not purely to personal convictions. It is advisable to choose one aspect, like racism in literature, or how racism affects self-esteem of a victim, or comparison of racial persecution in the past and nowadays, rather than to dissipate one’s energy on numerous questions. Then, one should search for examples to prove the given thesis. Sticking to these recommendations, one will be able to write an argumentative essay .
Short essay on racism
Teachers and professors often assign short essays to their students. Generally, a short essay implies a 4 or 5 paragraphs essay. To cope with numerous writing assignments well, you will have to stick to some guidelines. The most accepted structure for a short essay includes 1 paragraph of introduction, 2-3 paragraphs of a body and a 1-paragraph conclusion. Secondly, keep in mind that essay is not just a mere coverage of information; it has to be thought-provoking. That’s is why if you want to attract readers’ attention, do not pick common topics on color discrimination, but try to choose something specific that can cause discussion. For example, you can write an essay on the race card and consider whether it really makes any advantage for racial minorities. Or you can also express your point of view on the following: does the Internet contribute to the emergence of racial events or not. And the last essential point is to proofread the paper carefully and edit it so that you can avoid minor mistakes and see if the flow of thoughts is logical. Think of something interesting and specific when writing short essay , and you will end up with having a great paper!
Slavery and racism essay
“Slavery and racism” is a huge topic; therefore, a lot of things can be discussed. A student is more likely to express his point of view on the question what came first: slavery or racism. Some think that slavery caused racism, since slavery is deeply rooted in human mentality. Different nations enslaved each to have cheap workforce or for the psychological need to dominate and control other, as they thought, inferior nations, without the racial implications. Furthermore, the whites were enslaved as well as blacks, and this is an undeniable fact. Others support the opposite idea that racial bias caused slavery since it started even before the black trade appeared in the New World. Moreover, one can include facts from the latest researches on slavery. For example, Henry Louis Gates, the black scholar from Harvard University, discovered that free blacks came to Florida one hundred years before the official date of slavery beginning in 1619 in America, and that blacks were actually aware of Christianity before they were enslaved. One more discouraging fact was recently revealed: in the antebellum period, over 4 thousand black families have owned slaves!
4 page essay on racism
Though 4 page essay is a rather big assignment, it has the same structure as a 4 paragraph essay. To write such an essay, you will need to do a good research on the topic and find facts, arguments, and examples that will help you support your point of view. Mind that if the topic on intolerance will be too specific, you might face difficulties in finding enough information. You can consider, for instance, environmental racism. Start from writing what is environmental racism and who suffer from it. What term is more correct, environmental racism or environmental justice, and can they be used interchangeably? Also you may base an essay on comparing ethnocentrism and prejudice. Provide examples when ethnocentrism is natural and when it may lead to discrimination, persecutions, and even genocides. One more interesting topic on the issue is whether the election of a black president in the USA improved the longstanding situation with the prejudice.
Racism in art & literature
Racism in Disney films essay

There is hardly a person who doesn’t like Disney movies. At the same time, the issue of stereotypical portrayal of most characters raised a question of racial bias. Walt Disney started producing films in 1937, with the “Snow White and The Seven Dwarfs” being the first one, when the reality was so much different from what we have now. That is why, most people find it offensive that in “Jingle Book,” movie gorillas spoke in black vernacular, or that in “Lady and the Trump”, the cat-villains had slanted eyes and Asian accent. If we take, for example, “Peter Pan,” we can see that Native Americans are pictured as red-skinned gamblers who can hardly speak English. Aladdin in the same name movie looks pretty much like a European while Jafar looks much more exotic. It becomes obvious that positive characters are portrayed more like whites with regular features while negative characters possess extraordinary appearance. So it should be indicated in an essay on this topic that as soon as the main audience of Disney movies is children, such covert racism may affect their views about treating ethnically diverse people as equals.
Racism in Othello essay
Speaking about racism in literature, the first work you can write an essay about is William Shakespeare’s “Othello”. The writer was often criticized for using this topic in the play. At that time, white people were the majority and black people were known only as slaves and servants, thus racial discrimination was ordinary, and Shakespeare just depicted it as a part of reality. The characters like Emilia, Brabantio, Roderigo and, of course, Lago have shown great disrespect towards Othello who obviously had a black skin. They had been given him different humiliating names like “thick lips”, “Barbary horse” and “an old black ram.” and insulted for the marriage with the white Venetian girl Desdemona. Lago disregarded the feelings of both Othello and Desdemona and claimed that miscegenation goes “against all rules of nature”. A student writing an essay on racism in “Othello” should indicate that intolerance and conviction that one race is superior to others can have tragic consequences.
To Kill a Mockingbird essay on racism
Harper Lee’s “To Kill a Mockingbird” brings up many social problems, and the main of them is the problem of racism in the south of the USA in the 1930s. The black man Tom Robinson was accused of raping Mayella Ewell and took the stand before the white jury. The jury, guided by prejudice, found the defendant guilty due to the color of his skin and sentenced Tom to death, though he was actually innocent. Still there were people, among them Atticus Finch, Scout, Jem, who supported Tom and found it unfair to judge people by the color of their skin. They were called “nigger-lovers”, but Atticus responded that he loves all people and paid no attention to such insults. “To Kill a Mockingbird” shows the reality of the past century where black man’s words were worth nothing. This book is a good example when writing an essay on color discrimination.

Huckleberry Finn racism essay
“The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn” by Mark Twain has caused many debates on using offensive racist words (“nigger” was used more than 200 times) and using Black Vernacular in a speech of some of the characters. Thus, the question arose whether this piece should be included into the school program or not. Some people say that this novel depicts racism and is abusive to African American students and stir up enmity in many students. Others are convinced that the piece gives a good understanding of the historical background of that time when the word “nigger” was equal to the word slave. In an essay on racism in “The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn”, a student may express his point of view whether this novel is appropriate for reading in high schools or it should be removed from the program. Also, one may investigate how casual acquaintanceship with runaway slave Jim biased Finn’s moral and emotional maturation.
Deadly Unna essay about racism
“Deadly Unna” written by Phillip Gweynne depicts friendship between white fourteen-year-old Gary Black, known also as Blacky, and the aboriginal Dumby Red. This friendship contradicted the racial prejudice overt within the town, which was split into 2 parts: the first part, the Port, was inhabited by the white Goonyas, and the second, the Point, by the aboriginal Nungas. These two communities never interacted and even were at feud with each other. At the beginning of the novel, Blacky was hardly different from the rest of his prejudiced townspeople and even had been doing racist jokes by himself, but after meeting Dumby and recognizing him as a gifted footballer, his awareness towards injustice grows and strengthens. Writing an essay on this novel, one may express his own thoughts on why other people in the town couldn’t be more amicable towards aboriginals or why Blacky and his siblings decided to paint over offensive graffiti about indigenous people in the shed of the jetty.
Racism in the Great Gatsby essay
Scott Fitzgerald’s novel “The Great Gatsby” is considered by many as a literature masterpiece. It covers many problems of that time with racial intolerance being probably not the main one. Racism at the beginning of the 20 th century was an ordinary thing and black people still weren’t treated as equals by the white ones. It becomes apparent when reading the novel that the main racist is Tom Buchanan, who denoted the white race superiority over colored races. He expressed his misgivings that the “other races will have control of things” if the dominant (white) race won’t watch out. However, not only Tom had racist thoughts, but also Nick was surprised when saw 3 modish black people in a horse-drawn carriage driven by a white chauffeur and called them “bucks” as if they still were slaves. These examples can be used in an essay on racism to depict that wealthy white people of that time looked down upon colored people and weren’t ready to treat them as equals.
Uncle Tom’s Cabin racism essay
As Abraham Lincoln claimed, “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” by Harriet Beecher Stowe was one of the main reasons of the American Civil War as its influential and a bit exaggerated narrative caused a prompt anti-slavery opinion. The most controversial issue about the novel is that Harriet Beecher Stowe contradicts herself saying that black race, being more emotional and childlike, is different from the harsh Anglo-Saxon race in such a way denying the equality of white and black people. That is why she was sometimes accused of portraying all black characters, Uncle Tom, Topsy, and Eva, as uneducated and simple-hearted, which were also stereotypical convictions. “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” is a thought-provoking novel that offers many matters for discussion. For example, a student may express his point of view on following issues: Does the novel remain relevant in the 21 st century? Did the author care more about the abolition of slavery or saving slave-owners’ Christian souls? What effect did the book have on the North and the South?
Thesis statement about racism
Thesis statement is an argumentative sentence that reveals the main idea of your paper. Usually, it is written at the end of the essay’s introduction. A good thesis statement should be specific and showcase your objective thought or idea on the issue. Moreover, it should be somewhat controversial because some general statements like “prejudice remains a huge problem in multicultural societies” probably won’t surprise anyone and, therefore, the essay will be useless. The main goal of your thesis statement is to attract attention of a reader and persuade him to continue reading the whole work. Keep in mind that your statement may change while writing a paper. You can simply change your point of view or the researches will give you more interesting ideas for investigating. That is a common case; thus, don’t just forget to revise your thesis statement occasionally to make sure you are working in a right direction. For example, your thesis statement may sound like “Stereotypes of a particular race are usually based on judging the behavior of several people of this race who did something wrong” or “Racial bias affects workers’ well-being and can lower their working capacity even more”. In case you need thesis statement help , browse several web resources or turn to writing services for assistance.
Introduction for racism essay
To write a stellar essay, you will have to pay great attention to the introduction. The first sentence should be catchy so a reader wants to continue reading a paper. Some say that the best way to start an introduction is to use an inspiring quote of a well-known figure or to provide readers with some interesting facts. Something like “prejudice still remains a burning issue” won’t go. If you have a specific story dealing with racism that you want to tell, it would be also better to put it at the beginning of your essay. The most important part of any introduction, the thesis, should end the introductory paragraph. Keep in mind that thesis is the main idea of your essay. It has to be concise and clear and cannot be changed in body paragraphs and conclusion. Thus, when finishing an essay, check once again whether the thesis doesn’t contradict itself in next paragraphs.
Conclusion for racism essay
Conclusion is an important part of an essay, thus a student should pay attention to it. Generally, conclusion should include several items. First, you will have to give the summary of the whole essay. It is advisable to make reference to the thesis or opening statement mentioned in the introduction, but not to simply rewrite it. In such a way, you can emphasize the importance of delivering ideas to the readers. In some cases, it would be appropriate to link the summary to wider issues or more general problems if a reader wants to learn more on a discussed topic. For example, if you write an essay on intolerance in a particular literature piece, you can indicate what topics on racism it correlates with. Finally, express your own point of view on the subject based on the summary and explain how a paper can be useful to the readers.
Racism in America essay outline
Before starting to write an essay, you need to make an outline. This is a blueprint that will help you not to lose your train of thoughts. There are certain tips for making a good outline. Firstly, the sentences, statements, headings, and arguments have to be brief, usually one line long. The outline should include an introduction, at least 2 supporting ideas which are described in 2 paragraphs, then facts or arguments which support these ideas and a summary or conclusion. For example, if you want to write about structural racism in America, the first point of the outline will be the introduction: you will have to explain the term in general and define what a structural racism is, and then proceed with the background and the thesis statement on the topic. The next points of the outline will be several paragraphs, in each of which you will have to introduce some ideas with supporting facts. It may be, for instance, “the structural racism is embedded in police departments” or “the structural racism is predominant in higher educational institutions”. The last item of the outline is the conclusion with restated thesis and brief summary on the topic.
Good topics for Racism essays
Essay about racism in schools

Rampant racism is experienced in school in all forms: call-naming, teasing, verbal and even physical abuse. As a result, homeschooling is becoming a common thing among minority families for the supposed color blindness doesn’t exist actually in educational institutions. For example, African American parents claim that racial stereotypes come not only from fellow-students, but from white teachers, who make up 85% of all teachers in the USA, as well. This is due to a general misconception within a society that colored students, especially black ones are all without exception unintelligible, lazy and criminally inclined. Parents of black kids accuse teachers of being offensive, unresponsive, mean, super critical and sometimes unqualified. Moreover, students are usually making friendships with those of their race, which doesn’t contribute to the eradication of prejudice. Also, if you need to write about racial bias at school, you can enlarge upon negative effects of prejudice on students or why colored students sometimes reject their cultural identity and parental values.
5 paragraph essay about racism
If you need to write a 5 paragraph essay about racism, the most appropriate structure will be an introduction, then 3 body paragraphs and a conclusion. The best way to start an introduction and an essay, in general, is to cite a strong quote on racial intolerance said by a famous person like Martin Luther King Jr. and then either to support or refute it. Then you can choose either one big topic for all the 3 body paragraphs, for example, slavery is a rather broad theme, or if you want to consider different problems, you can pick one topic for each paragraph. Still, if you take different topics, it would be better if they somehow related to each other, like xenophobia in advertisement and on TV. Be concise and clear in conveying your thoughts. Finally, in conclusion, make a summary that will relate back to the main idea in an introduction.
Racism topics for research paper
Research paper is a rather complicated assignment. You will have to make sure that the topic you picked has enough information for researching. At the same time, if you choose a broad topic, you may be overwhelmed with materials and sources available. For example, you can consider the topic “how racial unfairness affects children and their perception of different people”. You should research the issue and preferably give some explanations why it is so important to bring up children without racial bias. In addition, you can investigate the main influencers in forming a child’s prejudice towards ethnically diverse people. Is media the main source of stereotyping, which lays the hatred in children’ minds?

Also, you can cover the topic on prejudice, such as negative impact of racism on physical and mental health of its victims. Here you can draw on general statistics that cultural minorities have poor access to quality health care. At the same time, if you face too many difficulties, rely on our research paper writing service and we will cover your back.
Topics about racism for essays
Discrimination gives a wide range of topics to be discussed. Different types of prejudice can be found in practically all spheres of life: politics, education, workplace, media and so forth. That is why you can first of all come up with covering the issue in social spheres, be it government, employment, sports, entertainment, neighborhoods… You can also build your essay on comparing racial discrimination in previous century and today, and how it is changing its face. If you make up your mind to write your paper on bias in history, so probably the topic of racism versus slavery will never be settled completely, and you can express your thoughts on it. You can also consider why prejudice is more experienced in certain sports and who are more bent to it: fans or sportsmen. One more interesting topic is why minorities have less access to healthcare and how it affects their physical and mental well-being. You can also deliberate on a matter of ending racism, what has already been done, and what efforts still have to be made.
Persuasive essay topics on racism
The main goal of a persuasive essay is to convince a reader that your point of view is right. Sometimes it’s even reasonable to criticize the opposite convictions and thoughts. When picking a topic for persuasive essay on racism, you will have to look for the most controversial ones. There should be two sides at least, so you will be able to choose the one you believe in or the one you have enough evidence to support. For instance, you can write on negative effects of stereotyping. Blacks are usually considered to be criminals, drug dealers living in ghettos. As a result, they are arrested twice often than white ones. The treatment of African Americans as being unintelligent and lazy causes huge problems when they are willing to enroll at a college or apply for a decent job. The opinion that almost all Arabs are terrorists makes police check Arab-looking people in airports much more attentively than people of any other race. There are many other stereotypes that can support your point of view on this topic. If these pieces of advice did not bring you somewhat closer to writing an excellent paper, get some persuasive essay help from us.
Argumentative essay topics about racism
The problem of discrimination gives a wide range of topics for writing argumentative essays. Generally, you will have to give explanation and convince the readers why racial bias is a bad thing. The name “argumentative” speaks for itself, so you will have to provide arguments, facts, examples of negative consequences of prejudice. Thus, to write an argumentative essay, you will have to conduct a good research, it can be some statistical or historical facts that can support your point of view on the issue. For example, if you want to write an argumentative essay on how to stop being a racist, you will have to find different studies and researches why some people are more bent on being racists, how environment influences people’s attitudes towards “others”, and how to reduce hatred and misunderstanding between different races. Or if the topic of your argumentative essay sounds like “Prejudice is a weapon which kills people”, then you will need to find certain pieces of evidences or facts indicating how many deaths have been caused by racial animosity.

No racism essay topics
One of the most popular questions on discrimination are whether it still exists in our society and how to overcome it. Some people claim that there no discrimination anymore, but why then we encounter it so often? The point is that by pretending it doesn’t exist anymore, we don’t fix it but even make matters worse. It is also a good idea to consider the Christian approach to the problem. It says that there can be no racism as we all of “one blood” or human race. The skin shade (that what is on the outside) has nothing to do with the inferior of a person. However, not everyone practices the holy writing. Thus, in your essay you may encounter ways how to overcome the prejudice. The first one is the necessity not to ignore the situation when it happens, but to help a victim or disrupt a conversation if you hear someone uses racial slurs. Then try to participate in anti-racial community events (not violent protests, but affirmative actions) and racist speech bans. One more step is to vote for those the candidates who support ending racism policy. Of course, there are many other ways, which you can mention in your essays.
Media and racism essay titles
As it was already mentioned, media plays a crucial role in portraying racial stereotypes. To eradicate racism from a society, actions should be taken to eradicate it from media first. You may consider racism, for instance, on television, in network news, in commercials or in prime time ads. According to the surveys, despite Latinos constitute one-tenth of U.S. population, they make up only 3-4% of TV characters. Moreover, their portrayal is hardly positive, which causes negative attitude of people, especially if these are children or people who rarely encounter Latinos towards them. The same thing is with the most of network news and prime time programs. The overall majority of news anchors, actors, musicians is whites. The minorities appear seldom on the screen. Usually, they are involved in natural disasters, foreign affairs, and crime topics. All in all, the news coverage is designated most of the times for white people and their interests.
Tips & Tricks
Anti-racism essay ideas
Anti-racism is a rather broad subject, so you will have to concentrate on the aspects that are more interesting for you. For example, you may ground your essay on comparing different types of anti-racism or vice versa focus on the one you want to cover. Among different types of anti-racism, you may consider everyday anti-racism, multicultural anti-racism, psychological anti-racism, radical anti-racism, and anti-nazi anti-racism. All of them have their own particularities, like the psychological one deals with individual challenging of prejudice, the radical claims that socio-economic powers and privileges mainly promote racial bias. One more good topic for writing an essay on is the Civil Rights movement in the U.S.A. in 1954-1968. Or you may consider what is the non-violent resistance and does it really help in suppressing racism.
Racism essay hooks
When writing any essay, including an essay on racial bias, one should use various hooks. What is a hook? A hook is a sentence or a fact that can attract attention of a reader. It is always a good way to start your essay with a real-life story or situation that encouraged you to write on this particular topic. One more useful hook is to somehow connect your essay with a popular culture. It will definitely be easier to kindle readers’ interest if you mention racism cases in their favorite movies, TV shows and programs. For example, you may take not only movies that deal with prejudice like “The Green Mile” or “Schindler’s List”, but it can be music as well. “Ebony and Ivory” by Paul McCartney and Stevie Wonder is a thought-provoking song, ideas of which can be used in your essay to attract attention. And, of course, your essay will grab attention if you can suggest any ideas how to solve the problem of racism. Keep in mind that the more sophisticated the methods you invent are, the better your essay will look like.
Racism & sports
Racism in sports today essay
Sport is an important part of our society. Millions of people have their favorite teams and players and watch games all the time. That is why, whatever happens on the playing field, especially if it is an incident that displays discrimination towards colored players, cannot be left without proper attention. The issue of racism in sports is an old but still hotly disputed problem. They claim that racism has already been conquered, but in reality, colored players are challenged greatly. Though a lot of black sportsmen, known as African Americans, be they individual athletes or team players, have already proved that they can succeed at any sport, they are still discriminated to the present day. The history gives us many examples of African American black legends, starting from Jesse Owens who has won 4 gold medals during the Berlin Olympics in 1936. Unfortunately, the display of racial intolerance still remains a tendency in some sports.
Racism in hockey essay
If you write about racism in hockey, we advise you to mention that the majority of hockey players has always been white. Though the hockey leagues, like NHL league, try to change the situation by increasing the number of ethnically diverse players, the issue of racism in the leagues gets more serious as well. For instance, a damnable incident happened to one of the few NHL’s African American player Wayne Simmonds during the game on September 23, 2011. One of the spectators threw a banana at Simmonds while the player was making a shootout attempt. Despite the shock, Simmonds managed to finish the game and commented later that if you are black playing white men’s sport, things like that are expected. However, NHL claims that the organization takes necessary steps to end this awful game’s practice by adopting inviting colored players to their league. This will also have a positive effect on the younger generation that still doubts whether they should go in for hockey or not.
Racism in football essay

Football is one the worldwide popular sports, and at the same time, it is considered to be the favorite sports of roughnecks and cads. As a result, the incidents of racist behavior happen on the field here and there. In most cases, such misconduct is shown by football fans, who often show their racist attitude. According to the surveys, the most ignorant football fans are those from Spain, Italy, Holland, and from Eastern-European countries. They display their intolerance towards ethnically diverse players in different ways: it can be offensive racist statements or chanting, inappropriate gestures, crowd violence, and other insulting acts. One of the most outrageous displays of racism happened in December 2011, when the Liverpool striker, Luis Suarez, abused Patrice Evra of Manchester United during the game. For such unacceptable behavior, Suarez received eight-match suspension and a fine, which is just one quarter of his monthly salary. Most experts believe that only more severe punishments for such acts can help to avoid intolerance on the soccer fields.
Racism in soccer essay ideas
It seems that soccer and racism are closely interrelated. That is why if you need to write an essay on racial bias in soccer, it won’t be difficult due to a huge number of examples of discrimination misbehavior on a playing field. For example, Euro 2012 hosted by Poland and Ukraine, was overflowed with rampant racism. More than one-quarter of all federations of countries participating in the event, primarily Russian, Spanish and Croatian soccer federations, were fined for the uncontrolled racist behavior of their fans during the games. The German federation particularly was fined since its fans exhibited neo-Nazi symbols when their team won a game with Denmark. The former captain of England’s federation even tried to persuade ethnically diverse English fans to stay at home not to “come back in a coffin”. Even if the most loyal and tolerant countries, like England and Germany, face the problem of racism in sports, then prompt steps should be taken in order to change such a plaguy situation in our community.
In case you are short of time or loaded with other work, order essay online at Pro-Papers.com, and we will write a top-quality paper on racism for you.
Your email address will not be published / Required fields are marked *
Order an essay!

Fill out the order form

Make a secure payment
Receive your order by email
Terrorism Essay Writing Guide
The phenomenon of terrorism has been known since the French Revolution (1789-1799) and the notorious period of Reign of Terror. Since that time, attempts of certain groups of society to threaten or…
15th Aug 2018
Cause and Effect Essay Topics
Working on a cause and effect essay can be considered the best task for a student because the structure of such papers is quite logical and straightforward. Moreover, it can be written within a…
31st Aug 2018

Homelessness Essay Writing Guide
Homelessness is an extremely pressing problem nowadays, which actually has always been a burning issue. It was first documented in America in 1640. Since that time, the number of homeless people has…
11th May 2019
Calculate your price
Number of pages:
Get your project done perfectly
Professional writing service
Reset password
We’ve sent you an email containing a link that will allow you to reset your password for the next 24 hours.
Please check your spam folder if the email doesn’t appear within a few minutes.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Thesis Statements About Racism Samples Racism in workplace Thesis statement examples. Racism is so rampant in the workplace. Thousands face discrimination daily in their workplaces. While this is definitely bad news, it gives us more data to choose from when working on an essay or research paper on racism in the workplace.
Look no further! In this list, you will find thesis statements about racism, essay titles, & examples. IvyPanda® Free Essays. Clear. Free Essays; Study Hub. Study Blog. Academic Writing 101. Q&A by Experts. Literature Guides. Tools. Essay Writing Tools ... 👍 Good Essay Topics on Racism. Racism in Contemporary North America; Racial and ...
Moreover, a hint to writing an excellent essay is good hooks considering the problem. You can find ideas for the thesis statement about racism that may help broaden your comprehension of the theme. It's crucial to study persuasive and argumentative essay examples about racism in society, as it may help you to compose your paper.
Start with a Strong Thesis Statement; Begin your essay with a clear and debatable thesis statement. This central argument will guide the direction of your essay and provide a foundation for your discussion. For example, your thesis could be: "Systemic racism is a significant barrier to equality in the United States." Conduct Thorough Research
Thesis Statement The fight for racial equality is a worldwide battle that will never end due to humans striving to become superior to all other races, genders, and religions; peace movements, and civil rights movements pushed to advance the world's mindset that all humans are equal and should be treated as such.
The document provides guidance on crafting an effective thesis statement about racism. It discusses that racism is a complex topic that requires thorough research and a nuanced approach. The document recommends beginning with research to gain a comprehensive understanding of the issue. It also stresses the importance of writing a clear and specific thesis statement that articulates the central ...
Now it's up to you to defend your thesis with good evidence and persuasive writing! Types of Essays • Analytical Breaks down and evaluates an issue. Example thesis statement: Shaped by religious tradition and belief the supremacy of Western culture, 20th century United States foreign policy has reinforced racism against the Middle East.
What is racism? According to Encyclopedia Britannica, the definition of racism is any action, practice, or belief that reflects the racial worldview—the ideology that humans may be divided into separate and exclusive biological entities called "races"; that there is a causal link between inherited physical traits and traits of personality, intellect, morality.
Thesis statement about racism. Thesis statement is an argumentative sentence that reveals the main idea of your paper. Usually, it is written at the end of the essay's introduction. A good thesis statement should be specific and showcase your objective thought or idea on the issue. Moreover, it should be somewhat controversial because some ...
THE THESIS STATEMENT The thesis statement is the key to a paper. Before you begin an essay, you must know ... simply stating a known fact. For example, the statement Racism in America today is a problem is not much of an argument. A more effective thesis statement would ... Your introduction is a good place to include background information ...